Ctsb
-
Official Full Name
cathepsin B -
Overview
Cathepsin B is an enzymatic protein belonging to the peptidase (or protease) families. In humans, it is coded by the CTSB gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a lysosomal cysteine protease composed of a dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. It is a member of the peptidase C1 family. At least five transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
CTSB;cathepsin B;EC 3.4.22.1;CPSB;amyloid precursor protein secretase;Cathepsin B1;cysteine protease;APPS;EC 3.4.22;APP secretase;OTTHUMP00000116009;OTTHUMP00000229510;OTTHUMP00000229511;OTTHUMP00000229512;OTTHUMP00000229514;OTTHUMP00000229515;OTTHUMP00000229516
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Bovine
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- Branchiostoma belcheri tsingtauense
- HEK293
- Human Liver
- Bovine Tissue
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HeLa
- Yeast
- Avi
- Fc
- His
- Non
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
Background
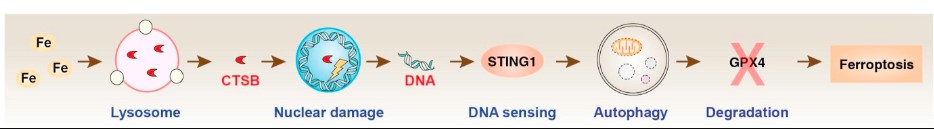
Fig1. Schematic depiction of the role of CTSB in ferroptosis by activating STING1-dependent autophagy. (Feimei Kuang, 2020)
What is CTSB protein?
CTSB (cathepsin B) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8p23. This gene encodes a member of the C1 family of peptidases. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. At least one of these variants encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate multiple protein products. These products include the cathepsin B light and heavy chains, which can dimerize to form the double chain form of the enzyme. This enzyme is a lysosomal cysteine protease with both endopeptidase and exopeptidase activity that may play a role in protein turnover. It is also known as amyloid precursor protein secretase and is involved in the proteolytic processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP). The CTSB protein is consisted of 339 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 37.8 kDa.
What is the function of CTSB protein?
CTSB mainly plays a role in the lysosome, which is responsible for the degradation of proteins and other biological macromolecules ingested within the cell, and participates in the protein turnover and energy metabolism of the cell. CTSB is involved in the degradation of proteins and organelles in autophagy, which is crucial for maintaining the stability of the intracellular environment and cell energy balance. CTSBS are capable of cutting extracellular matrix (ECM) components such as collagen and elastin, thus participating in cell migration and tumor cell invasion and metastasis. CTSB plays a role in antigen processing, helping to cut protein substrates into smaller fragments for presentation to the immune system by the Major histocompatibility Complex (MHC).
CTSB Related Signaling Pathway
CTSB is involved in protein degradation during autophagy and interacts with autophagy related proteins such as LC3 to regulate the smooth progress of autophagy flow. CTSB can affect apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway or death receptor pathway, and also participate in the regulation of anti-apoptotic signaling pathways, such as PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways. CTSB plays a role in tumor invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis, and interacts with molecules such as MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases) and VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) to affect tumor progression. CTSB is also involved in other signaling pathways, such as Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, and Hedgehog, which regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, and fate determination.
CTSB Related Diseases
CTSB proteins have been implicated in the occurrence and development of a variety of diseases, especially in metabolic diseases, cardiovascular diseases, cancers, and neurodegenerative diseases. In diabetes, CTSB is associated with the exacerbation of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM), affecting cardiac function and structure by promoting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. In the field of cancer, CTSB is involved in tumor growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis, and its overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in diseases such as breast cancer. In addition, the up-regulation of CTSB expression is related to tumor progression, and its knockdown can inhibit tumor cell proliferation and tumor formation. In neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease, variations in the CTSB gene are associated with increased disease risk and may be involved in the disease process by affecting autophagy and apoptosis pathways.
Bioapplications of CTSB
As a key protease in lysosomes, CTSB is particularly important in tumor therapy, especially in the development of antibody drug conjugators (ADCs). ADCs is a novel drug that combines the targeting of antibodies with cytotoxic drug destruction, among which CTSB is one of the commonly used targets of enzyme lytic Linker. These linkers are designed to be specifically cut by CTSB in the tumor microenvironment, thereby releasing cytotoxic drugs that precisely kill tumor cells.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Eun-Kyung Kim, 2020
Thyroid cancer incidence has increased worldwide; however, investigations of thyroid cancer-related factors as potential prognosis markers remain insufficient. Secreted proteins from the cancer secretome are regulators of several molecular mechanisms and are, thereby, ideal candidates for potential markers. This study aimed to identify a specific factor for thyroid cancer by analyzing the secretome from normal thyroid cells, papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) cells, and anaplastic thyroid cancer cells using mass spectrometry (MS). Cathepsin B (CTSB) showed highest expression in PTC cells compared to other cell lines, and CTSB levels in tumor samples were higher than that seen in normal tissue. Further, among thyroid cancer patients, increased CTSB expression was related to higher risk of lymph node metastasis (LNM) and advanced N stage. Overexpression of CTSB in thyroid cancer cell lines activated cell migration by increasing the expression of vimentin and Snail, while its siRNA-mediated silencing inhibited cell migration by decreasing vimentin and Snail expression. Mechanistically, CTSB-associated enhanced cell migration and upregulation of vimentin and Snail occurred via increased phosphorylation of p38.
.jpg)
Fig1. Western blot of secreted CTSB levels in conditioned media of cultured thyroid cancer cell lines (top).
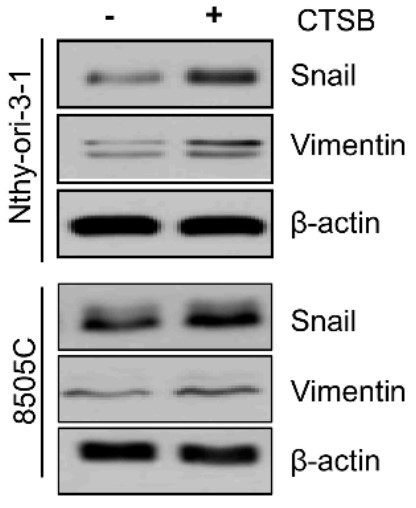
Fig2. Western blotting for Snail and vimentin in Nthy-ori-3-1 and 8505C cells after treatment with recombinant CTSB.
Case Study 2: Feimei Kuang, 2020
Ferroptosis is a type of non-apoptotic regulated cell death that involves excessive iron accumulation and subsequent lipid peroxidation. Although the antioxidant mechanisms of ferroptosis have been extensively studied recently, little is known about the interactions between the different organelles that control ferroptosis. This study shows that the translocation of lysosomal cysteine protease cathepsin B (CTSB) into the nucleus is an important molecular event that mediates organelle-specific initiation of ferroptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Iron-dependent lysosomal membrane permeability triggers the release of CTSB from the lysosome to nucleus during ferroptosis. Mechanistically, nuclear CTSB accumulation causes DNA damage and subsequent activation of the stimulator of interferon response CGAMP interactor 1 (STING1/STING)-dependent DNA sensor pathway, which ultimately leads to autophagy-dependent ferroptosis.
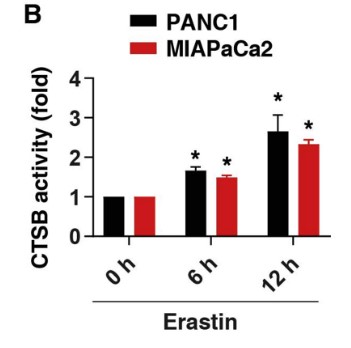
Fig3. Intracellular CTSB activity.
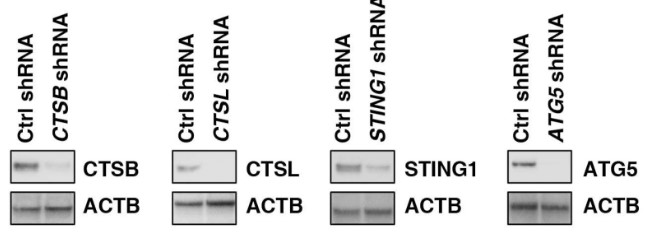
Fig4. Western blot analysis of protein expression in indicated gene knockdown PANC1 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CTSB-2099H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CTSB-757H)
Involved Pathway
Ctsb involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Ctsb participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System,Antigen processing and presentation,Assembly of collagen fibrils and other multimeric structures, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Ctsb were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Collagen formation | COL6A2,LEPRE1,LEPREL2,COL9A1A,LEPREL1,CTSL1,COL3A1,COL28A1,COL23A1,COL25A1 |
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | BMP1B,COL23A1,ADAMTS5,TLL2,COL9A3,CAPNS1,TLDC2,BMP1,ADAM8A,CTSD |
| Assembly of collagen fibrils and other multimeric structures | LOXL2,COL8A1,COL6A1,LOXL3,CTSS,COL5A2,COL4A4,LOX,LOXL1,COL10A1A |
| Antigen processing and presentation | NFYA,HLA-B,KIR2DS4,CALR,HLA-C,HSP90AB1,KLRC2,KIR2DS3,HLA-DMA,TAP1 |
| Collagen degradation | CTSD,COL17A1,MMP10,ADAM10,TLDC2,COL19A1,COL13A1,ADAM9,MGC174857,ELANE |
| Extracellular matrix organization | COL8A2,MGC174857,MFAP4,LOXL3,SERPINH1,LTBP4,FBLN1,MMP15,TIMP2A,COL4A5 |
| Adaptive Immune System | MICA,UBE2F,UFL1,ERAP2,TRIM9,AP1S1,TREM1,B2ML,ERAP1,TRIM69 |
| Immune System | AP1S3A,CYLD,C1rb,BTR22,SRMS,NOD1,DEFB129,TNFRSF13C,CD300LF,CLEC6A |
Protein Function
Ctsb has several biochemical functions, for example, collagen binding,cysteine-type endopeptidase activity,cysteine-type peptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Ctsb itself. We selected most functions Ctsb had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Ctsb. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cysteine-type peptidase activity | USP12A,CTSSA,SENP8,CTSBA,CASPB,CAPN2B,CASP3A,CAPN1B,ZRANB1B,OTUD6B |
| peptide binding | ERCC3,TPP1,PCSK5,PPIA,FNTB,QRFPR,LTA4H,TRHDE,NPFFR2,GPR37 |
| peptidase activity | PCSK7,ADAMTS12,TMPRSS11G,ELANE,GZME,PARK7,KLK1B26,PAPPAB,BACE1,MASP1 |
| kininogen binding | Ctsl,CTSL2,C1QBP |
| protein self-association | ADAM8,CCL5,NKX3,SYP,S100A7A,DYRK1A,PTH1R,AGTR1B,PCSK9,VAMP2 |
| proteoglycan binding | NID1,SLIT2,CTSL1,CTSS,CECR1,CTSK,UBE4A,COL5A1,CECR1A,FCN2 |
| collagen binding | ADAM9,LRRC15,C1QTNF1,TLL1,MMP13,SMAD7,ASPN,FN1,ITGA1,SERPINH1 |
| protein binding | LINGO1,UBE2Q1,ESRP1,UBE2K,MST1R,RIC8,KLHDC3,KCNE1L,CUL2,PYROXD1 |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | BLMH,DUB1,USP13,CTSL2,ATG4C,CTSBA,USP24,USP51,CTSSB.1,USP45 |
Interacting Protein
Ctsb has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Ctsb here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Ctsb.
AMBP;MLH1;RGS2;ADAMTSL4;gag-pol;CSTA;SPHK1
Resources
-
-cover.jpg)
Exploring the Vast Potential of Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
-

Exploring the Vast Potential of Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References



