EP300
-
Official Full Name
E1A binding protein p300 -
Overview
This gene encodes the adenovirus E1A-associated cellular p300 transcriptional co-activator protein. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription via chromatin remodeling and is important in the processes of cell proliferation and differentiation. It mediates cAMP-gene regulation by binding specifically to phosphorylated CREB protein. This gene has also been identified as a co-activator of HIF1A (hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha), and thus plays a role in the stimulation of hypoxia-induced genes such as VEGF. Defects in this gene are a cause of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and may also play a role in epithelial cancer. -
Synonyms
EP300;E1A binding protein p300;histone acetyltransferase p300;KAT3B;p300;p300 HAT;E1A-binding protein, 300kD;E1A-associated protein p300;RSTS2
Recombinant Proteins
- Monkey
- Dog
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Rat
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Sf21 Cells
- Insect Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- Non
- Flag
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- Myc
Background
What is ep300 protein?
EP300 protein, also known as histone acetyltransferase p300, is a transcriptional coactivator that functions in chromatin remodeling and regulation of gene expression. EP300 belongs to the p300/CBP family of proteins. It has histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity.As a HAT, it acetylates histones and other proteins, thereby regulating gene transcription. It adds acetyl groups to lysine residues on histone tails.This acetylation neutralizes the positive charge on histones and leads to an opened chromatin state, making DNA more accessible for transcription.
EP300 interacts with various transcription factors like p53, STAT3, HIF1-α, NF-κB, Smad7 etc and regulates their target genes. It plays a key role in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. EP300 is involved in many cellular processes like DNA damage response, cell cycle progression, DNA repair, cellular senescence and cancer development.Mutations and deletions in EP300 have been linked to Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and various cancers like liver cancer and leukemia.It acts as a transcriptional co-activator for CREB and p53 and regulates key genes involved in cell survival, proliferation and apoptosis.
What is the function of ep300 protein?
Histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity: EP300 has intrinsic HAT activity. It acetylates lysine residues on histone tails, especially H3K18 and H3K27. This acetylation neutralizes positive charge on histones and results in relaxed chromatin confirmation. This opens up chromatin structure and makes DNA accessible for transcription.
Transcriptional co-activator function: EP300 interacts with various transcription factors like p53, HIF1-α, NF-κB etc. It acts as a bridging factor between DNA-binding transcription factors and basal transcription machinery. This enhances transcription of target genes of these transcription factors.
Regulation of key cellular processes: EP300 regulates genes involved in cell cycle, apoptosis, DNA damage response etc. It is required for p53-dependent transcriptional activation and apoptosis in response to stress. Also involved in processes like cellular senescence, differentiation, DNA repair and cancer development.
Ep300 related signaling pathway
p53 signaling pathway: EP300 directly interacts with and acetylates p53 in response to various stresses. This acetylation enhances p53 stability, DNA binding and transcriptional activity. EP300 co-activates transcription of p53 target genes involved in cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and senescence.
Hypoxia signaling pathway: EP300 interacts with and acetylates hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF1α). This acetylation stabilizes HIF1α under hypoxic conditions and enhances its transcriptional activity. Induces transcription of genes regulating angiogenesis, metabolism, cell survival during hypoxia.
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: EP300 interacts with nuclear β-catenin and mediates its transcriptional co-activator function. Regulates Wnt target genes involved in proliferation, development, stem cell self-renewal and cancer.
NF-κB signaling pathway: Binds to NF-κB and enhances transcription of inflammation-related genes. Regulates immune response, inflammation, apoptosis, cell survival and proliferation.
Ep300 Related Diseases
- Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A genetic developmental disorder caused by mutations in EP300 or CBP genes. Features include broad thumbs/halluces and facial abnormalities.
- Cancers: Reduced EP300 expression in many cancers like liver, breast, colon cancers correlates with poor prognosis. It acts as a tumor suppressor.
- Lung cancer: EP300 mutations or reduced expression promote metastasis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness in lung cancers.
- Drug target for cancers: Inhibiting EP300 HAT activity can suppress tumor growth by modulating key oncogenic signaling pathways. EP300 inhibitors are in preclinical/clinical trials.
- Biomarker for cancer prognosis: EP300 levels can serve as biomarker for predicting cancer metastasis and survival outcomes to enable personalized medicine.
Biomedical Application of ep300 Protein
- Drug target for cancers: Inhibiting EP300 HAT activity can suppress tumor growth by modulating key oncogenic signaling pathways. EP300 inhibitors are in preclinical/clinical trials.
- Therapeutic approach for Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: Gene therapy using vectors to restore EP300 expression may help treat developmental defects in RTS patients.
- Dissecting p53 tumor suppression pathway: EP300 knockout and rescue models help elucidate precise mechanisms of p53 acetylation and target gene regulation in cancer.
- Dissecting p53 tumor suppression pathway: EP300 knockout and rescue models help elucidate precise mechanisms of p53 acetylation and target gene regulation in cancer.
Case Study
(Markus Vieweg, 2015)
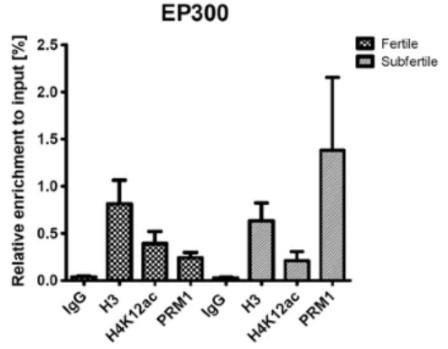
Fig3. Validation of enriched promoters with μChIP in combination with real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) between sperm of fertile donors and subfertile patients. Results from ChIP assay with anti-H4K12ac antibodies, with anti-protamine-1 in immunoprecipitated DNA of fertile donors (n = 5) and subfertile patients (n = 8). Unmodified H3 was used as a positive and IgG as a negative isotype control. Loss of interaction for H4K12ac was detected in selected promoters; however, a significant difference was observed in NCOA6, RUVBL1, and POU2F1. Depletion of H4K12ac binding is potentially replaced by either unmodified histone H3 or protamine 1.
(Ryan A. Henry, 2015)
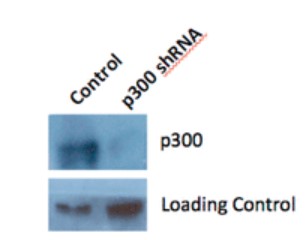
Fig4. Knockdown of p300 in BxPC3 cells causes a loss of the stimulatory effect of C646. BxPC3 cells were treated with shRNA against p300 as described in the Methods. (A) Knockdown of p300 was confirmed via Western blot. Alpha-tubulin was used as a loading control. BxPC3 p300 depleted cells were treated in triplicate with either a 0.2% DMSO control or varying concentrations of C646 in 0.2% DMSO for 4 h before harvesting and histone extraction.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
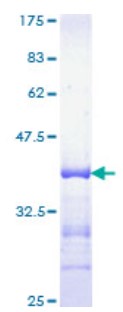
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (EP300-3346H)
High Bioactivity & Detection Sensitivity
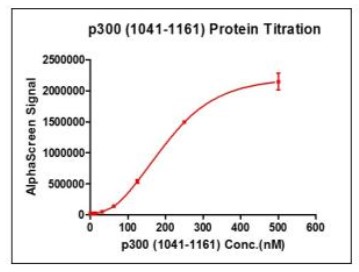
Fig2. This gene encodes the adenovirus E1A-associated cellular p300 transcriptional co-activator protein. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription via chromatin remodeling and is important in the processes of cell proliferation and differentiation. It mediates cAMP-gene regulation by binding specifically to phosphorylated CREB protein. This gene has also been identified as a co-activator of HIF1A (hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha), and thus plays a role in the stimulation of hypoxia-induced genes such as VEGF. Defects in this gene are a cause of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and may also play a role in epithelial cancer.
Involved Pathway
EP300 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways EP300 participated on our site, such as cAMP signaling pathway,HIF- signaling pathway,FoxO signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with EP300 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Pathways in cancer | HSP90B1,FGFR3,SLC2A1,LAMA4,FGF13,GNG11,RAC1,PTCH1,MMP9,GNA12 |
| Influenza A | HLA-DQA2,IRF3,MAPK13,HLA-DMB,IL33,BMA2,ACTB,BLB2,FAS,MAPK12 |
| Herpes simplex infection | Ifna15,PTPN11A,IFNA2,H2-AB1,SRSF5B,IFNG1-2,FB06F03,TAF9B,SRSF2A,SRSF2 |
| Cell cycle | GSK3B,NUF2,CHEK1,GSK3AA,KIF18A,CCP110,CENPE,MCM5,TUBGCP5,RAD50 |
| HTLV-I infection | NFKBIA,SLC25A31,ELK1,POLB,CDC20,TERT,STAT5A,DVL3,KRAS,WNT9A |
| HIF- signaling pathway | PDK1,IL6R,IFNGR2,GAPDH,ERBB2,MAPK3,HK1,ENO1,ALDOA,PIK3CA |
| Renal cell carcinoma | RBX1,PIK3CB,RAC1,PTPN11,SLC2A1,ARNT2,MAP2K2,GRB2,TGFB2,TCEB1 |
| Wnt signaling pathway | SFRP1,SMAD3,BTRC,SFRP5,RHOA,FZD3B,CTNNBIP1,NKD2B,CCND1,WNT7B |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | ITGB3,SOX4,DICER1,MMP16,ABCB1,ABL1,CD44,HOXD10,NOTCH4,TRIM71 |
Protein Function
EP300 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,NF-kappaB binding,RNA polymerase II activating transcription factor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by EP300 itself. We selected most functions EP300 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with EP300. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| nuclear hormone receptor binding | MED1,SNW1,NCOR1,TCF7L2,Ankar,SIRT1,NRIP1,BUD31,CRY1,ACTN4 |
| core promoter binding | SAFB,XBP1,INSM1A,REST,IFI203,NKX3,ELK1,HDAC5,MTF1,E2F7 |
| zinc ion binding | DTX1,RBX1,RABGGTA,PCGF5A,APOBEC3F,SETDB1A,MMEL1,ADAMTS10,TRIM61,APOBEC2 |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | ZGPAT,ZIC1,ETV6,GCFC2,PITX1,FOXJ2,GATA4,SALL1,RBPJ,NKX2-5 |
| peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding | NR0B2,CREBBP,IKBKG,MED1,ASXL2,ASXL1,PPARGC1A,NFATC4,HMGA1,PRMT2 |
| protein antigen binding | KLRD1,ITGA4,H2-AB1,KLRC2 |
| chromatin DNA binding | SLAMF7,H2AFZ,NOTCH1,HIST1H1E,FOXO3,FOXC2,GRHL2,HIST1H1D,MYOD1,GATA1 |
| damaged DNA binding | REV1,DCLRE1A,XRCC5,MGMT,HMGB2,RAD23AA,RBBP8,RPA2,ERCC1,APEX1 |
| pre-mRNA intronic binding | SOX9,RBM4,RBM41,RNPC3,HNRNPA2B1,PRPF8 |
Interacting Protein
EP300 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with EP300 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of EP300.
HIF1A;TP53
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Vieweg, M; Dvorakova-Hortova, K; et al. Methylation analysis of histone H4K12ac-associated promoters in sperm of healthy donors and subfertile patients. CLINICAL EPIGENETICS 7:-(2015).
- Cho, YA; Hong, JS; et al. The role of p300 in the tumor progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma. JOURNAL OF ORAL PATHOLOGY & MEDICINE 44:185-192(2015).