LTBR
-
Official Full Name
lymphotoxin beta receptor (TNFR superfamily, member 3) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of receptors. It is expressed on the surface of most cell types, including cells of epithelial and myeloid lineages, but not on T and B lymphocytes. The protein specifically binds the lymphotoxin membrane form (a complex of lymphotoxin-alpha and lymphtoxin-beta). The encoded protein and its ligand play a role in the development and organization of lymphoid tissue and tranformed cells. Activation of the encoded protein can trigger apoptosis. -
Synonyms
LTBR;lymphotoxin beta receptor (TNFR superfamily, member 3);D12S370;tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 3;TNF R III;TNFCR;TNFR RP;TNFR2 RP;TNFRSF3;CD 18;CD18;CD18 antigen;LT beta R;LTBETAR;Lymphotoxin B receptor;Lymphotoxin beta receptor;TNFR superfamily member 3;TNFR2RP;TNFRII;TNFRRP;TNFRSF 3;Tumor necrosis factor C receptor;Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 related protein;Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 3 precursor;TNF-RIII;TNFR-III;OTTHUMP00000238625;OTTHUMP00000238626;lymphotoxin-beta receptor;TNFR superfamily, member 3;tumor necrosis factor receptor type II;TNFR-RP;TNFR2-RP;LT-BETA-R;TNF-R-III
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- HEK293
- CHO
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Mouse
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Fc
- Avi
- His
- GST
- Non
Background
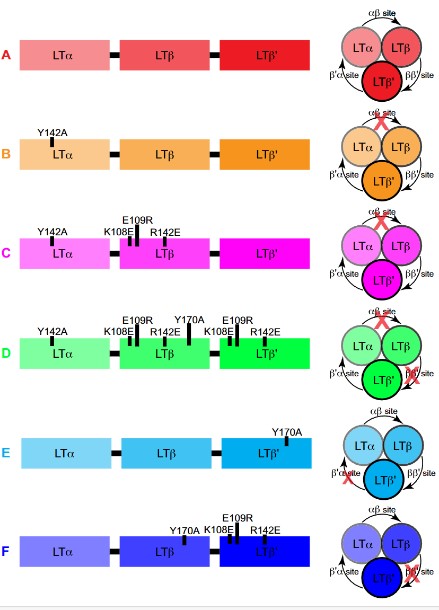
Fig1. The α–β and β–β' binding sites are essential for signaling. (Jawahar Sudhamsu, 2013)
What is LTBR protein?
LTBR (lymphotoxin beta receptor) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12p13. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of receptors. It is expressed on the surface of most cell types, including cells of epithelial and myeloid lineages, but not on T and B lymphocytes. The protein specifically binds the lymphotoxin membrane form (a complex of lymphotoxin-alpha and lymphtoxin-beta). The LTBR protein is consisted of 435 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 46.7 kDa.
What is the function of LTBR protein?
LTBR plays a role in signalling during the development of lymphoid and other organs, lipid metabolism, immune response, and programmed cell death. Activity of this receptor has also been linked to carcinogenesis. The LTBR activates two different NF-κB pathways that lead to distinct patterns of gene induction, including selected chemokines, and the cytokine BAFF, which is essential for the survival of mature B lymphocytes. LTBR activates the classical NF-κB (relA/p50) pathway, like the type 1 TNF receptor (TNFR1), that regulates proinflammatory genes, like the chemokine MIP1β. However, LTBR, unlike TNFR1, also activates the processing of p100 to form RelB/p52 complexes, which activate genes involved in lymphoid organ formation and lymphocyte survival.
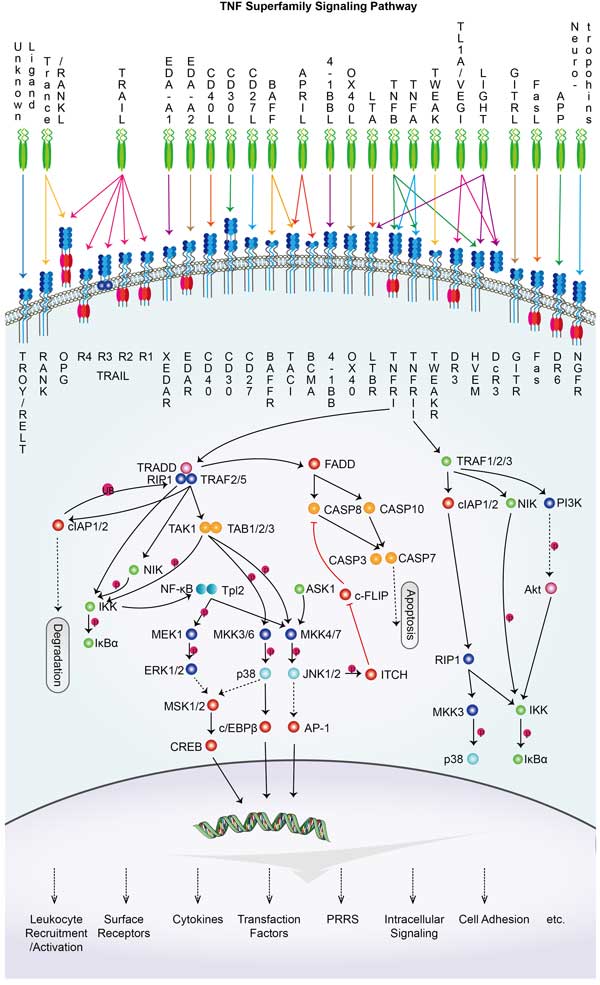
LTBR Related Signaling Pathway
Lβr activates the downstream NF-κB signaling pathway by binding to its ligand. It can also interact with other signal transduction molecules, such as TRAF2, TRAF6, etc., to regulate the activity of a variety of signal pathways. Activation of LβR activates the MAPK pathway by activating MAP3K, MAP2K, and MAPK cascases. The activated MAPK pathway can further activate multiple transcription factors and cytokines, which are involved in cell proliferation, survival and inflammation. Activation of LβR can lead to activation of JAK kinase, which phosphorylates STAT protein, thereby activating the JAK-STAT pathway.
LTBR Related Diseases
Lβr protein is related to the occurrence and development of tumors, and its abnormal expression may participate in the immune escape and angiogenesis of tumors, such as liver cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, etc. Dysfunctional LTBR is likely to lead to abnormal activation of immune cells and inflammatory response, leading to allergic diseases, infectious diseases and transplant rejection. Deficiencies in the LβR protein can lead to immune dysfunction and susceptibility to infections, such as the two types of inherited immunodeficiency, HIM (hyper IgM syndrome) and CVID (common variable immunodeficiency), and other autoimmune diseases.
Bioapplications of LTBR
The specific uses and effects of LβR protein in these application areas are still being studied, and some applications have not yet been used clinically. For example, it is used as a therapeutic target for immune, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor research, as well as a marker for new drug screening and disease detection.
Case Study
Case study 1: Małgorzata Maksymowicz, 2020
At the cellular level, upon ligand binding, the receptor activates the pro-inflammatory NF-κB and AP-1 pathways. Yet, the intracellular distribution of LTβR, the routes of its endocytosis and their connection to the signaling activation are not characterized. Here, the researchers investigated the contribution of LTβR internalization to its signaling potential.
Intracellular localization of LTβR in unstimulated and stimulated cells was analyzed by confocal microscopy. Endocytosis impairment was achieved through siRNA- or CRISPR/Cas9-mediated depletion, or chemical inhibition of proteins regulating endocytic routes. The activation of LTβR-induced signaling was examined. A transcriptional response to LTβR stimulation was assessed by qRT-PCR analysis. The results showed that LTβR was predominantly present on endocytic vesicles and the Golgi apparatus. Depletion of regulators of different endocytic routes (clathrin-mediated, dynamin-dependent or clathrin-independent) resulted in the impairment of LTβR internalization, indicating that this receptor uses multiple entry pathways. This work shows that the impairment of clathrin- and dynamin-dependent internalization amplifies a cellular response to LTβR stimulation.
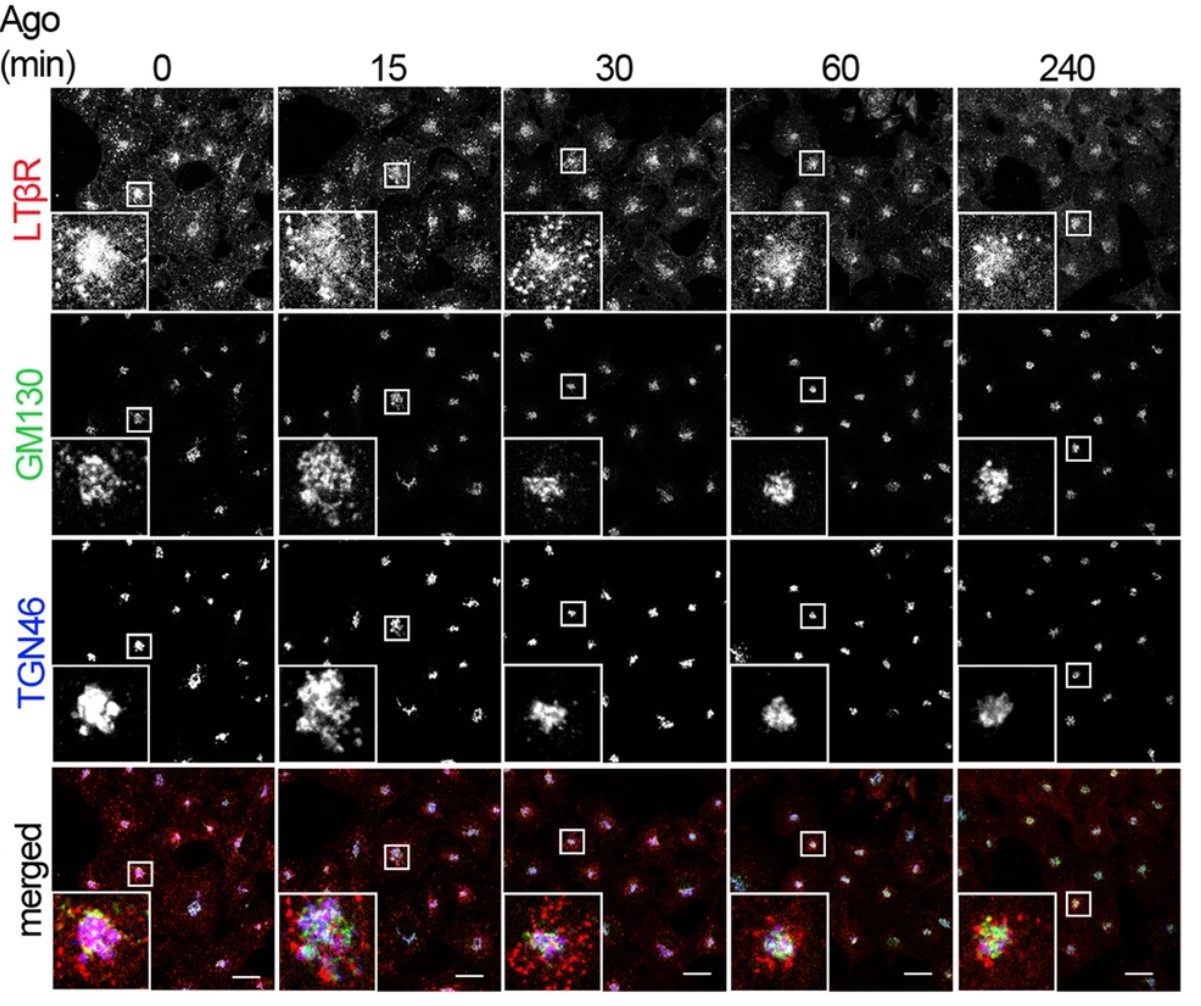
Fig1. A549 cells were stimulated with Ago for the indicated time periods and immunostained for LTβR, trans- (TGN46) and cis-Golgi (GM130).
Case study 2: Magdalena Banach-Orłowska, 2018
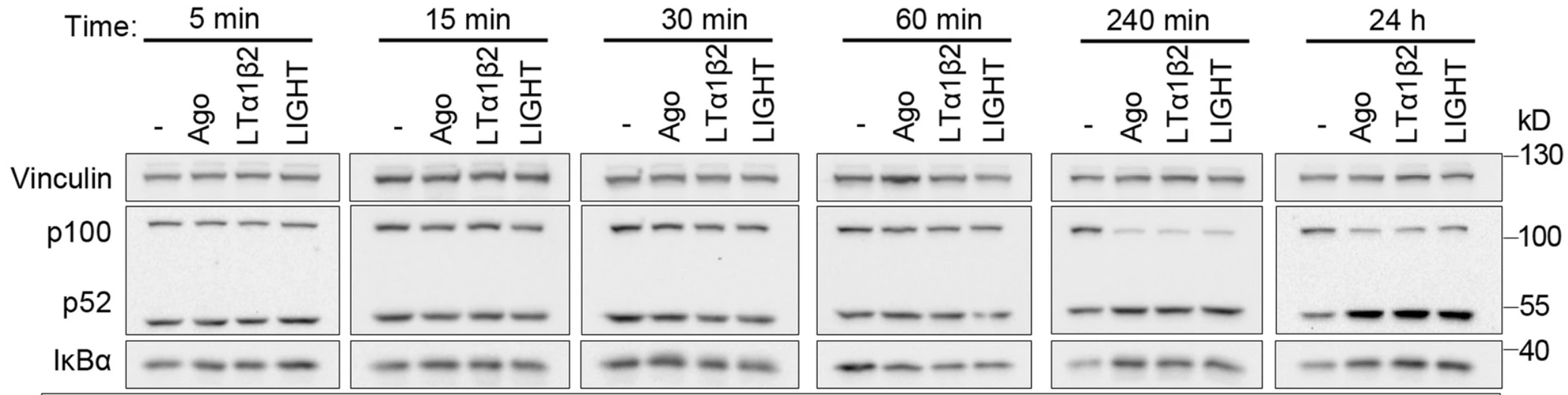
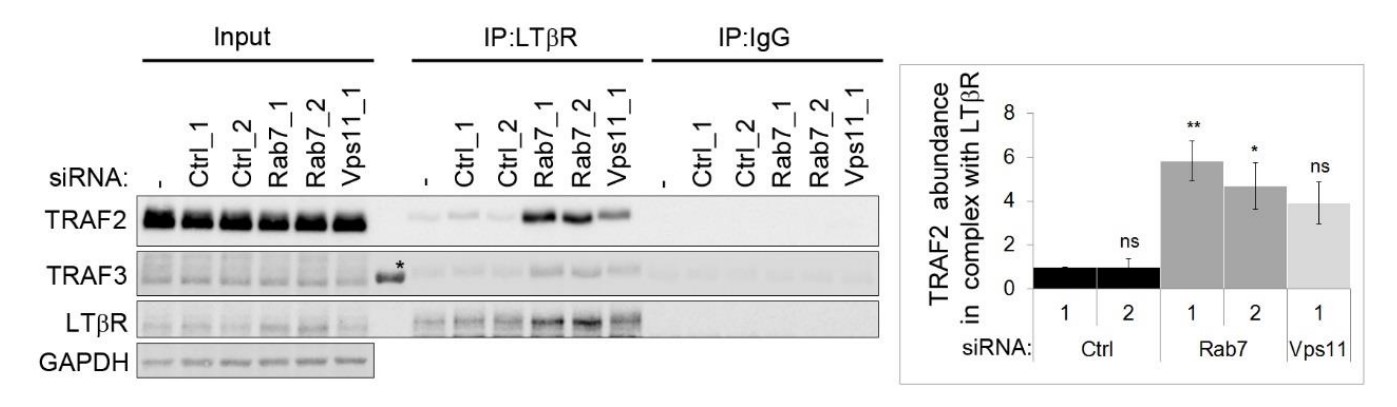
The researchers previously demonstrated that depletion of ESCRT components leads to endosomal accumulation of TNFRI and LTβR, and their ligand-independent signaling to NF-κB. Here, they studied if other perturbations of the endolysosomal system could trigger intracellular accumulation and signaling of ligand-free LTβR.
While depletion of CORVET had no effect, knockdown of HOPS or Rab7, or pharmacological inhibition of lysosomal degradation, caused endosomal accumulation of LTβR and its increased interactions with TRAF2/TRAF3 signaling adaptors. And the LTβR sequestration in intraluminal vesicles of endosomes precluded NF-κB signaling. Sequestration of LTβR in intraluminal vesicles of endosomes upon depletion of HOPS components or Rab7 precludes NF-κB signaling, whereas LTβR accumulation on the outer endosomal membrane after ESCRT depletion promotes signaling.
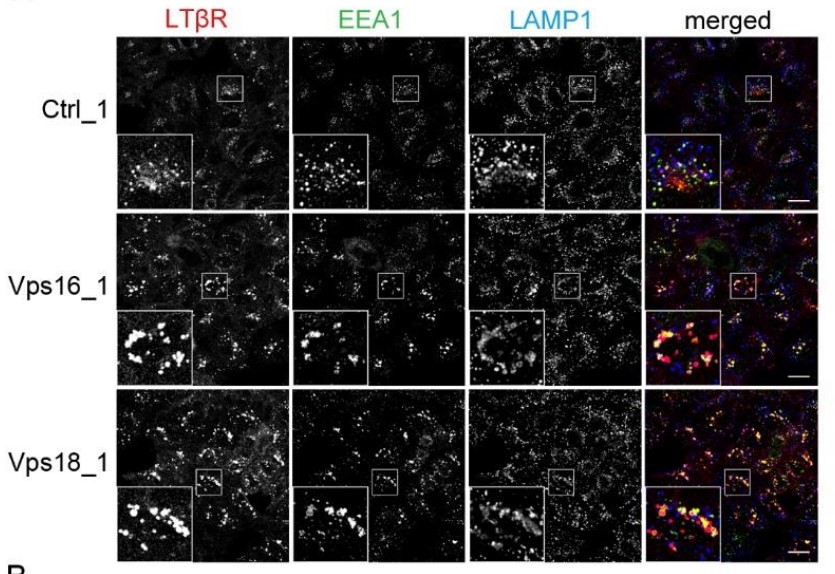
Fig3. Immunofluorescence staining of LTβR, EEA1 and LAMP1 in HeLa cells upon knockdown of Vps16 or Vps18 and in control (Ctrl) siRNA-transfected cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LTBR-2683H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
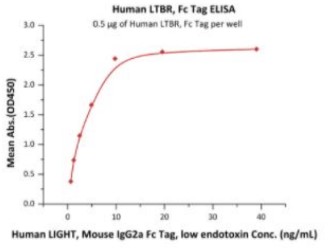
Fig2. Activity Data. (LTBR-399H)
Involved Pathway
LTBR involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LTBR participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,NF-kappa B signaling pathway,HIF- signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LTBR were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| HTLV-I infection | CCND2,SMAD4,PIK3CB,NFKB2,NFATC3,ETS2,FZD6,ATF3,MRAS,ANAPC5 |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | RELA,CXCL2,VCAM1,PIDD1,ATM,LAT,MAP3K7IP3,IKBKG,TRAF3,CD40LG |
| ne network for IgA production | HLA-DRB4,CD86,MHC2A,Il2,HLA-DPB1,TGFB1A,ITGA4,CXCL12B,TNFSF13,BMA2 |
| Intestinal i | IL4,CXCL12,CXCL12B,CCL25B,CXCL12A,BLA,TGFB1A,MHC2DCB,MAP3K14,HLA-DRB1 |
| Viral carcinogenesis | HIST1H2BN,HIST1H4I,HIST1H2BI,RBPJ,IRF7,RANBP1,RELA,GTF2A2,HIST1H2BM,HIST3H2BB-PS |
| HIF- signaling pathway | IL6R,Trf,TEK,MAP2K2,MTOR,TCEB2,PIK3CG,EP300,ENO1,IFNGR2 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | TNFRSF9A,IL12RB1,IFNB,CSF1R,EPOR,CXCL12,CNTFR,CCL23,IL22RA1,IL4 |
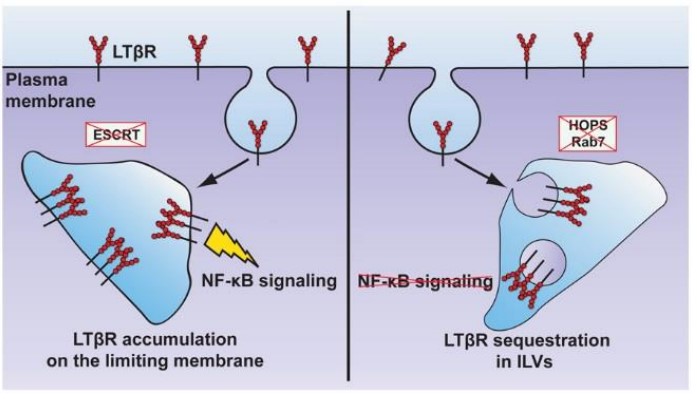
Fig1. Model of the different LTβR topology and signaling upon dysfunction of various trafficking regulators. (Magdalena Banach-Orłowska, 2018)
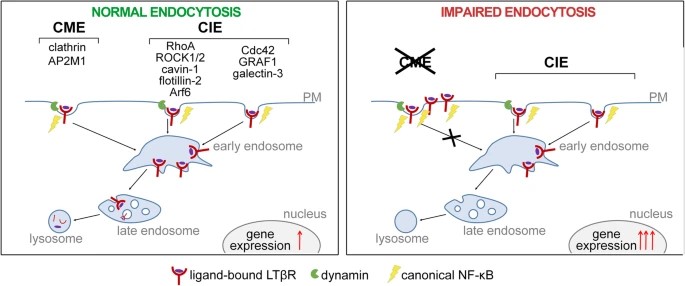
Fig2. LTβR was predominantly present on endocytic vesicles and the Golgi apparatus. (Małgorzata Maksymowicz, 2020)
Protein Function
LTBR has several biochemical functions, for example, identical protein binding,protein binding,tumor necrosis factor-activated receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LTBR itself. We selected most functions LTBR had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LTBR. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| tumor necrosis factor-activated receptor activity | TNFRSF10C,TNFRSF6B,TNFRSF1B,EDA2R,TNFRSF11A,CD27,TNFRSF21,NRADD,HDR,TNFRSF1A |
| identical protein binding | C10orf88,MCIN,ACADM,SF1,SRPX2,EPHA4,DNMT3A,EGFR,VIL1,CEP170L |
| protein binding | ATP11C,CRNKL1,EFNA3,EIF4ENIF1,ZNF286A,H2-AB1,TBC1D2,UNC119B,SPRTN,GPA33 |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | USP13,SMAD6,ERBB2,RB1,BCL2,RBX1,SNX9,TSG101,GABARAP,SNCAIP |
Interacting Protein
LTBR has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LTBR here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LTBR.
p29846-pro_0000037666;ZMYND11;DEAF1;TRAF2;TRAF3;BALF4 (provisional);HES1;q00653-pro_000003032;Bmpr1a;NFKB2
LTBR Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
- Endothelial Cell Markers
- Cytokine and Growth Factor Receptors on VSMC
- Myeloid Lineage Markers
- B Cell CD Antigen
- Other CD Antigen
- Granulocyte Markers
- Integrins
- Focal Adhesion Proteins in VSMC
- Basophils
- Eosinophils
- Neutrophils
- B Cell Chemotaxis, Migration, and Adhesion
- T Cell Migration
- CD Antigen (Basophils)
- CD Antigen (Eosinophils)
- CD Antigen (Granulocyte Markers)
- CD Antigen (Neutrophils)
- Macrophage Marker CD Antigen
- CD Antigen (T Cell Migration/Adhesion)
- TNF Receptor
- Macrophage Markers
- Monocyte Markers
- Integrins in Focal Adhesions
- Dendritic Cell Adhesion and Migration
Related Services
Related Products
References