B Cell CD Antigen
Related Symbol Search List
- ACP5
- ALCAM
- CD157
- Cd180
- CD19
- CD1B
- CD22
- CD24
- CD28
- CD300LD
- CD320
- CD37
- CD38
- CD3D
- CD40 Ligand
- CD5
- CD5L
- CD72
- CD74
- CD79A
- CD79B
- CD80
- CD81
- CD83
- CD84
- CD8A
- CR1
- CXCR5
- DPP4
- ENPEP
- ENTPD1
- FCER2
- CD32A
- Fcgr2b
- Flt3l
- IGLL1
- LTB
- LTBR
- LY9
- MS4A1
- CD45
- L-selectin
- SLAMF9
- ST6GAL1
- TNFRSF4
Immunology Background
Available Resources for B Cell CD Antigen Research
Creative BioMart offers a comprehensive resource platform for B cell CD antigens, providing researchers with valuable information, high-quality products, customized services, and technical support. Harness the power of B cell CD antigen research to advance scientific knowledge, develop novel therapies, and improve human health. Explore our resources and unlock new possibilities in B cell biology. We provide a comprehensive list of B cell CD antigens, including CD19, CD20, CD21, CD22, CD23, CD24, CD25, and many more.
- Creative BioMart provides a variety of antibodies, recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, and more kits targeting different B cell CD antigens. These products enable precise detection, characterization, and analysis of B cell subsets and their functions.
- We provide customized services to meet specific research needs. Our experienced team of scientists provides custom antibody development, protein engineering, recombinant antigen production, and assay development services. Leverage our expertise to generate custom tools for your B cell CD antigen research project.
- In addition, we provide rich resources covering multiple aspects of B cell CD antigens, such as pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, areas of research, and other relevant topics. These resources will help researchers better explore the diverse research areas and disease associations related to B cell CD antigens. Understand their roles in autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, cancer immunology, vaccine development, and transplantation research. Stay updated with the latest discoveries and advancements in the field.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD19-3309H | Active Recombinant Human CD19 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD22-562H | Active Recombinant Human CD22 protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| CD24-3133H | Active Recombinant Human CD24 protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| CD79A-10975H | Recombinant Human CD79A, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CD79B-239H | Recombinant Human CD79B protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | human/IgG1/Fc |
| CD80-581H | Active Recombinant Human CD80, His-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | Human Cell | His |
| CD81-3465H | Recombinant Human CD81 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CD83-3927H | Recombinant Human CD83 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
About B Cell CD Antigen
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the adaptive immune response. They are responsible for producing antibodies, which help to recognize and neutralize pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
B cells express a variety of cell surface proteins known as CD antigens, which serve as markers for identifying and characterizing different subsets of B cells. These CD antigens play important roles in various aspects of B cell function, including cell signaling, adhesion, and antigen recognition.
Some of the most well-known CD antigens expressed on B cells include CD19, CD20, CD21, and CD40. CD19 is a co-receptor that plays a critical role in B cell activation and signaling. CD20 is a protein involved in B cell development and differentiation. CD21, also known as complement receptor 2 (CR2), is a receptor for complement component C3d and plays a role in B cell activation. CD40 is a co-stimulatory molecule that is important for B cell proliferation and antibody production.
Understanding the expression and function of B cell CD antigens is essential for studying the immune response and developing strategies for treating immune-related diseases. By targeting specific CD antigens, researchers can modulate B cell activity and potentially improve the outcomes of conditions such as autoimmune diseases, allergies, and cancers.
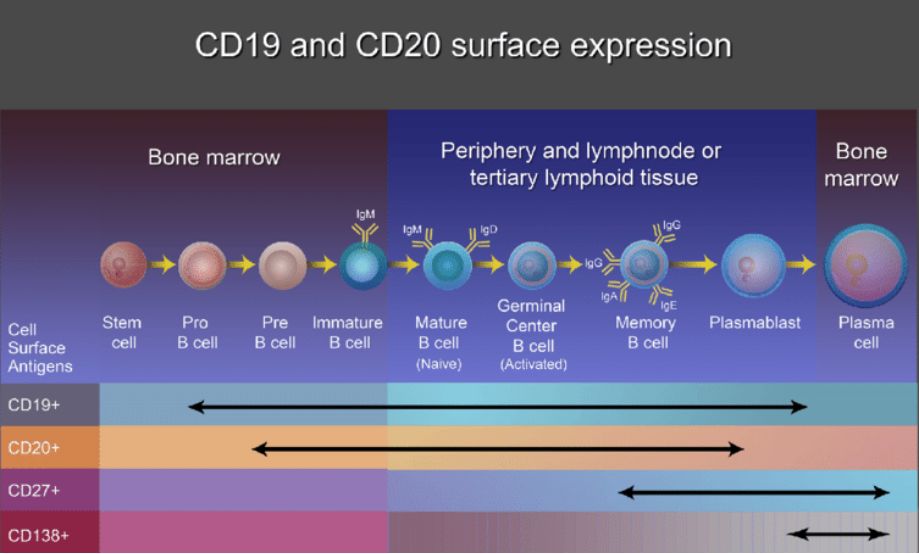 Fig.1 B cell CD markers. The B cell maturation process involves two phases of differentiation—an antigen-independent process in the bone marrow, where V(D)J recombination takes place, and an antigen-dependent process that occurs in secondary and tertiary lymphoid tissue. Specific CD (cluster of differentiation) markers such as CD19, CD20, CD27, and CD138 are helpful for distinguishing different maturation phases, including pro- and pre-B cells, immature and mature naïve B cells, memory B cells, plasmablasts, and plasma cells. (Stathopoulos P, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 B cell CD markers. The B cell maturation process involves two phases of differentiation—an antigen-independent process in the bone marrow, where V(D)J recombination takes place, and an antigen-dependent process that occurs in secondary and tertiary lymphoid tissue. Specific CD (cluster of differentiation) markers such as CD19, CD20, CD27, and CD138 are helpful for distinguishing different maturation phases, including pro- and pre-B cells, immature and mature naïve B cells, memory B cells, plasmablasts, and plasma cells. (Stathopoulos P, et al., 2022)
The Role of B-Cell CD Antigens in the Immune Response and in Immune-Related Diseases
B-cell Activation and Antibody Production
- CD19: CD19 is a key regulator of B-cell activation and signaling. It amplifies B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, leading to B-cell activation, proliferation, and antibody production.
- CD20: CD20 is involved in B-cell activation and differentiation. It is a target for therapeutic antibodies used in the treatment of B-cell lymphomas and autoimmune disorders.
- CD21: CD21 is a complement receptor on B cells that enhances B-cell activation by binding to complement components. It promotes antibody production and helps in the immune response against pathogens.
Immune Responses
- Humoral Immunity: B cells, through the action of CD antigens, produce antibodies that neutralize pathogens, facilitate their clearance, and prevent reinfection. CD antigens regulate B-cell activation, antibody class switching, and affinity maturation.
- Memory B Cells: CD27 is a B-cell CD antigen associated with memory B cells. Memory B cells, upon re-exposure to a pathogen, rapidly differentiate into antibody-secreting cells, leading to a faster and more robust immune response.
- Germinal Centers: CD77 (Stage-specific embryonic antigen 1, SSEA-1) is expressed on germinal center B cells. Germinal centers are specialized microenvironments where B-cell maturation, affinity maturation, and class switching occur during immune responses.
Immune-Related Diseases
- B-cell Lymphomas: Dysregulation of B-cell CD antigens can contribute to the development of B-cell lymphomas, including non-Hodgkin lymphomas and Hodgkin lymphoma. Aberrant expression or signaling of CD antigens can lead to uncontrolled B-cell proliferation and impaired apoptosis. Rituximab (Rituxan) is widely used in the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody against CD20, which inhibits tumor cell growth by binding to CD20 on the surface of B cells and inducing cytotoxic effects.
- Autoimmune Diseases: B cells and their CD antigens play a role in autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis. Dysregulated B-cell activation, antibody production, and autoantibody generation contribute to autoimmune pathology. Therapies targeting CD19 have been investigated for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. By inhibiting CD19 signaling, the autoimmune response can be reduced and arthritis symptoms relieved.
- Immunodeficiency Disorders: Defects in B-cell CD antigens can lead to immunodeficiency disorders. For example, deficiencies in CD19 or CD20 impair B-cell development and antibody production, resulting in increased susceptibility to infections. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) is an immunodeficiency disorder with impaired B-cell function. Defects in CD19 and CD20 may contribute to the development of CVID. In some studies, it has been possible to correct the immunodeficiency in patients with CVID by implanting hematopoietic stem cells with normal CD19 and CD20 expression.
Studying and understanding the function and regulatory mechanisms of B-cell CD antigens will contribute to a deeper understanding of the complexity of the immune system and provide new targets and strategies for the treatment of immune-related diseases.
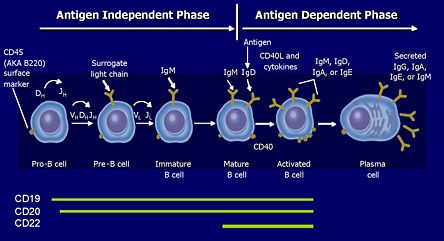 Fig.2 Targeting B Cell by CD surface marker in SLE. (Lyman D., 2017)
Fig.2 Targeting B Cell by CD surface marker in SLE. (Lyman D., 2017)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Stathopoulos P, Dalakas MC. Evolution of Anti-B Cell Therapeutics in Autoimmune Neurological Diseases. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(3):691-710.
- Lyman D. B cell Therapy to Treat an Axonal Neuropathy in Mixed Connective Tissue Disease. Caspian J Neurol Sci 2017; 3 (1):46-53

