CD Antigen (T Cell Migration/Adhesion)
Related Symbol Search List
- ALCAM
- CD45
- L-selectin
- ST6GAL1
- CD147
- ICAM-1
- CXCR1
- CXCR2
- ICAM-2
- LFA-1
- LTBR
- ITGA4
- Selplg
- L1CAM
- CD10
- CD31
- CD226
- CD2
- ITGAE
- CD200
- LAIR1
- SELE
- VCAM1
Immunology Background
Resources Available for the Study of CD Antigens (T-Cell Antigen/Recognition)
Creative BioMart is the premier destination for researchers seeking CD Antigen products for T cell migration and adhesion studies. Our dedication to providing top-notch products and personalized support ensures that you have everything you need to delve into the intricacies of T cell migration/adhesion.
- Our extensive product line includes recombinant proteins, native proteins, protein-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, GMP proteins, assay kits, and more. Each product is carefully crafted to meet your specific research needs with unmatched precision and expertise. We guarantee the highest quality and reliability of our products to ensure precise and reproducible results in your experiments.
- In addition to our wide range of products, we also offer a wealth of resources on CD antigens related to T cell migration/adhesion. Our comprehensive insights cover relevant pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, literature reviews, and other valuable information. These resources serve as an invaluable tool for gaining a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms and biological significance of T cell migration / adhesion-related CD antigens.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcam-3267M | Active Recombinant Mouse Alcam protein, His-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His |
| CD45-10957H | Recombinant Human CD45, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| ST6GAL1-1122H | Recombinant Human ST6GAL1, His tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD147-10906H | Recombinant Human CD147, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| ICAM1-2249H | Active Recombinant Human ICAM1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| ICAM2-3163H | Recombinant Human ICAM2 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| Ltbr-1219M | Active Recombinant Mouse Ltbr Protein, Fc-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | Fc |
| ITGA4 & ITGB7-163H | Recombinant Human ITGA4 & ITGB7 Protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | HEK293 | His/Avi |
| ITGAE-3118H | Recombinant Human ITGAE protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
About CD Antigen (T Cell Migration/Adhesion)
CD antigens are a group of cellular surface receptors that identify T cell type and differentiation stage. Some CD antigens associated with T cell migration and adhesion include:
- CD44: An adhesion receptor that regulates biological processes involving migrating cells, such as inflammation, angiogenesis, bone metabolism, and wound healing. In the immune system, CD44 levels increase when naive T lymphocytes are activated by microbes, and remain elevated on memory T cells after an infection is cleared.
- LFA-1: A key T cell integrin that regulates T cell activation and migration. Adhesion to LFA-1's ligand, intracellular adhesion receptor 1 (ICAM-1), allows for firm endothelium adhesion, prolonged contact with antigen-presenting cells, and binding to target cells for killing.
- CD62L (L-selectin): An adhesion molecule associated with differentiating naive and activated/memory T cells. Naive T cells express a CD62LhiCD44lo phenotype, while memory T cells exhibit a CD62LloCD44hi phenotype.
- Integrins (CD11a/CD18, CD11b/CD18, CD11c/CD18): Integrins are a family of heterodimeric adhesion molecules expressed on T cells and other immune cells. They mediate T cell adhesion and migration by interacting with various ligands, such as ICAM-1 (CD54) and VCAM-1 (CD106), on endothelial cells and other target cells. Integrins are crucial for T cell extravasation from blood vessels into inflamed tissues and immune cell clustering.
- Chemokine Receptors: Chemokine receptors, such as CCR7 and CXCR3, are G protein-coupled receptors expressed on T cells. They enable T cells to respond to chemotactic signals and migrate towards specific chemokines present in tissues or lymphoid organs. Chemokine receptors play a vital role in T cell homing, positioning, and recruitment to sites of inflammation or infection.
These CD antigens associated with T cell migration and adhesion contribute to the precise trafficking and positioning of T cells within the immune system. They facilitate interactions with endothelial cells, target cells, and extracellular matrix components, allowing T cells to navigate through tissues, enter lymphoid organs, and participate in immune surveillance and responses.
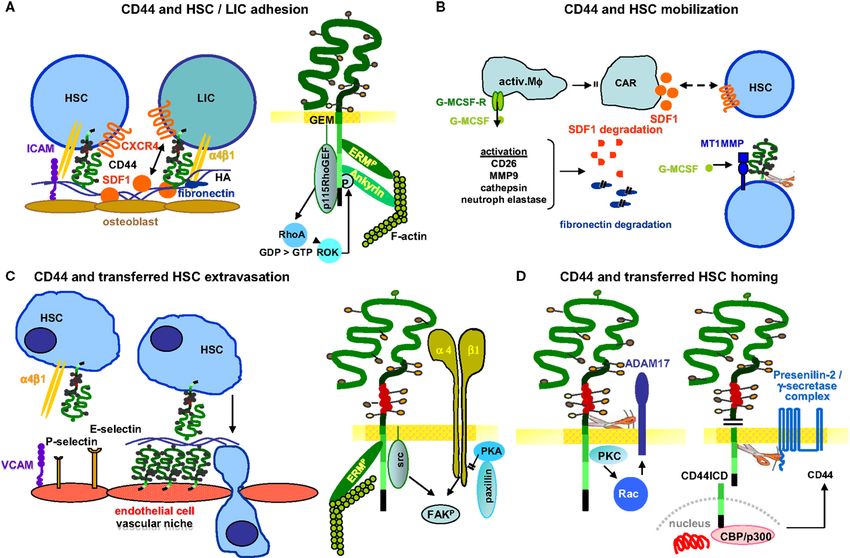 Fig.1 CD44-mediated adhesion, mobilization, migration, and homing in HSC/LIC. (Zöller M, et al., 2015)
Fig.1 CD44-mediated adhesion, mobilization, migration, and homing in HSC/LIC. (Zöller M, et al., 2015)
Functions of CD Antigens Associated With T Cell Migration/Adhesion
CD antigens associated with T cell migration and adhesion play important roles in facilitating T cell movement and interactions with other cells or molecules within the immune system. Here are the key functions of these CD antigens:
Mediating Cell Adhesion: CD antigens such as CD2, CD44, and integrins are involved in cell adhesion processes. They facilitate the attachment and binding of T cells to other cells or extracellular matrix components. By interacting with their ligands on target cells or endothelial cells, these CD antigens promote stable adhesion, which is crucial for T cell migration, extravasation, and immune cell clustering.
Enhancing T Cell Transmigration: CD antigens, including CD62L (L-selectin) and integrins, contribute to T cell transmigration across blood vessel walls or into lymphoid organs. They participate in the multistep process of extravasation, where T cells roll along endothelial cells, adhere firmly, and eventually traverse the endothelial barrier to enter tissues or lymphoid organs. CD62L, for instance, interacts with ligands on high endothelial venules (HEVs), facilitating T cell entry into lymph nodes.
Guiding T Cell Homing: CD antigens such as chemokine receptors are involved in T cell homing, directing T cells towards specific tissues or lymphoid organs. Chemokine receptors enable T cells to respond to chemotactic signals, guiding their migration along concentration gradients of chemokines. By recognizing and binding to specific chemokines, these CD antigens help T cells home to sites of inflammation, infection, or lymphoid compartments, contributing to immune surveillance and responses.
Supporting Immune Cell Interactions: CD antigens involved in T cell migration and adhesion also facilitate interactions and communication between T cells and other immune cells. For instance, CD2 on T cells interacts with CD58 (LFA-3) on APCs, promoting immune synapse formation and enhancing T cell activation and antigen presentation. These interactions are crucial for the coordination and regulation of immune responses.
Modulating Immune Cell Behavior: CD antigens associated with T cell migration and adhesion can modulate T cell behavior and immune responses. For example, the engagement of CD28, a co-stimulatory molecule, with its ligands on APCs provides important signals for T cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. In contrast, CTLA-4, another CD antigen, competes with CD28 for binding to B7 molecules and delivers inhibitory signals, dampening T cell activation and immune responses.
Understanding the functions of CD antigens associated with T cell migration and adhesion is crucial for deciphering the mechanisms underlying immune cell trafficking, immune responses, and the development of targeted therapies. These CD antigens enable T cells to navigate through tissues, interact with other cells, and contribute to effective immune surveillance and immune-mediated processes in health and disease.
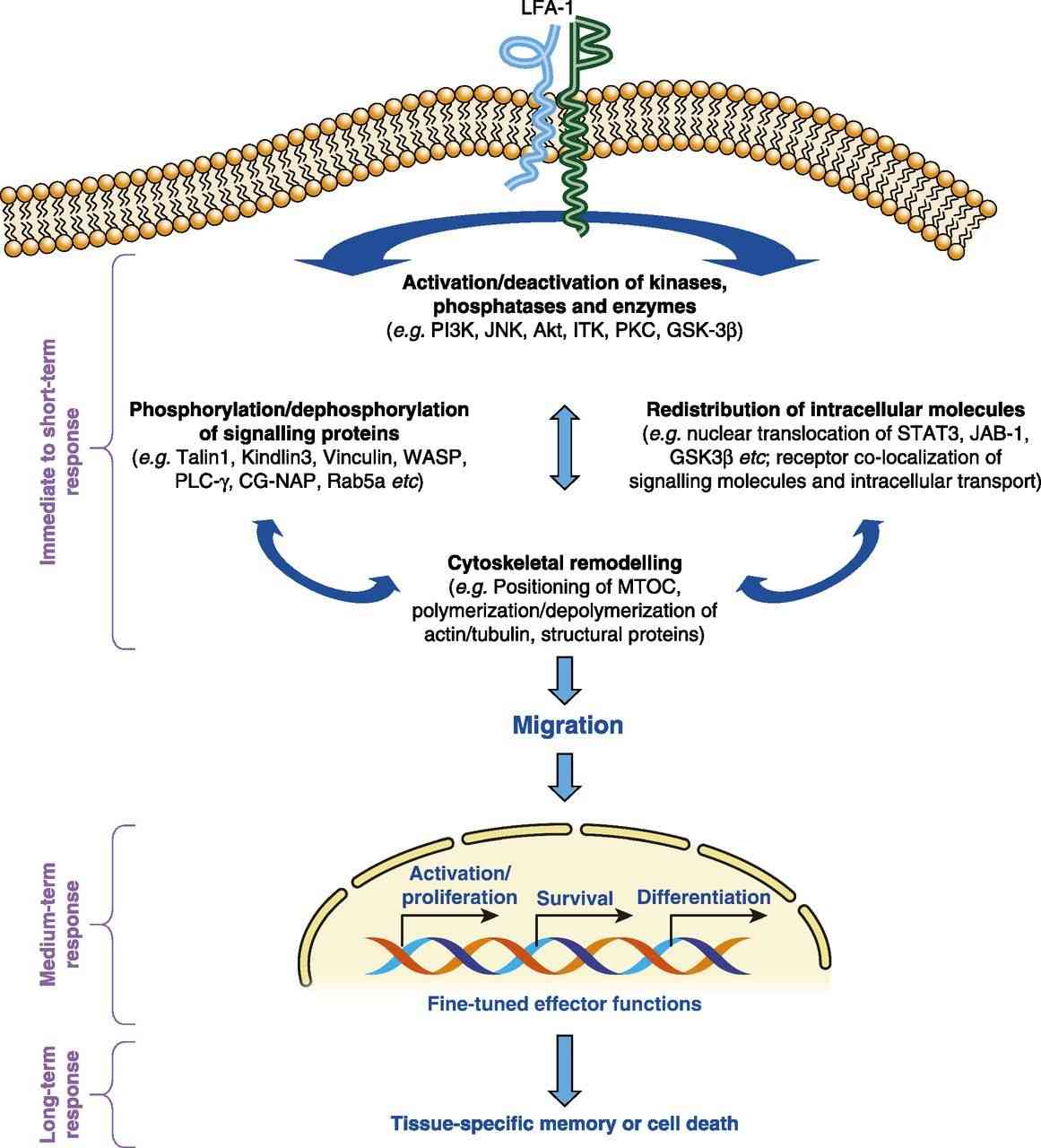 Fig.2 Divergent roles for LFA-1 contact in the regulation of T cell functioning. (Navin Kumar Verma, et al., 2017)
Fig.2 Divergent roles for LFA-1 contact in the regulation of T cell functioning. (Navin Kumar Verma, et al., 2017)
Choose Creative BioMart as your trusted partner, and embark on a journey of scientific exploration with confidence and precision. If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Walling BL, Kim M. LFA-1 in T Cell Migration and Differentiation. Front Immunol. 2018;9:952.
- Baaten BJ, Tinoco R, Chen AT, Bradley LM. Regulation of Antigen-Experienced T Cells: Lessons from the Quintessential Memory Marker CD44. Front Immunol. 2012;3:23.
- Zöller M. CD44, Hyaluronan, the Hematopoietic Stem Cell, and Leukemia-Initiating Cells. Front Immunol. 2015;6:235.
- Navin Kumar Verma, Dermot Kelleher; Not Just an Adhesion Molecule: LFA-1 Contact Tunes the T Lymphocyte Program. J Immunol 15 August 2017; 199 (4): 1213–1221.

