PIM1
-
Official Full Name
pim-1 oncogene -
Overview
PIM-1 is a member of the serine/threonine kinase PIM oncogene family. PIM-1 has been implicated in lymphomagenesis, cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation and tumourigenesis. The PIM-1 protein kinase is upregulated in prostate cancer. -
Synonyms
PIM1;pim-1 oncogene;PIM;serine/threonine-protein kinase pim-1;Oncogene PIM1;pim-1 kinase 44 kDa isoform;pim-1 oncogene (proviral integration site 1);proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase pim-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Sf21 Cells
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is PIM1 protein?
PIM1 (Pim-1 proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6p21. PIM1 belongs to the Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and PIM subfamily. This protein is expressed primarily in B-lymphoid and myeloid cell lines, and is overexpressed in hematopoietic malignancies and in prostate cancer. Both the human and orthologous mouse genes have been reported to encode two isoforms (with preferential cellular localization) resulting from the use of alternative in-frame translation initiation codons, the upstream non-AUG (CUG) and downstream AUG codons. The PIM1 protein is consisted of 313 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 35.7 kDa.
What is the function of PIM1 protein?
PIM1 is a proto-oncogene with serine/threonine kinase activity involved in cell survival and cell proliferation and thus providing a selective advantage in tumorigenesis. It regulates a variety of cellular processes such as cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. Pim-1 phosphorylates and regulates multiple substrate proteins, including transcription factors, cyclins, and other kinases and signaling molecules. In addition, Pim-1 is also involved in physiological and pathological processes such as tumor development, immune regulation, and cardiovascular disease.
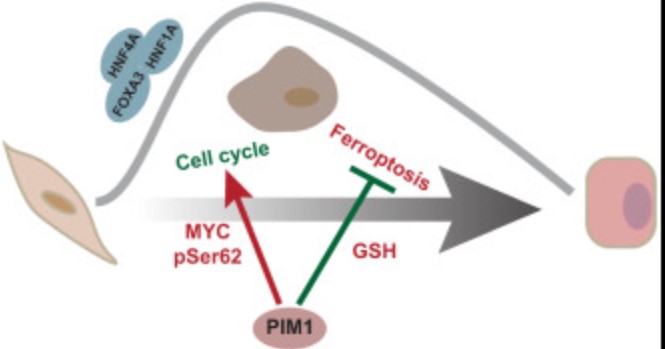
Fig1. Working model showing potential roles of PIM1 in hepatic lineage reprogramming. (Yangyang Yuan, 2022)
PIM1 Related Signaling Pathway
PIM1 performs its function by phosphorylating a variety of substrates, such as transcription factors, cell cycle regulatory proteins, and apoptosis-related proteins. The role of Pim-1 in cell signal transduction is mainly reflected in the following aspects: promoting cell cycle process, inhibiting cell apoptosis, regulating metabolism and influencing cell differentiation. In addition, Pim-1 also interacts with signaling pathways related to tumorigenesis and development, including PI3K/AKT, MAPK, mTOR, etc., thus playing an important role in cancer.
PIM1 Related Diseases
PIM1 is associated with a variety of diseases, especially in the field of cancer. Overexpression or enhanced activity of Pim-1 has been observed in many types of cancer, including prostate, breast, lung, and lymphoma. In addition, PIM1's role in cell survival and metabolic regulation also suggests that it may be associated with other diseases, such as cardiovascular disease and certain metabolic diseases.
Bioapplications of PIM1
Although clinical drugs that directly target PIM1 are not yet fully approved, several Pim inhibitors have entered clinical trials to evaluate their potential in the treatment of blood cancers and solid tumors. These inhibitors are typically multikinase inhibitors that simultaneously target members of the Pim family as well as other related signaling pathways.
Case Study
Case study 1: Ashley Y Gao, 2022
Cellular senescence is emerging as a driver of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a progressive and fatal disease with limited effective therapies. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), involving the release of inflammatory cytokines and profibrotic growth factors by senescent cells, is thought to be a product of multiple cell types in IPF, including lung fibroblasts. The purpose of this study was to assess the role of Pim-1 kinase as a driver of NF-κB-induced production of inflammatory cytokines from low-passage IPF fibroblast cultures displaying markers of senescence.
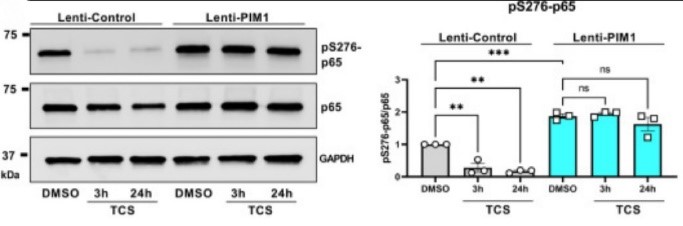
The results demonstrate that Pim-1 kinase phosphorylates p65/RelA, activating NF-κB activity and enhancing IL-6 production, which in turn amplifies the expression of PIM1, generating a positive feedback loop. In addition, targeting Pim-1 kinase with a small molecule inhibitor dramatically inhibited the expression of a broad array of cytokines and chemokines in IPF-derived fibroblasts. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting Pim-1 kinase to reprogram the secretome of senescent fibroblasts and halt IPF progression.
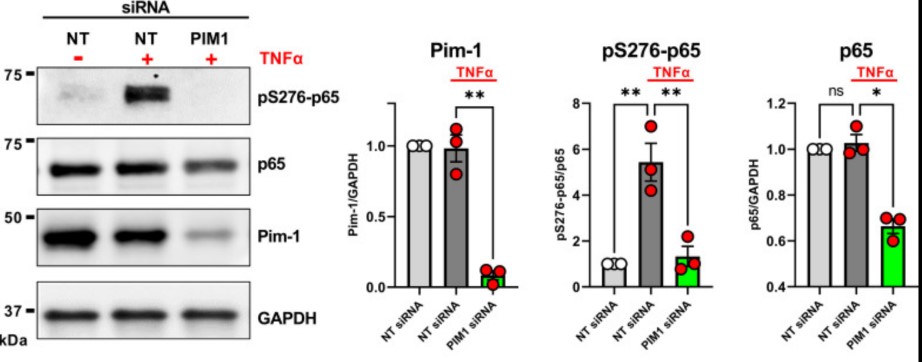
Fig1. Proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus 1 (Pim-1) regulates phosphorylation and activity of p65/RelA.
Case study 2: Yangyang Yuan, 2022
Protein kinase-mediated phosphorylation plays a critical role in many biological processes. However, the identification of key regulatory kinases is still a great challenge. Here, the researchers develop a trans-omics-based method, central kinase inference, to predict potentially key kinases by integrating quantitative transcriptomic and phosphoproteomic data. Using known kinases associated with anti-cancer drug resistance, the accuracy of our method denoted by the area under the curve is 5.2% to 29.5% higher than Kinase-Substrate Enrichment Analysis.
Further experiments reveal that a serine/threonine kinase, PIM1, promotes hepatic conversion and protects human dermal fibroblasts from reprogramming-induced ferroptosis and cell cycle arrest. This study not only reveals new regulatory kinases, but also provides a helpful method that might be extended to predict central kinases involved in other biological processes.
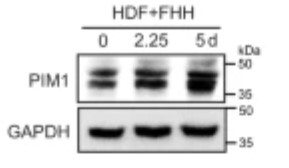
Fig3. Experimental analysis of PIM1 roles in hepatic reprogramming. Immunoblotting of PIM1 in HDFs infected with FHH for the indicated number of days.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
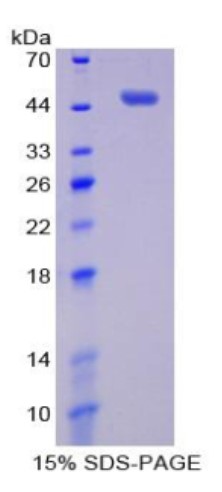
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PIM1-7906H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
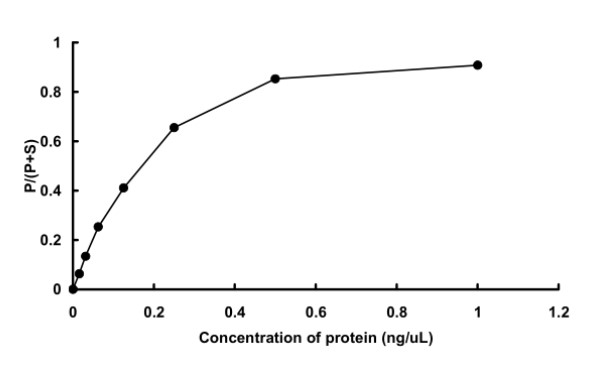
Fig2. Activity Data. (PIM1-2938HF)
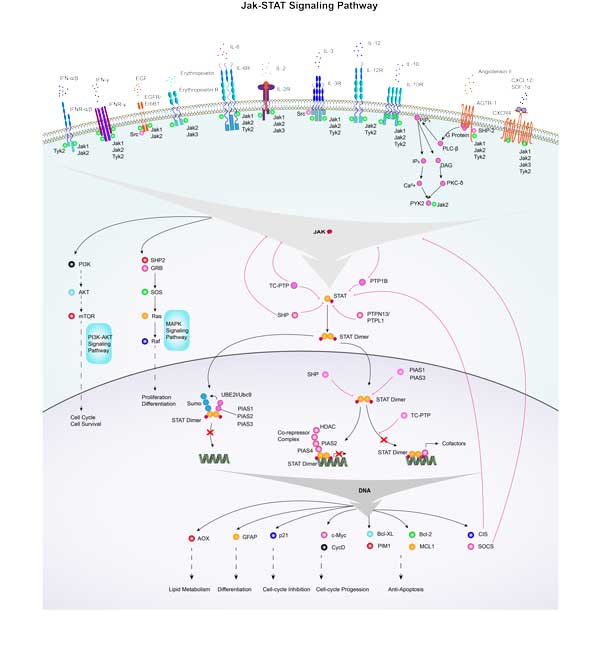
Involved Pathway
PIM1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PIM1 participated on our site, such as Jak-STAT signaling pathway,MicroRNAs in cancer,Acute myeloid leukemia, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PIM1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Acute myeloid leukemia | BRAF,CCND1,KRAS,AKT3,RUNX1T1,RPS6KB1,NRAS,PML,RUNX1,STAT5A |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | ABCB1,PRKCG,RAF1,RHOA,BMPR2,MAP2K2,ABCC1,UBE2I,PIK3R2,PDGFRA |
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | AOX1,GFAP,IL2RGB,CTF1,PRLR,IL20RA,IL2RB,SOS1,IL2RGA,IL10RA |
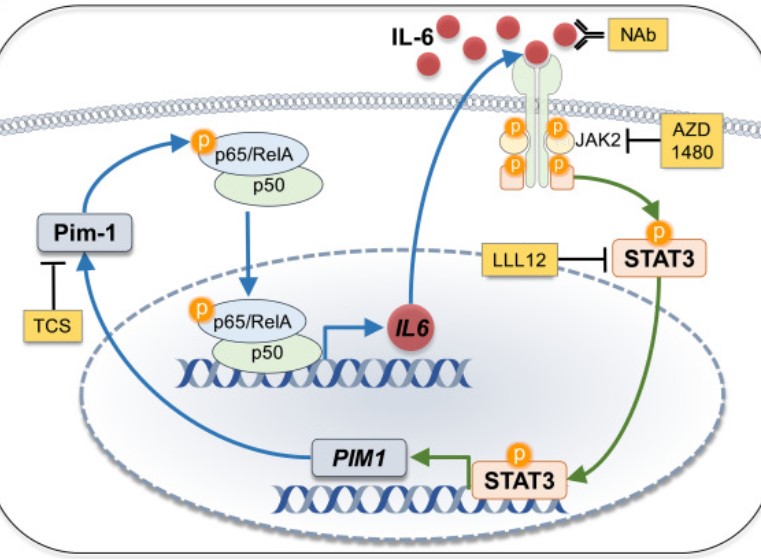
Fig1. Pim-1 phosphorylates p65/RelA, supporting NF-κB transcriptional activity that stimulates IL-6 synthesis. (Ashley Y Gao, 2022)
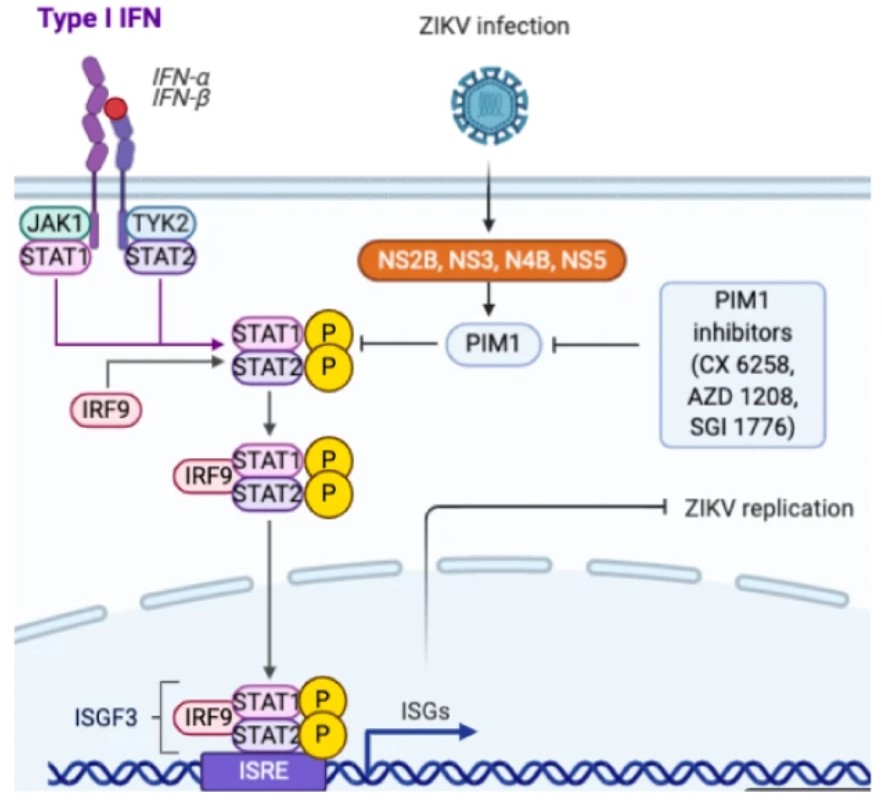
Fig2. The mechanism by which PIM1 mediates ZIKV replication. (Fanghang Zhou, 2021)
Protein Function
PIM1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,manganese ion binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PIM1 itself. We selected most functions PIM1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PIM1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | STK31,ACTC1,PRPF4B,EGFR,ABCG5,TP53RK,PSMC2,NMRK2,LACE1B,PPIP5K1 |
| transcription factor binding | HES4,TRIB2,ID1,KAT2A,CEBPA,POU1F1,APBB1,PRKDC,HEYL,STK4 |
| manganese ion binding | GALNT1,ME1,NPEPL1,PPEF1,FAM20C,DYRK2,MRE11A,HMGCL,PPM1N,TDP2B |
| ribosomal small subunit binding | ERAL1,DHX29,CPEB2,DDX3X,NPM1,PTCD3,NME1,MTIF3 |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | BMPR1B,ACVR1BA,BRAF,ULK1A,TSSK1,NEK6,RPS6KB1B,STK17A,MAP3K14,NIM1K |
| protein binding | RMND5A,SLN,TDRD1,F11R,DPY30,RPA3,GEMIN4,CD247,HIST1H3A,SORBS2 |
Interacting Protein
PIM1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PIM1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PIM1.
RPS19;TFPT;FH;FXR2;NHLH1;BEND7
PIM1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Perera, GK; Ainali, C; et al. Integrative Biology Approach Identifies Cytokine Targeting Strategies for Psoriasis. SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE 6:-(2014).
- Dourado, IBZ; Batista, WL; et al. Dual localization of Mdj1 in pathogenic fungi varies with growth temperature. MEDICAL MYCOLOGY 52:187-195(2014).