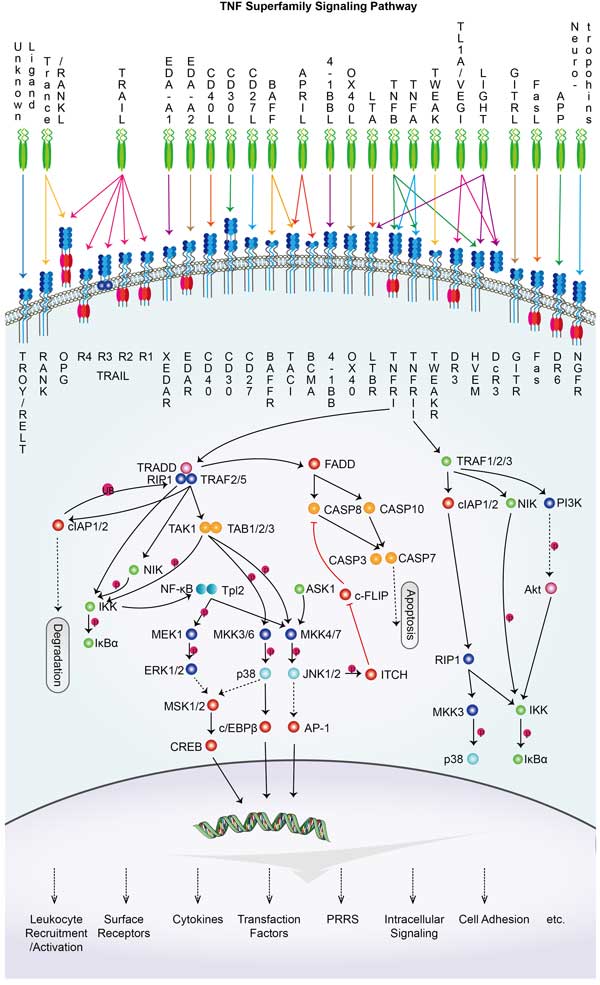
TNFSF14
-
Official Full Name
tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 14 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This protein is a ligand for TNFRSF14, which is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, and which is also known as a herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM). This protein may function as a costimulatory factor for the activation of lymphoid cells and as a deterrent to infection by herpesvirus. This protein has been shown to stimulate the proliferation of T cells, and trigger apoptosis of various tumor cells. This protein is also reported to prevent tumor necrosis factor alpha mediated apoptosis in primary hepatocyte. Two alternatively spliced transcript variant encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. -
Synonyms
TNFSF14;tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 14;tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 14;CD258;HVEM L;LIGHT;LTg;delta transmembrane LIGHT;herpesvirus entry mediator A;herpesvirus entry mediator ligand;herpesvirus entry mediator-ligand;herpes virus entry mediator ligand;ligand for herpesvirus entry mediator;tumor necrosis factor receptor-like 2;tumor necrosis factor superfamily member LIGHT;TR2;HVEML
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Rat
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- CHO
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Insect Cells
- His
- Fc
- Non
- rFc
- Myc
- Flag
- S
- DDK
- mIgG2a
- Avi
Background
What is TNFSF14 protein?
TNFSF14 gene (TNF superfamily member 14) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This protein is a ligand for TNFRSF14, which is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, and which is also known as a herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM). This protein may function as a costimulatory factor for the activation of lymphoid cells and as a deterrent to infection by herpesvirus. This protein has been shown to stimulate the proliferation of T cells, and trigger apoptosis of various tumor cells. The TNFSF14 protein is consisted of 240 amino acids and TNFSF14 molecular weight is approximately 26.4 kDa.
What is the function of TNFSF14 protein?
The TNFSF14 protein, also known as LIGHT, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily and is expressed primarily on activated T cells, natural killer cells (NK cells), and immature dendritic cells. LIGHT can act as a soluble and cell-surface bound type II membrane protein and must interact in its trimer form with its two main functional receptors, the herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) and the lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTβR). LIGHT signaling through these receptors has different functions that depend on cell type, but interactions with both types of receptors have immune-related implications in tumor biology. LIGHT has shown potential in tumor immunotherapy because of its ability to promote anti-tumor immune responses by altering the tumor microenvironment (TME). In addition, LIGHT-LTβR signaling is also responsible for creating highly efficient endothelial veins (HEVs), which are the primary sites where white blood cells leak into the target tissue.
TNFSF14 related signaling pathway
TNFSF14 exhibits inducible expression, and competes with HSV dUTPase for binding to herpesvirus entry mediator, a receptor expressed by T lymphocytes), interacts with its receptors, HVEM and LTβR, to initiate downstream signaling cascades. This interaction can lead to activation of the NF-κB pathway, promoting inflammation and immune cell survival, or induce apoptosis through the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, depending on the cellular context and receptor engagement. The balance between these effects is essential for maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity or chronic inflammation. Dysregulation of this pathway has been implicated in various diseases, including autoimmune disorders and cancer, highlighting its significance in both immune modulation and disease pathogenesis.
TNFSF14 related diseases
TNFSF14-related diseases encompass a spectrum of conditions primarily associated with dysregulated immune responses and inflammation. This includes autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, where overactive TNFSF14 signaling can contribute to joint destruction and chronic inflammation. Additionally, TNFSF14's role in apoptosis regulation links it to cancer development, particularly in malignancies where apoptosis resistance is a hallmark feature. Furthermore, its involvement in T cell co-stimulation suggests a potential role in transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. The fine balance between promoting immune activation and apoptosis underscores the complexity of TNFSF14's involvement in health and disease, making it a critical target for therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating immune system activity.
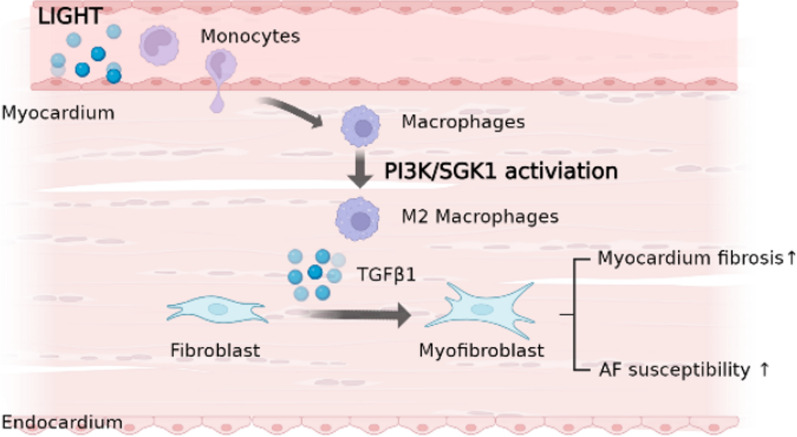
Fig1. Schematic diagram of the potential effect of LIGHT in promoting cardiac fibrosis and atrial fibrillation vulnerability. (Yirong Wu, 2023)
Bioapplications of TNFSF14
By interacting with its receptors, HVEM and LTβR, rhTNFSF14 can either enhance or suppress immune cell activity, depending on the context. This dual capacity makes it a promising therapeutic candidate for conditions characterized by excessive inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis, where inhibiting its signaling may alleviate symptoms. Conversely, in scenarios requiring immune enhancement, such as certain cancer immunotherapies, stimulating the TNFSF14 pathway could boost anti-tumor immunity. Additionally, its role in apoptosis regulation suggests potential applications in managing cancers by promoting cell death in malignant cells. Thus, rhTNFSF14 holds significant promise for advancing treatments across a range of immune-mediated diseases, leveraging its ability to fine-tune immune system function.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Sook-Kyoung Heo, 2023
Liver transplantation is optimal for liver failure but faces limitations due to donor scarcity, surgical risks, costs, and ongoing immunosuppression. Liver cell transplantation is a viable alternative. LIGHT, a TNF superfamily member, may enhance the differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hBM-MSCs) into hepatocyte-like cells. This study found that recombinant human LIGHT (rhLIGHT) induced hBM-MSCs to adopt hepatocyte-like characteristics, expressing liver-specific markers and improving glycogen storage and indocyanine green uptake. rhLIGHT also boosted cell proliferation via the STAT3 and STAT5 pathways, suggesting its potential in liver cell therapy.
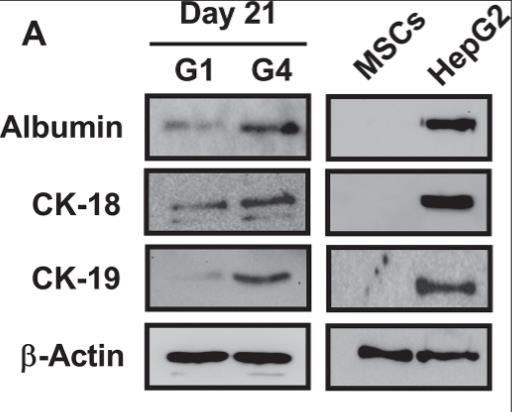
Fig1. RhLIGHT enhanced the expression of hepatocyte-specific marker proteins in hBM-MSCs.
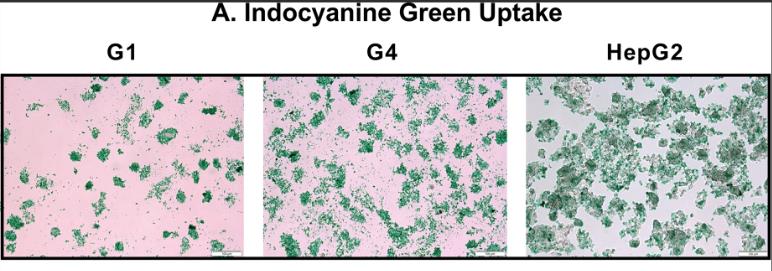
Fig2. Differentiated hBM-MSCs by rhLIGHT exhibited positivity for ICG after incubation in ICG solution.
Case Study 2: Sook-Kyoung Heo, 2021
Osteoporosis, characterized by reduced bone density and quality, impacts millions globally and is currently treated with drugs that can have severe side effects. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy could offer an alternative. LIGHT, a TNF superfamily member, may influence osteogenesis in human bone marrow-derived MSCs (hBM-MSCs). This study found that recombinant LIGHT (rhLIGHT) treatment increased calcium and phosphate deposition in hBM-MSCs, as indicated by Alizarin red and von Kossa staining. rhLIGHT also upregulated osteogenic markers in a dose-dependent manner, with the WNT/β-catenin pathway playing a key role in enhancing hBM-MSC differentiation into osteocytes.
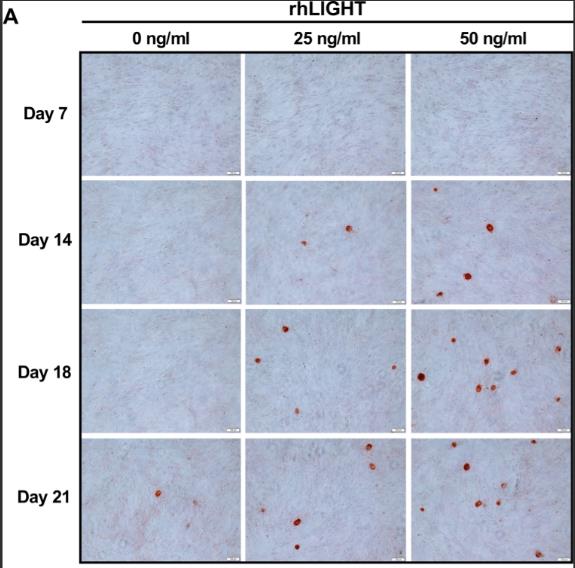
Fig3. Cells were incubated with 0, 25, and 50 ng/ml concentrations of rhLIGHT and stained with 2% Alizarin red to confirm calcium deposits.
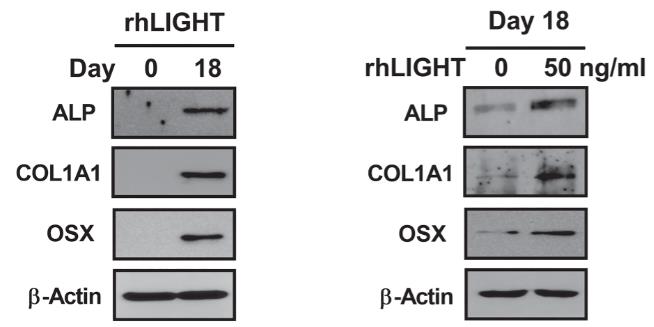
Fig4. Cells were stimulated with 0 and 50 ng/ml rhLIGHT and were tested the protein level.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TNFSF14-7782H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TNFSF14-552H)
Involved Pathway
TNFSF14 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TNFSF14 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,NF-kappa B signaling pathway,Herpes simplex infection, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TNFSF14 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | TNFRSF1A,IKBKG,ERC1,DDX58,ICAM1,LTA,BCL2A1,TAB2,MYD88,Ccl21a |
| Herpes simplex infection | NXF2,ABCB3L1,HCFC1A,MAPK8B,PVRL1,SRSF5A,SRSF1B,PER2,TBPL1,BMA2 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | CXCL10,IL20RA,CX3CL1,CXCL2,CCL19,TGFBR2,PRLRA,PRL,IL15,PRL2 |
Protein Function
TNFSF14 has several biochemical functions, for example, cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process,cytokine activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TNFSF14 itself. We selected most functions TNFSF14 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TNFSF14. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cytokine activity | BMP7B,Flt3l,INHBAA,IL36B,TNFSF10,IL7,SPP1,RNF207B,THPO,CMTM7 |
| protein binding | COPS8,MAZ,RNF144B,FAM189B,TRIM35,UBA52,ERBB4,GLIS2,SDHA,MYOM1 |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process | RPS6KA3,BIRC3,PRDX5,XIAP,C1QL4L,IGF1RB,RPS6KA1,LEF1,BIRC8,TFAP2B |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | TNFSF10L4,TNF,TNFSF11,FADD,TNFB,LTB,TNFSF12,TNFSF8,EDA,TNFSF13B |
| receptor binding | NXPH1,SCP2,MTSS1,HFE2,INSL3,IAPP,NRG2,NXPH3,SLC39A1,ALCAM |
Interacting Protein
TNFSF14 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TNFSF14 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TNFSF14.
TNFRSF14;TNFRSF6B;LTB
TNFSF14 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- del Rio, ML; Fernandez-Renedo, C; et al. Therapeutic Blockade of LIGHT Interaction With Herpesvirus Entry Mediator and Lymphotoxin beta Receptor Attenuates In Vivo Cytotoxic Allogeneic Responses. TRANSPLANTATION 98:1165-1174(2014).
- Kojima, R; Kajikawa, M; et al. Molecular Basis for Herpesvirus Entry Mediator Recognition by the Human Immune Inhibitory Receptor CD160 and Its Relationship to the Cosignaling Molecules BTLA and LIGHT. JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 413:762-772(2011).