Embryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Creative BioMart Embryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Product List
Immunology Background
About Lymphoid Lineage Markers
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are capable of differentiating into two main lineages of cells: lymphocytes and myeloid cells. Lymphoid lineage cells develop during lymphangiogenesis and include B-cells, T-cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells, which play a critical role in the adaptive immune response. Many lymphocytes have a short lifespan, and homeostasis of the immune system requires continuous self-renewal and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells. Lymphoid lineage markers play a role in identifying and characterizing lymphoid lineage cells, including T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. Numerous research efforts have been devoted to understanding the expression patterns and functional roles of lymphoid lineage markers. CD3 has been shown to be a key marker for T cells, CD19 for B cells, and NKp46 and CD56 for NK cells. These cell surface/intracellularly expressed markers provide valuable insights into lymphocyte development, differentiation, and function.
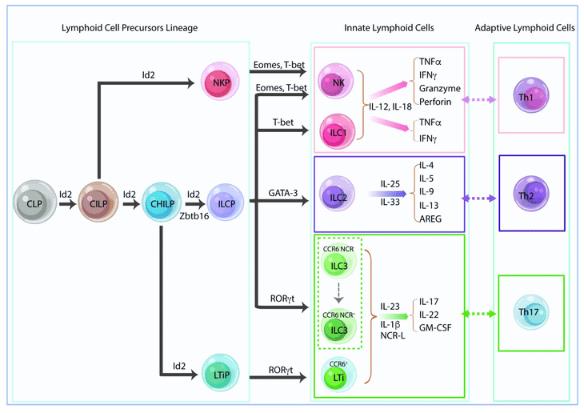 Fig.1 Innate lymphoid cell lineage and classification. (An Z, et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Innate lymphoid cell lineage and classification. (An Z, et al., 2019)
Functions of Lymphoid Lineage Markers
- Cell identification
Lymphatic lineage markers provide a way to identify and distinguish lymphocytes from other cell types in complex cell populations. By detecting the presence or absence of specific markers, researchers can accurately identify lymphocytes and study their properties.
- Cell differentiation and maturation
Lymphoid lineage markers are often differentially expressed at different stages of lymphocyte development, differentiation, and maturation. Monitoring the expression of these markers allows researchers to track and analyze the progress of lymphocyte differentiation and functional specialization.
- Immunophenotyping
Lymphoid lineage markers are widely used in immunophenotyping studies to characterize lymphocyte subpopulations and assess their functional properties. By combining different markers, researchers can create immunophenotypic profiles that provide insight into the heterogeneity and functional diversity of lymphocytes.
- Disease diagnosis and monitoring
Altered expression patterns of lymphoid spectrum markers can be used as diagnostic or prognostic indicators of various diseases. Abnormal expression or absence of specific markers on lymphocytes may indicate certain pathological conditions such as lymphoma, leukemia and immunodeficiency.
Available Products and Resources of Lymphoid Lineage Markers
Creative BioMart offers a wide range of quality tools for hematopoietic stem cell differentiation studies, including recombinant proteins, native proteins, cell and tissue lysates, transfected stabilized cell lines, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, chromatography reagents, and assay kits. We also offer a range of individual antibodies to study the expression of hematopoietic lineage-specific markers. Differentiated lymphocytes can be identified by analyzing the expression of specific cell surface markers, such as clusters of differentiation (CD) proteins and interleukin (IL) receptors. For example, common lymphoid progenitor cells express IL-7 R α/CD127, and differentiated B cells can be identified by the expression of MS4A1/CD20. We offer a variety of products for the following lymphoid lineage markers:
You can choose the right product for your needs based on species, source, labeling, and more. Our products are widely used in immunology, cell biology, drug discovery, clinical diagnostics, and other fields. We provide researchers with a series of resources about each myeloid lineage marker, such as involved pathway, protein function, interacting protein, related articles, related articles, and related research area, please check the product details page.
Our products are characterized by high quality, diversity, and a wide range of applications to help you succeed in your research. We also offer services to customize products to meet the needs of specific research projects. Whether it is customized expression and purification of specific proteins, or customized experimental protocols and technical support, our team can provide personalized solutions according to customer requirements.
If you are interested in our products, services, or resources, please contact us immediately for more information, thank you for your attention!
References:
- Martin CH, Aifantis I, Scimone ML, von Andrian UH, Reizis B, von Boehmer H, Gounari F. Efficient thymic immigration of B220+ lymphoid-restricted bone marrow cells with T precursor potential. Nat Immunol. 2003 Sep;4(9):866-73. doi: 10.1038/ni965. Epub 2003 Aug 17. PMID: 12925850.
- An Z, Flores-Borja F, Irshad S, Deng J, Ng T. Pleiotropic Role and Bidirectional Immunomodulation of Innate Lymphoid Cells in Cancer. Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 4;10:3111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03111. PMID: 32117199; PMCID: PMC7010811.

