Other G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
About Other G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Other G protein-coupled receptors are a class of GPCRs that do not belong to the categories of biologically active lipid G protein-coupled receptors, chemokine receptors, Frizzled receptors, neurotransmitter G protein-coupled receptors, or orphan G protein-coupled receptors. This category encompasses a wide range of different receptor types with diverse roles and functions. e.g., GPR35, F2R, F2RL1, GPBAR1, P2RY6.
Other G protein-coupled receptors have a variety of endogenous ligands, including peptides, hormones, neurotransmitters, and sensory molecules. Binding of these ligands to the receptor triggers the activation of intracellular signaling pathways.
Mechanism of Action of Other G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Other G protein-coupled receptors are functionally regulated by typical mechanisms, including activation of G proteins and subsequent intracellular signaling cascade reactions. Upon ligand binding, the receptor undergoes a conformational change that activates the heterotrimeric G protein. Activated G proteins modulate downstream signaling effectors such as adenylate cyclase, phospholipase C, and ion channels, resulting in diverse cellular responses.
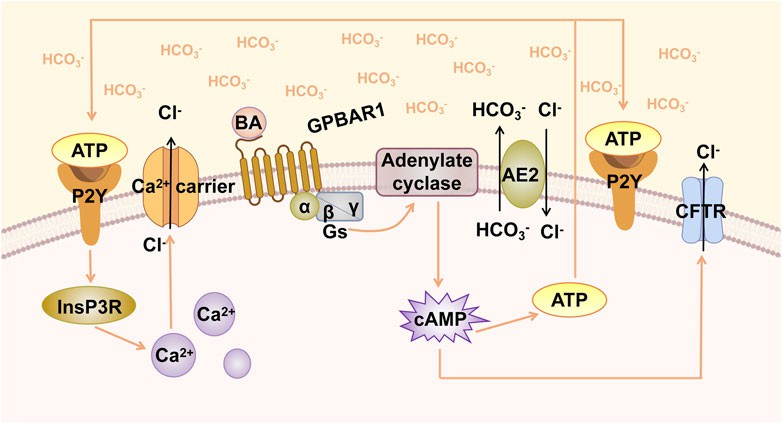 Fig.1 GPBAR1-induced biliary HCO3− umbrella. (Zhang F, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 GPBAR1-induced biliary HCO3− umbrella. (Zhang F, et al., 2022)
GPBAR1 is activated by BA, leading to the activation of stimulatory G-protein (Gs) and adenylate cyclase, resulting in increased intracellular cAMP levels. cAMP activates CFTR, triggering the secretion of Cl−. AE2 mediates the exchange of Cl−/HCO3− on the apical membrane and promotes the formation of HCO3− umbrella. Increased cAMP levels induce the release of ATP, and ATP binds to the P2Y receptor and activates Ca2+-dependent chloride channels.
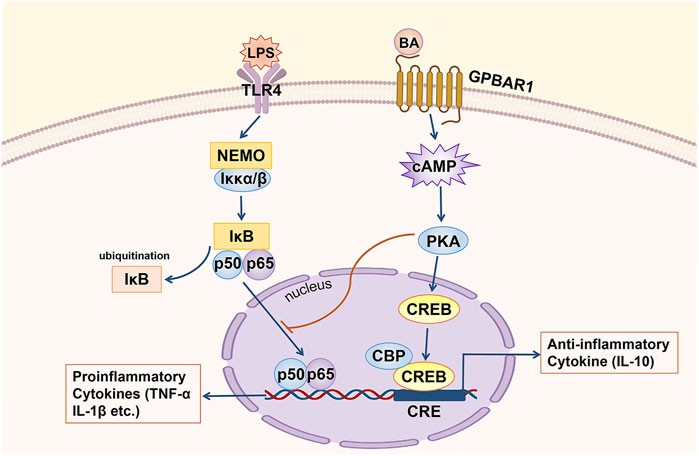 Fig.2 GPBAR1 relieves hepatic inflammation. (Zhang F, et al., 2022)
Fig.2 GPBAR1 relieves hepatic inflammation. (Zhang F, et al., 2022)
GPBAR1 through the cAMP pathway inhibits the transcription of proinflammatory cytokines mediated by NF-κB (IL-1α, IL-1β and TNF-α, etc.) and maintains the expression of an anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10).
Functions of Other G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Other G protein-coupled receptors are involved in many physiological processes and are implicated in a variety of biological functions, including:
- Endocrine Regulation
Some other G protein-coupled receptors are involved in endocrine regulation, mediating responses to hormones and neuropeptides. They regulate hormone release, and hormone synthesis, and modulate endocrine signaling pathways associated with processes such as metabolism, reproduction, and growth.
- Sensory Perception
Certain other G protein-coupled receptors play a key role in sensory perception, including vision, taste, and smell. They are responsible for detecting light, chemicals, and odorants, initiating signaling cascades that allow sensory stimuli to be perceived and interpreted.
- Cardiovascular Function
Several other G protein-coupled receptors are key regulators of cardiovascular function. They regulate heart rate, blood pressure, vascular tone, and platelet aggregation and help to regulate cardiovascular homeostasis.
- Immune Response
Other G protein-coupled receptors are involved in the immune response, including inflammation, immune cell migration, and immune cell activation. They regulate interactions between immune cells and their microenvironment and influence the ability of the immune system to recognize and respond to pathogens and exogenous substances.
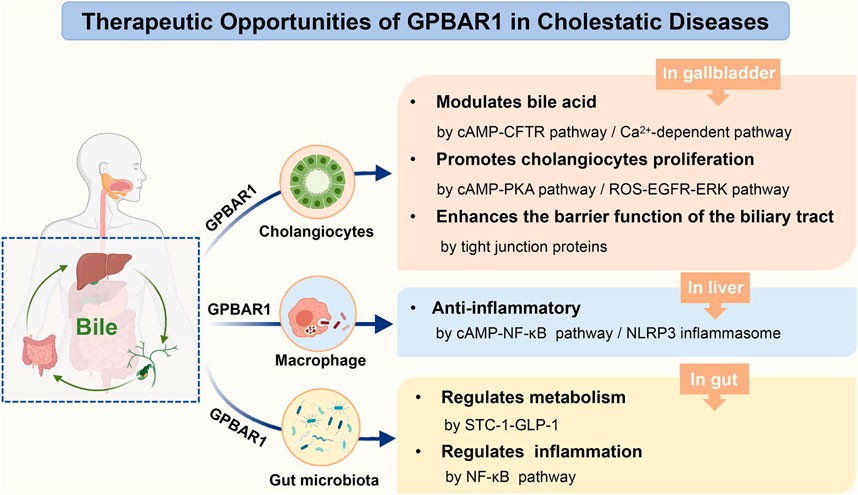 Fig.3 The role of GPBAR1 in cholestatic diseases. (Zhang F, et al., 2022)
Fig.3 The role of GPBAR1 in cholestatic diseases. (Zhang F, et al., 2022)
Available Resources for Other G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Other G protein-coupled receptors represent diverse receptors with different functions and mechanisms. Understanding their roles in various physiological processes is critical to improving our understanding of cell signaling and developing therapeutic interventions. Creative BioMart offers a wide range of products and services related to other GPCRs including recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, assay kits, and customized services to support researchers' understanding of the mechanism, function, and ligands of other GPCRs, contributing to our understanding of their importance in health and disease. The following other G protein-coupled receptors are displayed, click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. Please feel free to contact us with any questions or requests.
Reference:
- Zhang F, Xiao X, Li Y, et al. Therapeutic opportunities of GPBAR1 in cholestatic diseases[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2022, 12: 805269.

