Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases (RSK)
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
About Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases (RSK)
Ribosomal protein S6 kinases (RSK) are a class of signaling protein kinases belonging to the AGC family of protein kinases. Members of the RSK family are downstream effectors of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. They are activated by extracellular stimuli such as growth factors, hormones, and stress signals and regulate the activity of various downstream targets, including transcription factors and other kinases. S6 phosphorylation in vivo is catalyzed by (at least) two distinct families of mitogen-activated S6 kinases (the 70 kDa and the 90 kDa S6 kinases), which can be differentiated based on size. Both S6 kinases are activated by serine/threonine phosphorylation.
They regulate a variety of cellular processes such as cell growth, cell motility, cell survival, and cell proliferation. RSK plays an important role in the roadmap for numerous diseases and is important for research in cancer, diabetes, neurological disorders, and others.
Mechanism of Action of Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases (RSK)
The mechanism of action of Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases (RSKs) is a complex process involving multiple signaling pathways and molecular interactions. The following is an overview of the main mechanisms of action of RSKs:
- Activation Process
RSK activation is achieved through a cascade of phosphorylation events. External stimuli (e.g., growth factors, hormones, or stress signals) activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, which leads to phosphorylation of RSK by downstream kinases (e.g., MAPK-kinase-activated protein kinases and phosphatidylinositol-dependent protein kinases.) These phosphorylation events activate RSK and promote its translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus.
- Substrate Phosphorylation
Activated RSK achieves its biological functions by phosphorylating its substrates. RSK regulates processes such as gene expression, the cell cycle, and cell growth primarily by phosphorylating transcription factors and other kinases. RSK phosphorylates several transcription factors, including CREB (cAMP response element binding protein), ATF1 (activating transcription factor 1), and c-Fos. These phosphorylation events enhance the transcriptional activity of these factors and affect the expression of genes associated with cell growth and survival, cell cycle regulation, and neural function.
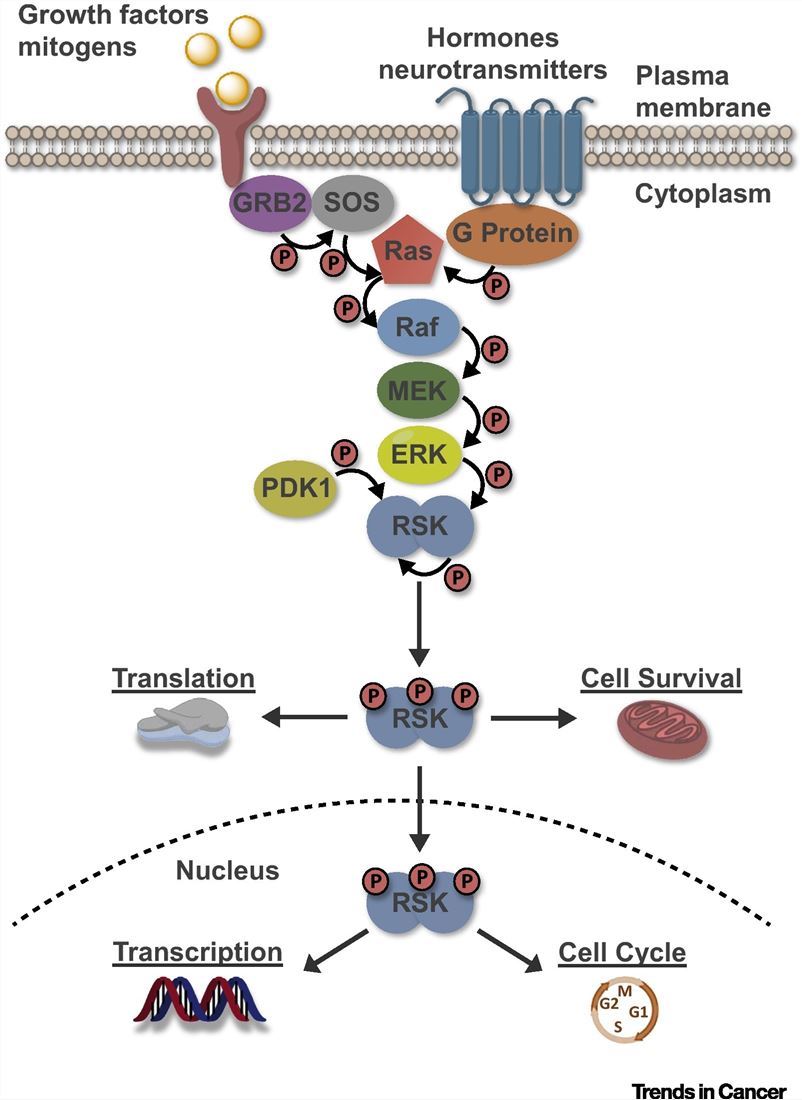 Fig.2 Selective targeting of RSK isoforms in cancer. (Casalvieri KA, et al., 2017)
Fig.2 Selective targeting of RSK isoforms in cancer. (Casalvieri KA, et al., 2017)
Functions of Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases (RSK)
- Gene Expression Regulation
RSKs play a critical role in regulating gene expression by phosphorylating various transcription factors, including CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein), ATF1 (activating transcription factor 1), and c-Fos. This phosphorylation enhances the transcriptional activity of these factors and influences the expression of genes involved in cell growth, survival, and differentiation.
- Cell Cycle Progression
RSKs contribute to cell cycle progression by modulating the activity of cell cycle regulators, such as cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). They phosphorylate and regulate the function of proteins involved in cell cycle checkpoints, ensuring proper cell division and proliferation.
- Cell Growth and Survival
RSKs are involved in the regulation of cell growth and survival pathways. They modulate the activity of key signaling molecules, such as mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) and BAD (Bcl-2-associated death promoter), which control protein synthesis, cell growth, and apoptosis.
- Neuronal Functions
RSKs play a role in neuronal functions, including synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory formation. They are implicated in the regulation of neurotransmitter release and the modulation of neuronal signaling pathways.
Available Resources for Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases (RSK)
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RSK) is an important signaling molecule involved in a variety of cellular processes. Creative BioMart provides comprehensive resources and services related to RSK that enable researchers to study and understand the function and mechanism. The following RSKs are displayed, click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. For further information or to purchase products, please contact us. We are committed to providing the highest quality resources and support for your research to help you succeed.
Reference:
- Casalvieri KA, Matheson CJ, Backos DS, Reigan P. Selective Targeting of RSK Isoforms in Cancer. Trends Cancer. 2017 Apr;3(4):302-312.

