What is C1S Protein
The Complement Component 1S (C1S) protein, also known by its official full name as Complement C1s subcomponent, belongs to the family of serine proteases. This crucial protein is encoded by the C1S gene and has garnered attention in recent research advances for its pivotal role in the immune system. Synonyms for C1S include C1 esterase, C1 esterase subcomponent, and C1sA.
C1S Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
C1S, a serine protease, exhibits a distinctive structural arrangement crucial for its functionality. This protein is a part of the larger complement system, which forms a crucial component of the innate immune system. The complement system comprises a cascade of proteins that defend the body against pathogens. C1S plays a vital role in the initiation of the classical complement pathway, where it cleaves C4 and C2, facilitating the formation of the C3 convertase.
Recent research advances in structural biology have unveiled intricate details of C1S, shedding light on its conformational changes during activation and interaction with other complement components. Understanding these structural nuances provides valuable insights into potential therapeutic interventions targeting the complement system.
C1S Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of C1S extend beyond its role as a mere protease. This protein serves as a linchpin in the immune system, orchestrating a cascade of events that culminate in the elimination of pathogens. C1S is primarily involved in the clearance of immune complexes and apoptotic cells, contributing to the body's defense against infections. At the molecular level, C1S participates in the cleavage of complement proteins, leading to the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) and subsequent destruction of foreign invaders. Moreover, C1S activation triggers an inflammatory response, further amplifying the immune reaction against potential threats.
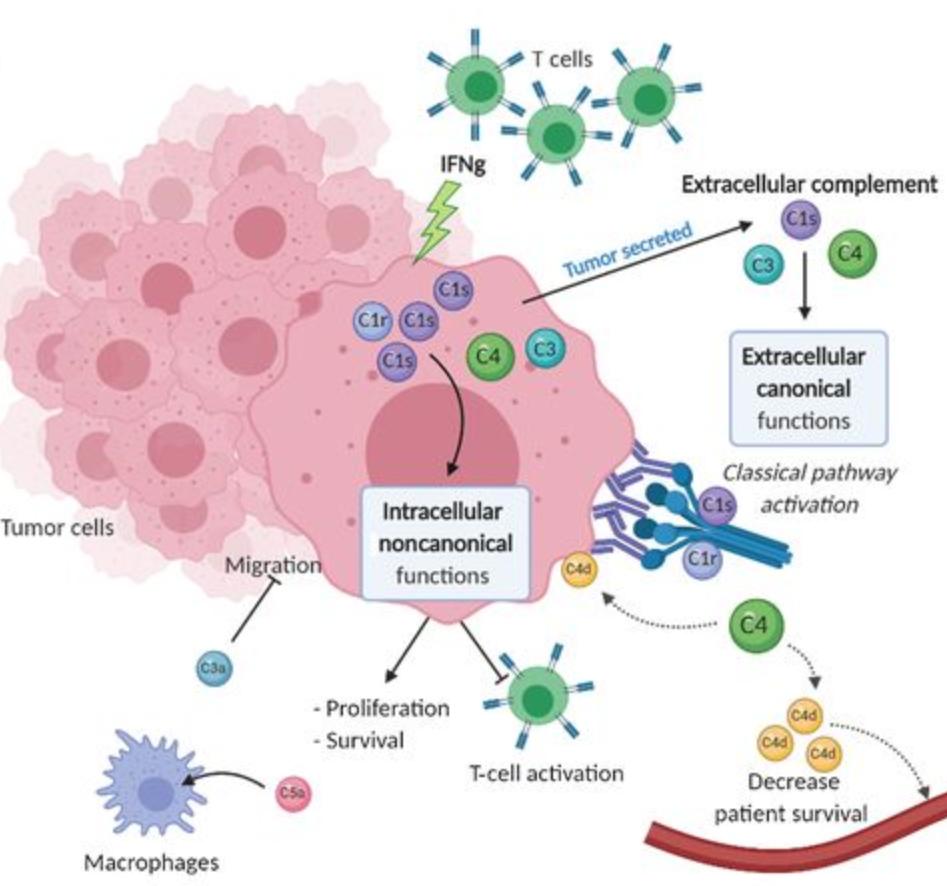
Figure 1. C1s production by tumor cells impacts CD8 T cells. (Daugan M V, et al., 2021)
C1S Related Signaling Pathway
The signal pathway involving C1S is an intricately choreographed molecular dance that starts with the recognition of immune complexes or pathogen surfaces. Once activated, C1S cleaves C4 and C2, generating the C3 convertase. This convertase, in turn, leads to the opsonization of pathogens and the initiation of an inflammatory response.
Decoding the signal pathway of C1S provides a roadmap for understanding how the complement system senses and responds to threats. This knowledge is pivotal for devising interventions that modulate the immune response for therapeutic purposes.
C1S Related Diseases
While C1S is a key player in immune defense, dysregulation or mutations in the C1S gene can lead to pathological conditions. Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is one such disorder associated with C1S, characterized by recurrent episodes of swelling in various body parts. In HAE, a deficiency or dysfunction of C1 inhibitor, a regulator of C1S, results in uncontrolled activation of the complement system, leading to excessive inflammation and tissue swelling.
Understanding the molecular basis of C1S-related diseases is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic strategies that aim to restore the balance within the complement system.
C1S's Applications in Biomedicine
The versatile nature of C1S extends its utility beyond understanding immune responses. In the realm of biomedical applications, C1S has become a valuable tool for diagnostic development, vaccine design, and therapeutic interventions.
In diagnostic development, the measurement of C1S levels can serve as a biomarker for certain immune-related disorders, aiding in early detection and monitoring of disease progression. Additionally, the role of C1S in the complement system positions it as a potential target for therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating immune responses in conditions like autoimmune diseases.
Vaccine development has also benefited from insights into C1S function. Understanding how C1S contributes to the immune response enables the design of vaccines that leverage the complement system for enhanced efficacy.
In therapeutics, researchers are exploring the possibility of targeting C1S for the treatment of complement-related disorders. Modulating C1S activity could offer a novel approach to regulate immune responses and mitigate the pathological effects associated with dysregulation of the complement system.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
C1S-26615TH |
Human |
Wheat Germ |
N/A |
|
|
C1S-10489H |
Human |
E.coli |
GST |
|
|
C1S-1407H |
Human |
E.coli |
His |
|
|
C1S-1788H |
Human |
E.coli |
His/T7 |
|
|
C1S-597H |
Human |
Human Cell |
His |
|
|
C1S-120H |
Human |
Mammalian cells |
His |
|
|
C1S-5143H |
Human |
Mammalian cells |
C-His |
|
|
C1S-2572H |
Human |
HEK293 |
His (Fc)-Avi |
|
|
C1S-5501H |
Recombinant Human C1S Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled |
Human |
HEK293T |
Myc/DDK |
|
C1S-0278H |
Human |
E.coli |
N-His |
Reference
- Daugan M V, et al. Complement C1s and C4d as prognostic biomarkers in renal cancer: emergence of noncanonical functions of C1s. Cancer Immunology Research. 2021, 9(8): 891-908.

