What is CD34 Protein
CD34 protein, an integral member of the sialomucin protein family, is an important cellular molecule that serves critical functions in cell development and research. The discovery of this significantly versatile protein has contributed greatly to several spheres of the biomedical domain, proffering an improved understanding of cellular biology, pathological relationships, and potential for advancements in medical treatment modalities.
The gene encoding CD34 was discovered and isolated in the late 1980s. Researchers were able to identify a novel protein exhibiting characteristics of a cell surface antigen on hemopoietic stem cells. Named accordingly, the CD34 refers to the cluster of differentiation 34, which stands for a specific group of molecules involved in cell signaling and immune response. The CD34 gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 1 in the q32.2 locus. Encoded by the gene, CD34 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein featuring an extracellular region, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail. Numerous studies have suggested that this protein's cytoplasmic domain is likely to have a role in intracellular signaling.
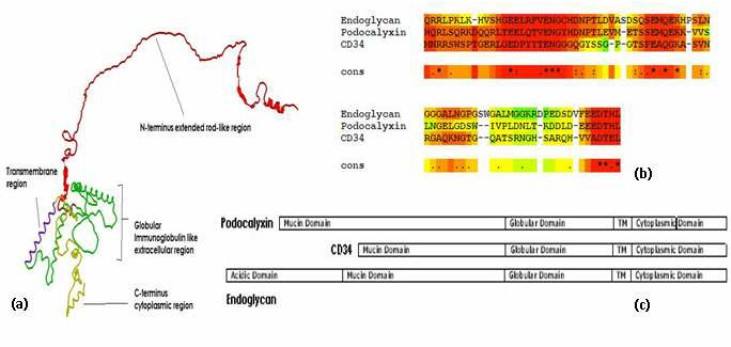
Fig1. CD34 Structure(Singh, Vimal & Tsuji, et al. 2012)
Function of CD34 protein
The primary functionality of the CD34 protein lies in its role as a marker of hematopoietic precursor cells, including the identification and isolation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. CD34 is also known to play a role in the adhesion of stem cells to specific tissues in the body, including the bone marrow and endothelial cells in blood vessels. This is significant as the regulation of adhesion can greatly influence a cell's migration and differentiation capacity, which is crucial in developmental and healing processes.
CD34 protein related signal pathway
In cellular signaling, CD34 has been suggested to be associated with a crucial role in the transduction of intracellular signals, affecting cell growth and differentiation. Though the complete mechanism is not entirely understood, several studies showcase the triggering of complex downstream pathways influenced by CD34, which can regulate cellular behavior and fate.
CD34 protein related diseases
Various disorders and diseases have been associated with abnormal expression or mutations in the CD34 gene. Altered CD34 protein expression can lead to an immense impact on cellular adhesion, migration, and differentiation, leading to pathological conditions. Certain forms of cancers, particularly leukemia and lymphoma, often display anomalous CD34 expression. Moreover, some non-malignant pathologies such as Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and Dermatomyositis also exhibit abnormal CD34 expression levels, thereby suggesting an important role of this protein in the pathogenesis of diverse diseases.
CD34 protein's applications in biomedical
In addition to the integral role that CD34 plays in cellular development and disease manifestation, its discovery has had a substantial impact on biomedical research and application, specifically in the fields of immunology and stem cell research. CD34 protein provides a greater understanding and ability to identify, isolate, and study hematopoietic stem cells. Its significant role in cellular adhesion also makes it a valuable tool in the research and development of new therapeutic modalities, including cell-based therapies and tissue engineering.
Moreover, in the clinical setting, CD34+ cells, which express the CD34 protein, are used extensively in bone marrow transplantation. This procedure relies on the ability to isolate a pure population of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells using CD34 as a marker. The stem cells are then used to repopulate the bone marrow of patients who have undergone chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
In conclusion, CD34 proteins, driven by their distinct structural and functional attributes, exhibit a crucial role in maintaining normal cellular health and in manipulating pathological conditions. Owing to their contributions to the process of hematopoiesis, cell adhesion, and intracellular signaling, they are fundamental in the progression of several porphyrias and malignancies. However, the same properties make the CD34 protein a key player in translational medicine and the development of advanced therapeutics, holding substantial promise for future biomedical breakthroughs.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD34-652H | Active Recombinant Human CD34 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD34-3685H | Recombinant Human CD34 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CD34-3650H | Recombinant Human CD34 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Cd34-3313M | Recombinant Mouse Cd34, His tagged | Mouse | Human Cell | His |
| Cd34-7475R | Recombinant Rat Cd34, Fc tagged | Rat | Human Cell | Fc |
| RFL26530HF | Recombinant Full Length Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Antigen Cd34(Cd34) Protein, His-Tagged | Human | E.coli expression system | His |
| CD34-2632H | Recombinant Human CD34 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CD34-3099H | Recombinant Human CD34 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
Reference
- Singh, Vimal & Tsuji, Kohichiro & Sharma, P. & Chandra, Ramesh. (2012). 13. Multidimensional role of CD34 protein in hematopoietic Stem cell biology. Vimal Kishor Singh1,$, Kohichiro Tsuji2, PB Sharma1, Ramesh Chandra. Int J Sci Tech Manag, 3, 42-72, 2012. INTERNATIONAL. JOURNAL OF SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT.

