What is CD3E Protein
CD3E, also known as CD3ε, represents a crucial player in the intricate symphony of our immune system. This protein, with its official full name Cluster of Differentiation 3E, is a key member of the CD3 complex, an integral component of T-cell receptors. In this article, we delve into the structural characteristics, biological functions, associated diseases, signal pathways, and the burgeoning applications of CD3E in the biomedical realm.
CD3E Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
CD3E, classified under the CD3 family, is officially recognized as Cluster of Differentiation 3E. It is also known by the synonymous term CD3ε, where the 'ε' denotes the Greek letter epsilon. This nomenclature reflects the specific isoform of the CD3 complex to which CD3E belongs.
Belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, CD3E is a transmembrane protein primarily found on the surface of T cells. Structurally, it comprises an extracellular domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular domain is notable for its immunoglobulin-like structure, facilitating interactions with other proteins involved in the immune response.
Recent research has illuminated the dynamic nature of the CD3E complex during T-cell activation. Advanced imaging techniques and molecular studies have unraveled the intricacies of how CD3E undergoes conformational changes, contributing to the initiation of immune responses.
CD3E Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
CD3E acts as a critical component of the T-cell receptor (TCR) complex, functioning as a signal transducer. Upon encountering antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells, TCRs, including CD3E, initiate a cascade of events leading to T-cell activation. CD3E ensures the transmission of signals that are vital for the proliferation, differentiation, and effector functions of T cells.
The molecular mechanisms underlying CD3E function involve phosphorylation events triggered by antigen recognition. CD3E, along with its CD3 complex counterparts, plays a central role in transmitting these signals from the TCR to the intracellular signaling machinery. This intricate dance of molecular interactions culminates in the activation of T cells, priming them to mount a targeted immune response against specific pathogens.
CD3E Related Signaling Pathway
CD3E is a linchpin in the signal transduction pathway triggered by TCR activation. Upon antigen recognition, CD3E undergoes phosphorylation, initiating a cascade of events involving other signaling molecules. This culminates in the activation of transcription factors and the expression of genes involved in T-cell activation and effector functions.
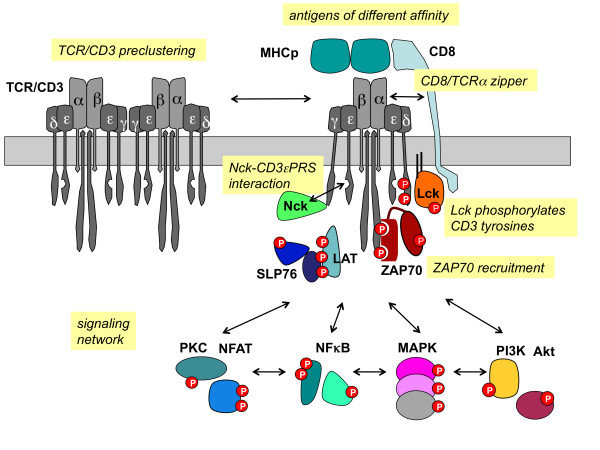
Figure 1. TCR/CD3 signaling. (Louis-Dit-Sully C, et al., 2012)
CD3E Related Diseases
While CD3E is pivotal for normal immune function, dysregulation or aberrant signaling can lead to various diseases.
- Autoimmune Diseases: In autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, an overactive immune response driven by T cells, including those expressing CD3E, can result in the immune system attacking the body's own tissues.
- Cancer: In certain cancers, including T-cell lymphomas, alterations in CD3E expression or function may contribute to the escape of cancer cells from immune surveillance, allowing them to proliferate unchecked.
CD3E's Applications in Biomedicine
- Diagnostic Development: CD3E has found utility in diagnostic development, particularly in flow cytometry-based assays. Its presence on the surface of T cells allows for the identification and characterization of specific T-cell subsets, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of immune-related disorders.
- Vaccine Development: Understanding the molecular nuances of CD3E-mediated T-cell activation is crucial in designing effective vaccines. Researchers are exploring ways to harness the power of CD3E in vaccine development, aiming to enhance immune responses against specific pathogens.
- Therapeutics: The role of CD3E in T-cell activation makes it an attractive target for therapeutic interventions. Immunotherapies, including CAR-T cell therapies, leverage the principles of CD3E-mediated signaling to enhance the ability of T cells to recognize and eliminate cancer cells.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3E-274C | Active Recombinant Cynomolgus CD3E, His-tagged, Biotinylated | Cynomolgus | HEK293 | His |
| CD3E-163C | Recombinant Cynomolgus CD3E protein, His-tagged | Cynomolgus | HEK293 | His |
| CD3E-306C | Recombinant Cynomolgus CD3D & CD3E, His-Fc & Flag-Fc tagged | Cynomolgus | Human Cell | Fc |
| CD3E & CD3D-377H | Active Recombinant Human CD3E & CD3D Protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | HEK293 | His-Avi |
| CD3E & CD3D-376H | Active Recombinant Human CD3E & CD3D protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD3E-2194H | Recombinant Human CD3E, His tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD3E-2193H | Active Recombinant Human CD3E Protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | HEK293 | His/Avi |
| CD3E-275H | Recombinant Human CD3E, His-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD3E-8541H | Recombinant Human CD3E protein, His/Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His/human/IgG1/Fc |
| CD3E-10952H | Recombinant Human CD3E, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
Reference
- Louis-Dit-Sully C, et al. Meeting report: Signal transduction meets systems biology. 2012.

