What is CEACAM6 Protein
CEACAM6, officially known as Carcinoembryonic Antigen-Related Cell Adhesion Molecule 6, is a protein that plays a pivotal role in cellular processes. This multifaceted protein, also recognized by its synonyms such as CD66c and NCA, belongs to the Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) family. Structurally, CEACAM6 is characterized by its glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor, a distinguishing feature of proteins tethered to the cell membrane. Recent research advances have shed light on the intricate details of CEACAM6, unraveling its significance in various biological phenomena.
CEACAM6 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
CEACAM6 orchestrates a symphony of biological functions, influencing cellular processes at the molecular level. Primarily expressed in epithelial tissues, this protein acts as a mediator of cell adhesion. Its role in modulating cellular interactions is crucial for processes like tissue development and immune response. Furthermore, CEACAM6 is implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation, contributing to the maintenance of tissue homeostasis.
At the molecular level, CEACAM6 engages in intricate signaling pathways. It participates in transmembrane signaling, impacting cellular responses to external stimuli. The molecular mechanisms underlying its functions involve interactions with other cell surface molecules, fostering a network of communication essential for cellular homeostasis.
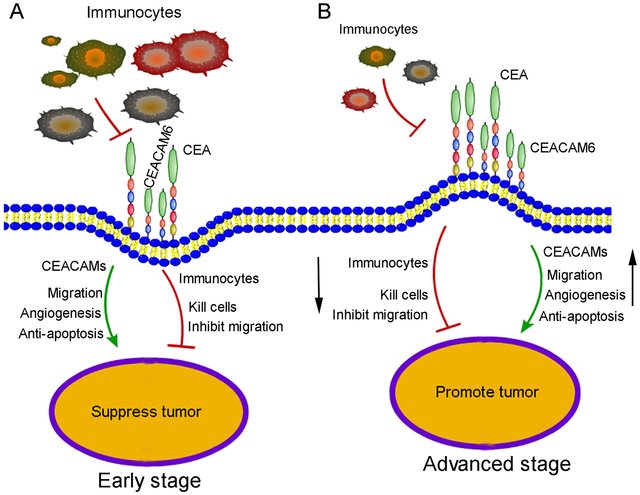
Figure 1. Proposed mechanism for CEACAM6 function in early-and advanced-stage gastric cancer. (Zang M, et al., 2017)
CEACAM6 Related Signaling Pathway
CEACAM6 exerts its influence through complex signal pathways that govern cellular behavior. One such pathway involves the activation of intracellular signaling cascades in response to extracellular stimuli. The interaction of CEACAM6 with other molecules on the cell surface initiates a cascade of events that regulate cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation.
Understanding the intricacies of CEACAM6-related signal pathways is crucial for unraveling its role in health and disease. Researchers are delving into the molecular details of these pathways to identify potential therapeutic targets for conditions associated with CEACAM6 dysregulation.
CEACAM6 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of CEACAM6 is associated with various diseases, marking its significance in clinical contexts. Overexpression of CEACAM6 has been linked to certain cancers, including colorectal and pancreatic cancer. The aberrant expression of this protein is thought to contribute to tumor progression and metastasis, highlighting its potential role as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target in cancer treatment.
Beyond cancer, CEACAM6 has been implicated in inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. The dysregulated immune response observed in these conditions is intricately linked to the functions of CEACAM6, making it a subject of interest in understanding and treating inflammatory disorders.
CEACAM6's Applications in Biomedicine
The versatile nature of CEACAM6 has paved the way for its applications in various biomedical domains. In the realm of diagnostics, CEACAM6 serves as a promising biomarker for certain cancers. Its overexpression in cancer cells makes it a target for diagnostic tests, aiding in early detection and monitoring of disease progression.
Beyond diagnostics, CEACAM6 holds promise in vaccine development. The protein's involvement in immune response regulation positions it as a potential target for therapeutic vaccines, harnessing the body's immune system to combat diseases associated with CEACAM6 dysregulation.
In the therapeutic landscape, CEACAM6-targeted therapies are under exploration for conditions such as cancer and inflammatory disorders. By modulating CEACAM6 activity, researchers aim to develop interventions that can effectively manage diseases where CEACAM6 plays a pivotal role.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEACAM6-664H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CEACAM6-3191H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CEACAM6-664HB | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CEACAM6-3275HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CEACAM6 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| CEACAM6-1096H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein, GST-Tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| CEACAM6-42H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein (ECD), His-tagged(C-ter) | Human | HEK293 | His(C-ter) |
| CEACAM6-2684H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | Human | E.coli | His-SUMO |
| CEACAM6-179H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CEACAM6-335H | Active Recombinant Human CEACAM6 Protein, His & Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | HEK293 | His/Avi |
| CEACAM6-3324H | Recombinant Human CEACAM6 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
Reference
- Zang M, et al. Dual role of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 expression in predicting the overall survival of gastric cancer patients. Scientific Reports. 2017, 7(1): 10773.

