What is CLDN2 Protein
CLDN2, or Claudin-2, discovered and chronicled in scientific literature since the 1990s, has emerged as significantly influential on human health and disease progression.
CLDN2 belongs to the Claudin family, primarily involved in cell-cell communication and establishing the tight junction strands responsible for regulating selective paracellular ion permeability. This protein is typically expressed in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop and in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidneys, and the hypothalamus.
The CLDN2 gene is situated at locus 9q34.11, which means it is mapped onto the long (q) arm of chromosome 9 at a position 34.11 from the centromere. The specific place is vital, and alterations could induce or exacerbate various health conditions. The CLDN2 gene efficiently shapes a protein containing 228 amino acids making up four transmembrane helices, with both N and C termini existing within the cytoplasm.
The CLDN2 protein architecture is worthy of note due to its ability to construct two extracellular loops. The first loop, usually larger and predominant, facilitates the formation of paracellular tight junctions, chiefly in epithelial or endothelial cells.
Function of CLDN2 protein
Regarding the function of CLDN2, it plays a vital role in influencing the paracellular permeability of epithelial and endothelial cells. Through this protein, cells can selectively allow certain ions or molecules across cells without involving active transport mechanisms. In addition, the presence of CLDN2 has been directly linked to water reabsorption as it provides channels to blanket the passage of water through the tight junction.
CLDN2 protein related signal pathway
Simultaneously, the actions of CLDN2 exist within certain cellular signal pathways relevant to multiple health conditions. Its role in the Hippo signal pathway is evident, affecting the transcription co-activator YAP's function, allowing control over cell proliferation and apoptosis. Thus, any alterations in these cellular processes due to CLDN2 disruption can lead to disease manifestations.
CLDN2 protein related diseases
Notably, multiple diseases have been linked to changes in CLDN2 protein expression. One prominent disease is diabetes insipidus, a condition characterized by frequent urination and persistent thirst. The lack of CLDN2 protein in the kidneys can negatively impact water reabsorption, leading to a high volume of diluted urine, characteristic of this condition.
In addition, evidence points to an association with CLDN2 and certain cancers. Observational studies have indicated increased expression of CLDN2 in instances of colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers; this invariably points to further exploration of the protein's role within oncogenesis.
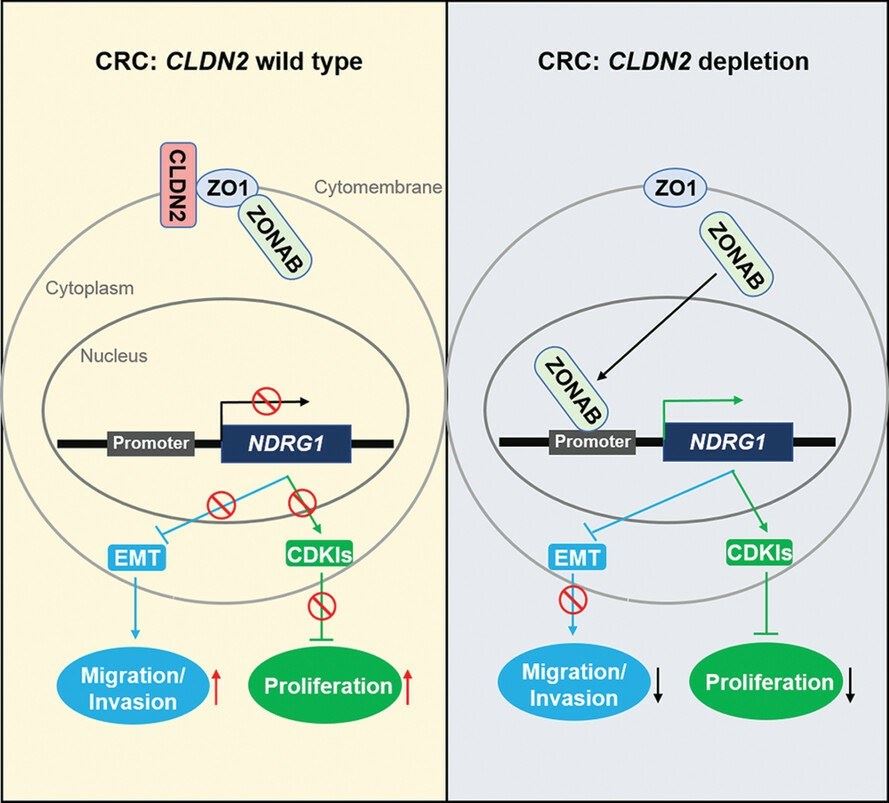
Fig1. CLDN2 promotes colorectal cancer growth (Wei, M., et al. 2021)
Moreover, helicobacter pylori, a common causative agent for gastric ulcers and cancers, has been found to exploit the CLDN2 protein to enter gastric epithelial cells. This potential manipulation of CLDN2 contributes to bacterial survival and disease progression in the host.
Consequently, CLDN2 protein holds strong potential for biomedical applications. Its significant role in the paracellular passage of ions and water molecules makes it a potential target for rehydrating strategies or anti-diuretic treatments. For instance, controlling CLDN2 expression might help manage diabetes insipidus symptoms.
Furthermore, given its association with cancer, CLDN2 could become a novel target for anticancer therapies. Available anticancer drugs could be optimized to manipulate CLDN2 proteins and prevent abnormal cell proliferation and survival, which are hallmarks of cancer, thus opening up a new frontier in cancer therapeutics.
In conclusion, further investigations into CLDN2 will be crucial to fully unravel its varied applications in biomedical sciences. Strikingly, unearthing its role in critical physiological processes and disease pathogenesis may revolutionize disease treatment paradigms, including cancer, making it a hotspot research area for the scientific world.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLDN2-11292H | Recombinant Human CLDN2, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CLDN2-2052HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CLDN2 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| CLDN2-2948H | Active Recombinant Human CLDN2 Full Length Transmembrane protein(Nanodisc) | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| Cldn2-900M | Recombinant Mouse Cldn2 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | MYC/DDK |
| CLDN2-1282Z | Recombinant Zebrafish CLDN2 | Zebrafish | Mammalian Cell | His |
| CLDN2-5001C | Recombinant Chicken CLDN2 | Chicken | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Wei, M., Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Ma, P., Li, Y., Wu, Y., Chen, X., Deng, X., Yang, T., Mao, X., Qiu, L., Meng, W., Zhang, B., Wang, Z., & Han, J. (2021). Claudin-2 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by suppressing NDRG1 transcription. Clinical and Translational Medicine, 11(12), e667. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.667

