What is FGFR3 Protein?
The Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3 (FGFR3) protein was discovered as part of a family of four receptors (FGFR1 - FGFR4). These receptors are considered integral players in several main regulatory pathways and biological functions such as cell division, differentiation, and migration. FGFR3, unique in its functions compared to their kin, is located on chromosome 4p16.3, as discovered by molecular genetic studies in the late 20th century.
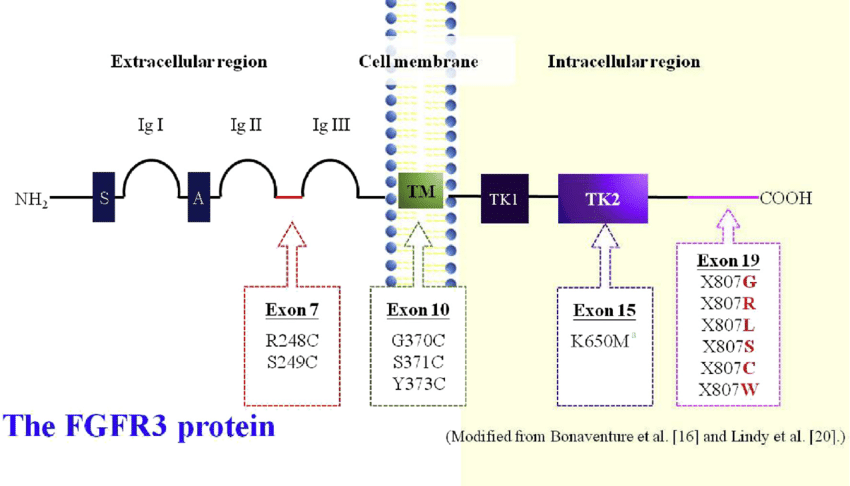
The FGFR3 protein is encoded by the FGFR3 gene in humans. The gene is approximately 16.3 kb long and contains 19 exons. The complex protein structure contains an N-terminal signal sequence, three extracellular Ig-like domains, a single helical-span transmembrane region, and a split, intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. The external part of the protein allows it to bind to fibroblast growth factors, which then results in dimerization and auto-phosphorylation of the intracellular kinase domain.
Function of FGFR3 protein
The FGFR3 protein functions as a receptor for basic Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGF). The interaction with the FGF results in the auto-phosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase, ultimately triggering the downstream signal cascade involved in regulating cell growth and development. FGFR3 seems to be involved chiefly in regulating bone growth by controlling cell division in growth plate chondrocytes. Therefore, although FGFR3 is less expressed in tissues compared to other FGF receptors, alterations in its function or structure can have significant pathological consequences.
FGFR3 protein related signal pathway
The FGFR3 signaling pathway typically operates by binding fibroblast growth factors, leading to receptor dimerization, phosphorylation, and subsequent signal transduction through several downstream pathways. The two primary transducers of FGFR3 signals are the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway. These pathways are integral to the regulation of cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, and migration.
FGFR3 protein related diseases
Distinct mutations of the FGFR3 gene can lead to an array of skeletal disorders such as achondroplasia, hypochondroplasia, and thanatophoric dysplasia, known collectively as FGFR3 chondrodysplasia syndromes. These conditions result in abnormal bone growth, leading to dwarfism. Other mutations have been identified in relation to some cases of bladder, cervical, and colorectal cancer. In cancer, FGFR3 mutations often result in a constitutively active receptor, resulting in the uncontrolled growth of cells.
FGFR3 protein's applications in biomedical
Understanding the role of FGFR3 in these diseases has led to the development of targeted therapeutics in the biomedical field. For skeletal disorders, targeted antibody-based therapies are being developed to inhibit FGFR3 activity, aim to improve bone growth. On the other hand, several drugs have been developed to target FGFR3 in cancer. For instance, Erdafitinib is a drug that inhibits FGFR1-4 and has been approved by the FDA for treating locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with FGFR3 mutations.
Moreover, advances in diagnostic testing for FGFR3 mutations have significant implications for personalized treatment plans. Identifying genetic variations responsible for specific disease phenotypes aids in early diagnosis and intervention, leading to better patient care and prognosis.
The FGFR3 protein, with its unique functions and pathway signaling, plays a vital role in many diseases. Continued research into this protein and its related pathways will undoubtedly uncover further diseases associated with FGFR3 and continue to drive the development of targeted therapeutics. Research into FGFR3 to understand its precise role in normal biological functions and diseases is an exciting frontier in biomedical research. The more we learn, the closer we get to more effective treatments for diseases like achondroplasia and certain cancers, saving and improving many lives.
Our Featured Products
Reference
- Chen, Shin-Wen & Chen, Chih-Ping & Wang, Liang-Kai & Chern, Schu-Rern & Wu, Pei-Chen & Chen, Yen-Ni & Lin, Chen-Ju & Chen, Wen-Ling & Wang, Wayseen. (2017). Perinatal imaging findings and molecular genetic analysis of thanatophoric dysplasia type 1 in a fetus with a c.2419T>G (p.Ter807Gly) (X807G) mutation in FGFR3. Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 56. 87-92. 10.1016/j.tjog.2016.12.013.

