What is LTF Protein
Lactotransferrin (LTF), also known as lactoferrin, stands as a multifaceted protein with a plethora of biological roles. Its official full name, lactotransferrin, aptly describes its dual functionality: "lacto" referring to its abundance in milk, and "transferrin" indicating its role in iron transport. Synonyms for LTF include lactoferrin, lactotransferrin, and lactoglobulin.
Belonging to the transferrin family, LTF boasts distinctive structural characteristics that set it apart. Its iron-binding capability is central to its function, providing an essential avenue for regulating iron metabolism. Recent research advances have further illuminated the protein's versatility. Studies delve into its interaction with various pathogens, shedding light on its potential in immune modulation.
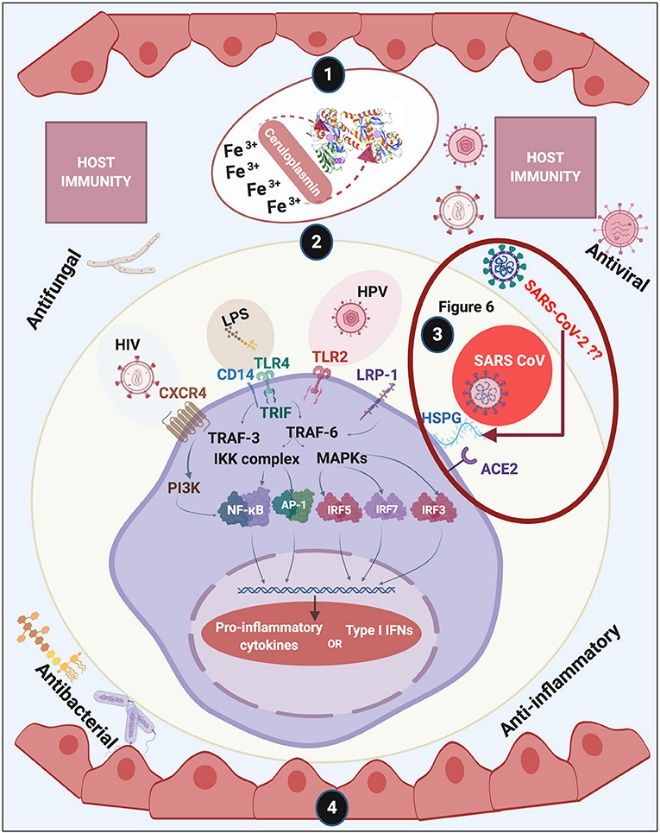
Figure 1. Overview of lactoferrin. (Kell D B, et al., 2020)
LTF Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
LTF's biological functions extend far beyond its initial recognition as an iron transporter. The protein's innate ability to bind and sequester iron plays a pivotal role in depriving pathogens of this essential nutrient, forming a formidable defense mechanism against microbial invaders. Additionally, LTF exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to its significance in immune regulation.
Molecular mechanisms underpinning LTF's diverse functions involve its interaction with cell surface receptors. LTF acts as a modulator, influencing signaling pathways that regulate immune responses. Its multifaceted nature positions LTF as a key player in maintaining homeostasis, showcasing its indispensability in the intricate web of molecular interactions governing cellular functions.
LTF Related Signaling Pathway
The signal pathway orchestrated by LTF is a complex symphony of molecular interactions. LTF engages with specific receptors on cell surfaces, initiating cascades that regulate immune responses and inflammation. This intricate signaling pathway highlights the nuanced role LTF plays in modulating cellular behavior, offering potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
LTF Related Diseases
While LTF is primarily celebrated for its protective roles, imbalances in its expression or function can lead to disease states. Aberrations in LTF levels have been associated with conditions such as inflammatory disorders and certain cancers. Understanding the delicate equilibrium of LTF expression is crucial in unraveling its implications in disease pathology.
LTF's Applications in Biomedicine
Beyond its intrinsic biological significance, LTF has found a prominent place in biomedical applications. Its unique properties have made it a valuable asset in diagnostic development, where its presence or absence can serve as a diagnostic marker for certain conditions. In the realm of vaccine development, LTF's immunomodulatory effects open avenues for enhancing vaccine efficacy, providing a promising avenue for future research.
In therapeutics, LTF's anti-inflammatory properties are harnessed for conditions where immune dysregulation plays a pivotal role. Its potential as a therapeutic agent continues to be explored, with ongoing research aiming to leverage its multifaceted nature for targeted interventions in various disease states.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTF-154H | Recombinant Human LTF protein | Human | Rice Grain | N/A |
| LTF-7666H | Recombinant Human LTF protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| LTF-155H | Recombinant Human LTF | Human | Rice Flour | N/A |
| LTF-1062HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human LTF Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| LTF-257H | Recombinant Human LTF | Human | Mammalian Cell | His |
| LTF-4587H | Recombinant Human LTF Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| LTF-1327H | Recombinant Human LTF Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| LTF-1229H | Recombinant Human LTF Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| LTF-3873H | Recombinant Human LTF, His tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| LTF-5074H | Recombinant Human LTF Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
Reference
- Kell D B, Heyden E L, Pretorius E. The biology of lactoferrin, an iron-binding protein that can help defend against viruses and bacteria. Frontiers in Immunology. 2020, 11: 1221.

