What is MADCAM1 Protein
MADCAM1, also known as mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1, is a crucial protein that plays a pivotal role in cell adhesion and trafficking within the immune system. This molecule is officially classified under the immunoglobulin superfamily and is also recognized by its synonyms such as MADCAM, MCAM, and VCAM1. The protein is primarily found in the endothelial cells of the mucosal venules in the gastrointestinal tract, where it facilitates the selective recruitment of lymphocytes to these specialized tissues.
In terms of structural characteristics, MADCAM1 boasts an immunoglobulin-like domain, essential for its adhesive properties. This feature aligns it with other members of the immunoglobulin superfamily, emphasizing its significance in mediating cellular interactions. Recent research advances have shed light on the complex nature of MADCAM1, unraveling its nuanced involvement in immune responses and inflammatory processes.
MADCAM1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of MADCAM1 are intricately tied to its role in facilitating lymphocyte trafficking, particularly in the gut-associated lymphoid tissues. The protein acts as a homing receptor for lymphocytes expressing α4β7 integrin, guiding them to the mucosal sites within the gastrointestinal tract. This selective recruitment is crucial for the surveillance and defense against pathogens in the mucosal tissues.
At a molecular level, MADCAM1 engages in adhesion mechanisms through interactions with α4β7 integrin expressed on lymphocytes. This binding initiates a cascade of events, promoting the migration of lymphocytes to specific mucosal sites. The adhesive properties of MADCAM1 are finely tuned, ensuring a targeted and controlled immune response within the mucosal environment.
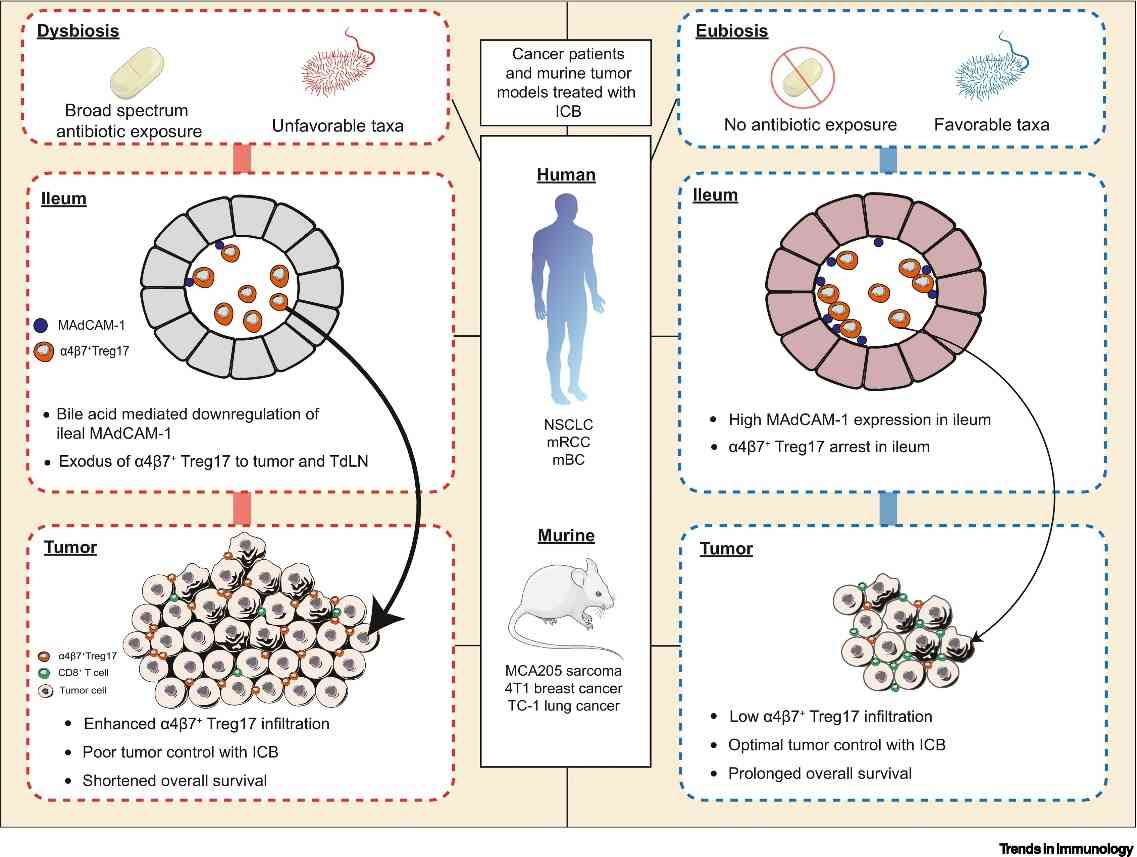
Figure 1. MADCAM1 biological functions. (Chelvanambi M, et al., 2023)
MADCAM1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways associated with MADCAM1 are integral to its function in immune cell trafficking. The engagement of α4β7 integrin with MADCAM1 triggers intracellular signaling cascades that coordinate the adhesion and migration of lymphocytes. These pathways involve intricate interactions with cytoskeletal elements, ultimately guiding the precise movement of immune cells to mucosal tissues.
Understanding the nuances of MADCAM1-related signal pathways provides valuable insights into the regulation of immune responses. This knowledge is instrumental in developing targeted therapies that aim to modulate these pathways for therapeutic benefit.
MADCAM1 Related Diseases
Anomalies in MADCAM1 function have been implicated in various diseases, highlighting the significance of this protein in maintaining immune homeostasis. Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, often exhibit altered MADCAM1 expression levels. This dysregulation contributes to the inappropriate trafficking of lymphocytes, exacerbating inflammation and tissue damage in the gastrointestinal tract.
Understanding the role of MADCAM1 in disease pathology opens avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions. Researchers are actively exploring strategies to modulate MADCAM1 expression or function as a potential therapeutic approach for inflammatory conditions involving aberrant immune responses.
MADCAM1's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of MADCAM1 have paved the way for its applications in various biomedical domains. In diagnostic development, the detection of MADCAM1 expression levels can serve as a biomarker for certain inflammatory conditions, aiding in early disease diagnosis and prognosis. Additionally, the protein's role in immune cell trafficking makes it a promising target for vaccine development, aiming to enhance mucosal immunity against specific pathogens.
Therapeutically, MADCAM1 is garnering attention as a potential target for novel treatment strategies in inflammatory diseases. Researchers are exploring the development of antibodies or small molecules that can modulate MADCAM1 function, offering a tailored approach to intervene in immune-mediated pathologies.
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MADCAM1-3982H | Active Recombinant Human MADCAM1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| MADCAM1-30133H | Recombinant Human MADCAM1 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| MADCAM1-5684H | Active Recombinant Human Mucosal Vascular Addressin Cell Adhesion Molecule 1, Fc-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Fc |
| MADCAM1-5690H | Recombinant Human MADCAM1, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| MADCAM1-3943H | Recombinant Human MADCAM1 protein, His/sumo-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/SUMO |
| MADCAM1-5196H | Recombinant Human MADCAM1 Protein (Met1-Leu318), C-Fc tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | C-Fc |
| MAdCAM1-2179H | Active Recombinant Human MAdCAM1 protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| MADCAM1-2538H | Recombinant Human MADCAM1 protein, His-tagged | Human | Yeast | His |
| MADCAM1-3983H | Recombinant Human MADCAM1 Protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| MADCAM1-5303HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human MADCAM1, Flag-tagged | Human | Mamanlian cells | Flag |
Reference
- Chelvanambi M, Wargo J A. MAdCAM-1: a newly identified microbial'gut check'for T cells. Trends in Immunology. 2023.

