What is PLK1 Protein
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1), also known as serine/threonine-protein kinase PLK1 or PLK, is a crucial regulatory protein that plays a pivotal role in controlling various cellular processes. PLK1 belongs to the polo-like kinase family, which consists of four closely related members, PLK1 to PLK4. PLK1, also referred to as PLK, is the most extensively studied member of this family, primarily due to its central role in cell cycle regulation and cell division.
PLK1 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
PLK1 is characterized by a conserved C-terminal kinase domain and an N-terminal domain containing a Polo-box domain (PBD), which facilitates its interaction with various substrates. The kinase domain is responsible for the phosphorylation of target proteins, while the PBD helps in substrate recognition. PLK1 is classified as a serine/threonine kinase, with a molecular weight of approximately 68 kDa.
Recent Research Advances about PLK1 Protein
Recent research on PLK1 has unveiled new insights into its role in the regulation of various cellular processes. Advances in structural biology and molecular techniques have allowed for a better understanding of the intricate mechanisms by which PLK1 operates. Researchers have identified specific substrates and interaction partners of PLK1, shedding light on its involvement in cell cycle progression, DNA damage repair, and cellular stress responses. Furthermore, scientists have developed specific inhibitors that target PLK1 for therapeutic purposes, particularly in the treatment of cancer.
PLK1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
PLK1 is primarily known for its role in the regulation of the cell cycle, particularly during mitosis. It ensures proper progression through the various stages of cell division, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. PLK1 orchestrates the intricate process of spindle formation, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis.
PLK1 functions by phosphorylating a wide array of substrates involved in these processes. It promotes the activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and the initiation of mitosis. Additionally, PLK1 regulates centrosome maturation, spindle assembly, and microtubule dynamics. Its precise control of these events is vital to prevent errors in chromosome segregation and aneuploidy, which can lead to diseases like cancer.
Apart from its role in mitosis, PLK1 is involved in DNA damage response and repair. It assists in the repair of DNA lesions, thereby maintaining genomic stability. PLK1 also plays a role in cellular stress responses, orchestrating the cellular adaptation to various stressors, such as heat shock and oxidative stress.
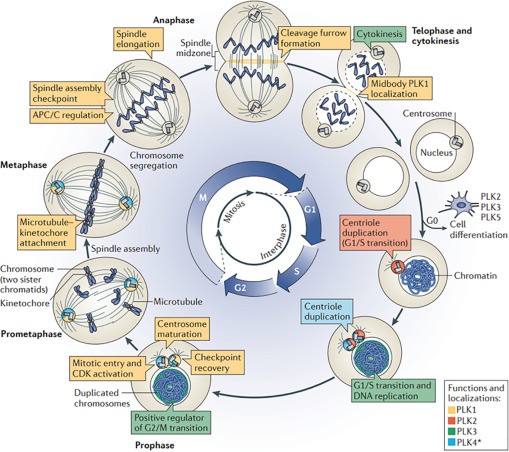
Figure 1. PLKs play multiple roles during the mammalian cell cycle. (Dube D, et al., 2022)
PLK1 Related Signal Pathway
The main signaling pathway involving PLK1 is its role in the cell cycle, where it regulates mitotic events. PLK1 is activated by phosphorylation at multiple sites, primarily at the G2/M transition, allowing it to execute its functions during mitosis. Its substrates include proteins like cyclin B, Cdc25C, and the cohesin complex. By phosphorylating these targets, PLK1 promotes cell cycle progression and accurate chromosome segregation.
PLK1 Related Diseases
PLK1's association with diseases, particularly cancer, has been extensively studied. The overexpression of PLK1 is frequently observed in various cancer types and is associated with poor prognosis. Its dysregulation can lead to uncontrolled cell division and genomic instability, contributing to tumorigenesis. Therefore, PLK1 has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
PLK1's Applications in Biomedical
- Diagnostic Development
PLK1 has been explored as a potential diagnostic marker in cancer. Elevated PLK1 expression is often indicative of malignancy, making it a valuable biomarker for disease prognosis. By measuring PLK1 levels in tumor tissues or blood samples, clinicians can assess the severity of cancer and monitor treatment responses.
- Vaccine Development
Recent research has also focused on utilizing PLK1 as an immunogenic target in cancer vaccines. The idea is to stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells overexpressing PLK1. This approach holds promise in enhancing the body's natural defenses against cancer.
- Therapeutics
Pharmaceutical companies have developed PLK1-specific inhibitors for cancer treatment. These small molecules interfere with the kinase activity of PLK1, preventing it from promoting cell division and DNA repair. In clinical trials, PLK1 inhibitors have shown potential as anti-cancer agents, providing a targeted therapy option for patients with PLK1-overexpressing tumors.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLK1-5411HF | Active Recombinant Full Length Human PLK1 Protein, BTN-tagged | Human | Insect (sf21) | BTN |
| PLK1-785H | Recombinant Human PLK1, His tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His |
| PLK1-1085H | Recombinant Human Polo-Like Kinase 1, His-tagged | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | His |
| PLK1-9946HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human PLK1 protein, Flag-tagged | Human | Mamanlian cells | Flag |
| PLK1-7304HF | Active Recombinant Full Length Human PLK1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Insect (sf21) | GST |
| PLK1-352H | Recombinant Human PLK1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293 | C-Myc/DDK |
| PLK1-1162H | Recombinant Human PLK1 Protein (D371-S603), Tag Free | Human | E.coli | No tag |
| PLK1-3863H | Recombinant Human PLK1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PLK1-1163H | Recombinant Human PLK1 Protein (D371-S603), His tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PLK1-4935H | Recombinant Human PLK1 Protein (Val415-Ser603), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
Reference
- Dube D. Polo-like kinases: An antimitotic drug target for cancer therapy. Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Academic Press, 2022: 457-477.

