What is TFF1 Protein?
Discovered and identified in 1991, TFF1 (Trefoil Factor 1) protein, also known as pS2, serves a profound role in the human body. It owes its name to "trefoil," due to a unique fold structure resembling a three-leaf clover in the protein. Its corresponding gene, the TFF1 gene, is located on the 21st chromosome at locus 21q22.3. The TFF1 gene codes for a 6.5 kilodalton protein of 60 amino acids. The protein structure contains a signal peptide at the N-terminal, followed by a trefoil domain and a C-terminal region lacking known functional domains.
Function of TFF1 protein
TFF1 protein comes under a group of small proteins, typified by a trefoil domain. The TFF1 protein is mainly expressed in gastrointestinal mucosa, particularly in the stomach's surface mucous cells. Functionally, it plays a critical role in maintaining the stomach's mucosal integrity, aiding in repair and regeneration after injury. Its co-expression with mucin, a major component of the mucosal barrier, underscores its role in stabilizing this physical barricade against physical, chemical or microbial threats. Moreover, motogenic effects, inducing cell migration, have been associated with TFF1, advantageous in wound healing.
In addition to the physical protection and restitution, TFF1 has intricate involvement in cellular signaling pathways. Notably, the protein plays a role in the ERK/MAPK pathway, crucial for many cellular functions, including cell division, differentiation, and apoptosis. Moreover, TFF1 has been linked to the PI3K/Akt pathway, influencing cell cycle progression and survival.
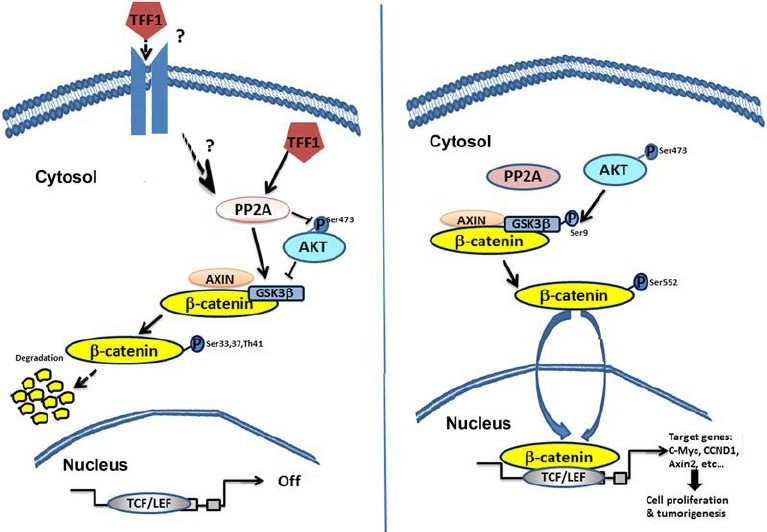
Fig1. the role of Trefoil factor 1 (TFF1) in suppressing AKT- β -catenin pathway
TFF1 protein related diseases
Despite its protective roles, the aberrant expression of TFF1 protein is implicated in many diseases, especially malignancies. Overexpression of TFF1 has been noted in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer, acting as an important prognostic tool. Intriguingly, research also suggests its downregulation in gastric cancer. This dichotomy proposes TFF1 as a double-edged sword, functioning as a tumor suppressor in one context while behaving as an oncogene in another. In addition to cancer, TFF1 holds implications in other gastrointestinal disorders like peptic ulcer disease and gastritis due to its critical role in mucosal repair.
TFF1 protein's applications in biomedical
Understanding TFF1's diverse roles opens new horizons for its applications in biomedicine. In therapeutics, TFF1 might serve as a target for drug development, potentially manipulating its levels to maintain mucosal integrity or to curb malignant progression. As a diagnostic tool, measurement of TFF1 levels may provide valuable prognostic insights. Given its overexpression in breast cancer, TFF1 may serve as an essential marker in predicting disease progression and treatment response. On the other hand, its reduced expression in gastric cancer could direct attention to potential malignancies in patients presenting with gastrointestinal discomfort or unexplained weight loss.
Further revolutionary uses of TFF1 are expected in regenerative medicine. By leveraging its motogenic and wound healing properties, TFF1 can be exploited to enhance tissue engineering strategies. More speculative and experimental applications might involve the development of TFF1-embedded bio-scaffolds aimed at regenerating epithelial surfaces in injuries or pathological states.
In conclusion, TFF1 protein, from its unique structure to its role in health and disease, continues to be a versatile player in modern biology. While our understanding of TFF1 remains incomplete, the continued unraveling of its functions holds much promise. TFF1 embodies the complexity and adaptability of biological systems, exemplifying the potency of molecular research to improve our understanding and treatment of diseases. Although the challenges in implementing TFF1-based therapeutics are significant, the potential benefits to patient care could be immense - promising a brighter future in the interface of molecular biology and medicine.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFF1-1435H | Recombinant Human TFF1 protein, His & GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/GST |
| TFF1-244H | Recombinant Human TFF1 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| TFF1-27974TH | Recombinant Human TFF1, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Tff1-1436M | Recombinant Mouse Tff1 protein, His & GST-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His/GST |
| TFF1-16690M | Recombinant Mouse TFF1 Protein, His-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His |
Reference
- Soutto, Mohammed & Peng, DunFa & Katsha, Ahmed & Chen, Zheng & Piazuelo, Maria & Washington, Mary & Belkhiri, Abbes & Correa, Pelayo & El-Rifai, Wael. (2014). Activation of β-catenin Signaling by TFF1 Loss Promotes Cell Proliferation and Gastric Tumorigenesis. Gut. 64. 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307191.

