Principle and Protocol of Expression and Purification of His Fusion Protein
Polyhistidine fusion protein is purified through Ni2+ resin by virtue of the characteristic that polyhistidine can combine with a variety of transition metals and transition metal chelates.
To understand the basic principle of fusion protein expression and purification. Master the expression and purification methods of histidine labeled fusion protein, as well as the main operation steps and precautions.
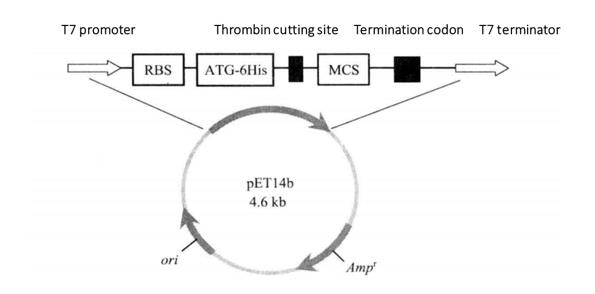 Figure 3-3-1 Schematic Diagram of pET14b Expression Vector
Figure 3-3-1 Schematic Diagram of pET14b Expression Vector
pET series carriers are histidine labeled (6 × His) expression vector of fusion protein (Figure 3-3-1). The major components include T7 phage promoter, lactose operon, ribosome binding site (RBS), 6 × His tag sequence, thrombin cutting site, polyclonal site, T7 thallus terminator, lactose repressor sequence (LacZ), kanamycin screening tag sequence, etc. T7 promoter and ribosome binding site guide efficient transcription and translation of foreign genes. His label is conducive to the separation and purification of proteins by his chelating chromatography (His. Bind resin), and then the removal of label proteins by thrombin cutting. The receptor strain of pET expression vector is Escherichia coli which can produce T7RNA polymerase. The commonly used strains are BL21 (DE3) and BL21 (DE3) plysS. BL21 strain lacks lon and ompT sites, and the level of expressed target protein is greatly improved. The genome of DE3 strain carries T7 RNA polymerase gene in the form of lysogens. IPTG can induce a large number of synthesis of T7 RNA polymerase, and foreign genes can be highly expressed. His fusion protein can combine with Ni2+ resin, wash with appropriate buffer solution (PBS) to remove other impurities, and then elute with imidazole to recover the target protein.
1. Main Instruments and Equipment
Pipette, micro centrifuge, 1.5mL and 50mL centrifuge tubes, ice maker, thermostatic shaker, ultra clean workbench, thermostatic incubator, oscillator, centrifuge, metal bath, chromatographic column, ultrasonic crusher, centrifugal filter tube (10000).
2. Experimental Materials
Vector: pET 14b
E. coli strain: BL21 (DE3)
3. Main Reagents
(1) Binding buffer (pH8.0): 20 mmol/L Tris-base; 30 mmol/L NaCl; 10 mmol/L imidazole.
(2) W1 washing buffer: 20 mmol/L Tris-base; 30 mmol/L NaCl; 20 mmol/L imidazole.
(3) W2 washing buffer: 20 mmol/L Tris-base; 30 mmol/L NaCl; 30 mmol/L imidazole.
(4) W3 washing buffer: 20 mmol/L Tris-base; 30 mmol/L NaCl; 40 mmol/L imidazole.
(5) Elution buffer: 20 mmol/L Tris-base; 30 mmol/L NaCl; 250 mmol/L imidazole.
(6) Triton X-100 (10% volume fraction).
(7) 0.1mol/L IPTG.
(8) Separation gel: 12% SDS-PAGE.
(9) Nitrilotriacetate (NTA) Ni2+-agarose.
1. Preparation of Ni2+ Affinity Columns
(1) Rinse the chromatography column 3 times with 2 mL of deionized water and equilibrate the column 3 times with 2 mL of binding buffer.
(2) Invert and mix the nitrilotriacetate (NTA) Ni2+ -agarose, and take 100 μL into the chromatography column.
(3) Resuspend the agarose 3 times with 2 mL of binding buffer.
2. Purification of Polyhistidine Labeled Protein
(1) Expression of polyhistidine-tagged proteins, expanded culture, and preparation of bacterial protein crude extracts.
(2) The supernatant after centrifugation of the bacterial protein crude extract was added to the chromatography column and combined at 4°C for 30 min*1.
(3) Rinse Ni2+-agarose with 600 μL W1 wash buffer and collect the effluent*2.
(4) Rinse Ni2+-agarose with 600 μL W2 wash buffer and collect the effluent.
(5) Rinse Ni2+-agarose with 600 μL W3 Wash Buffer and collect the effluent.
(6) Elute 3 times with 250 μL Elution Buffer and collect the effluent.
(7) Prepare the samples for 12% SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis*3.
(8) Coomassie brilliant blue staining or silver staining, or immunoblotting (Figure 3-3-2).
(9) Refer to the following steps for filter purification of fusion proteins.
Add 2 mL of purified protein to the centrifuge filter tube, not exceeding the maximum capacity of the tube.
Centrifuge at 5000g for 5 min at 4°C. Repeat several times until there is approximately 500 μL of liquid in the centrifuge tube.
Add 2mLPBS buffer or other buffer to the centrifuge tube and centrifuge at 5000g for 5min at 4°C. Repeat (3) 3 times until there is approximately 500μL of liquid in the centrifuge tube.
Repeat (3) 3 times until there is approximately 200 - 300 μL of liquid in the centrifuge tube.
Uncap the centrifuge tube and transfer the liquid from the tube to a new 1.5 mL tube using a pipette.
Detected by Coomassie brilliant blue staining or determined by protein concentration.
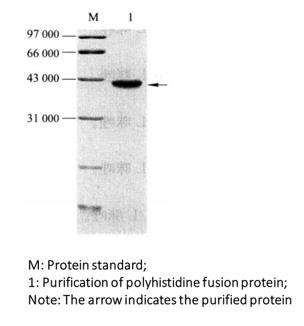 Figure 3-3-2 Purified Gel Electrophoresis of Polyhistidine Fusion Protein
Figure 3-3-2 Purified Gel Electrophoresis of Polyhistidine Fusion Protein
*1 The combination time can be extended or overnight.
*2 Add the washing buffer solution to the chromatographic column and allow it to stand for 5min, then release the washing buffer solution.
*3 SDS polypropylene gel electrophoresis with different concentrations should be used according to the relative molecular weight of the fusion protein.

