NCR1
-
Official Full Name
natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 1 -
Overview
Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCR1 gene. NCR1 has also been designated as CD335 (cluster of differentiation 335). -
Synonyms
NCR1;natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 1;LY94, lymphocyte antigen 94 (mouse) homolog (activating NK receptor;NK p46);CD335;NK p46;NKP46;FLJ99094;hNKp46;Ly94;Lymphocyte antigen 94;Lymphocyte antigen 94 homolog (activating NK receptor;Lymphocyte antigen 94 homolog;Natural killer cell p46-related protein;NCT1;NCTR1_HUMAN;NK cell activating receptor;NK cell-activating receptor;NK-p46;lymphocyte antigen 94 homolog (activating NK-receptor;NK-p46)
Recombinant Proteins
- Cynomolgus
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- C-hFc
- Human Cells
- Flag
- His
- Fc
- lFc
- Avi
- mFc
- Non
- hIgG4
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
Background
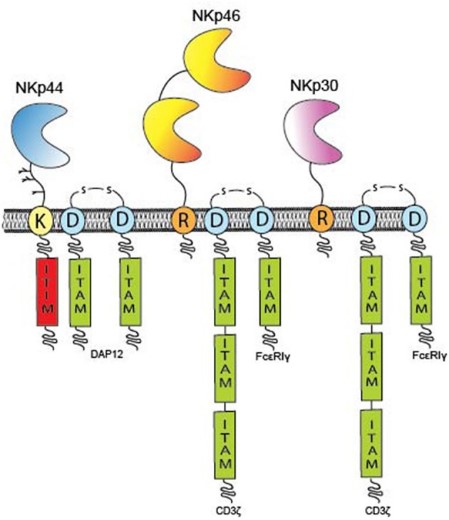
Fig1. Overview of individual NCR domain structures. NKp46 (yellow) has two Ig-like domains. (Alexander David Barrow, 2019)
What is NCR1 protein?
NCR1 (natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19q13. NCR1 is a protein that is mainly expressed on natural killer (NK) cells. NK cells are part of the immune system and are essential for recognizing and killing infected or mutated cells, such as cancer cells. NCR1 is a transmembrane protein whose extracellular portion contains multiple immunoglobulin-like domains. The NCR1 protein is consisted of 304 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 34.5 kDa.
What is the function of NCR1 protein?
NCR1 activates NK cells by recognizing their ligands, such as certain molecules expressed on the cell surface, triggering an immune response against infectious pathogens, tumor cells, and damaged normal cells. The function of NCR1 is involved in promoting the secretion of cytotoxins from NK cells, such as perforin and granzidase, and producing multiple cytokines, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), which enhances the immune response and is involved in regulating immune surveillance and anti-tumor response.
NCR1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathway involved in NCR1 is mainly involved in cell recognition and clearance, especially for virus-infected cells and certain tumor cells. When NCR1 binds to its ligand, it activates downstream signaling pathways such as the PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK, and NF-κB signaling pathways. Activation of these pathways further promotes degranulation of NK cells, releasing cytotoxins such as perforin and granzidase, leading to apoptosis of target cells. In addition, NCR1 can also work synergistically with other NK cell receptors, such as CD16 and NKG2D, to enhance the cytotoxic effects of NK cells.
NCR1 Related Diseases
Mutations in the NCR1 gene are associated with a variety of diseases, including: Inherited NCR1 deficiency, a rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder in which patients are susceptible to infections, autoimmune diseases, and malignancies due to abnormalities in NK cell function caused by mutations in the NCR1 gene. Other autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and multiple sclerosis (MS) have been associated.
Bioapplications of NCR1
In recent years, this protein has become the focus of cancer immunotherapy and drug development. Researchers are exploring the use of NCR1 agonists or its signaling pathway modulators to enhance the activity of NK cells, thereby providing new strategies for cancer treatment. At the same time, antibodies against NCR1 are also being studied for targeted therapies to improve the selective killing effect of tumor cells.
Case Study
Case study 1: Chiyuki Ueshima, 2015
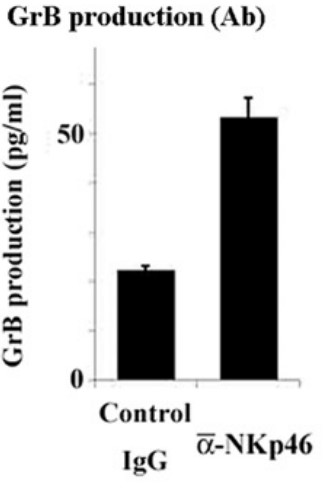
NKp46 (natural cytotoxic receptor 1/CD335) is expressed on natural killer cells and Th2-type innate lymphocytes. However, NKp46 expression in human mast cells has not yet been reported. Here, the researchers explored the expression of, and possible role played by, NKp46 in such cells. NKp46 protein was expressed in human mast cells in urticaria pigmentosa principally of the tryptase-positive/chymase-negative type (MCT), but not in human non-neoplastic skin mast cells of the tryptase-positive/chymase-positive (MCTC) type. NKp46 expression was also evident in the human neoplastic mast cell line HMC1.2. NKp46 knockdown changed the phenotype of this cell line from MCT to MCTC and downregulated GrB production, but did not influence IL-22 production. An agonistic anti-NKp46 antibody upregulated production of GrB and IL-22, but did not change the MCT-like phenotype of HMC1.2 cells. NKp46 was thus involved in the production of serine proteases and IL-22 in human mast cells.
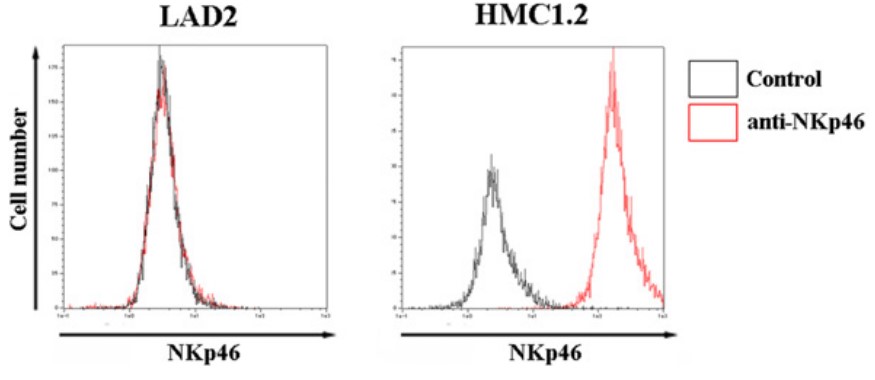
Fig1. Flow cytometric analysis showed NKp46 protein expression in the human cultured neoplastic mast cell line HMC1.2.
Case study 2: Pascal F Durrenberger, 2012
Pathogenic or regulatory effects of natural killer (NK) cells are implicated in many autoimmune diseases, but evidence in multiple sclerosis (MS) and its murine models remains equivocal. In an effort to illuminate this, the researchers have here analysed expression of the prototypic NK cell marker, NCR1 (natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor; NKp46; CD335), an activating receptor expressed by virtually all NK cells and therefore considered a pan-marker for NK cells. In this study, the researchers investigated whether there were differences in NCR1+ cells in the peripheral blood of MS patients and whether NCR1+ cells are present in white matter lesions.
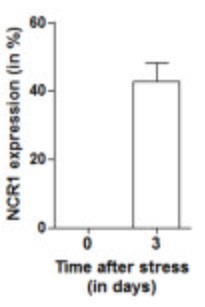
NCR1 transcripts were increased more than 5 times in active disease lesions. However when they performed immunohistochemical staining of this tissue, few NCR1+ NK cells were identified. Rather, the major part of NCR1 expression was localised to astrocytes, and was considerably more pronounced in MS patients than controls. In order to further validate de novo expression of NCR1 in astrocytes, they used an in vitro staining of the human astrocytoma U251 cell line grown to model whether cell stress could be associated with expression of NCR1. They found up-regulation of NCR1 expression in U251 cells at both the mRNA and protein levels.
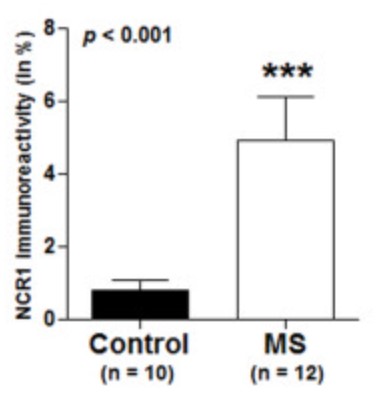
Fig3. Immunoreactivity was quantified and a significant increase (p = 0.0003) in WML (4.945 ± 1.174) compared to controls (0.801 ± 0.27) was found when conducting a Mann Whitney test.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
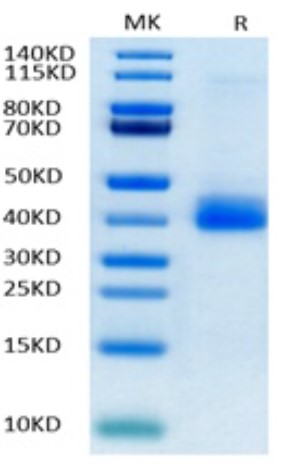
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NCR1-897H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
High Bioactivity
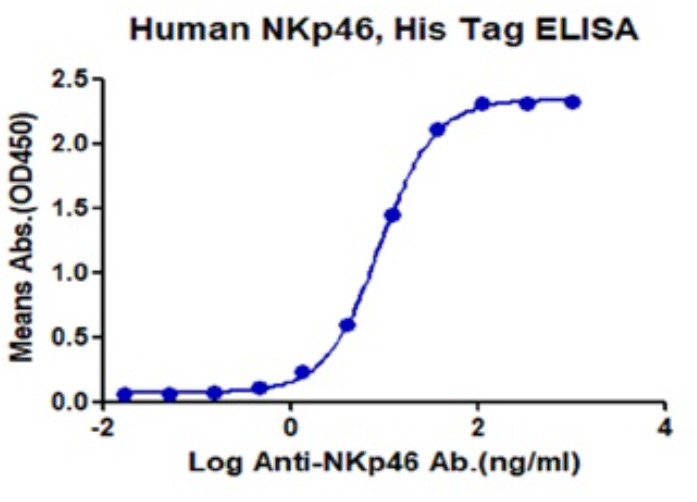
Fig2. Activity Data. (NCR1-897H)
Involved Pathway
NCR1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NCR1 participated on our site, such as Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NCR1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | RAC1,NFATC2,VAV3,NCR3,IFNA4,FYN,PPP3R2,KIR2DL1,IFNGR2,SH3BP2 |
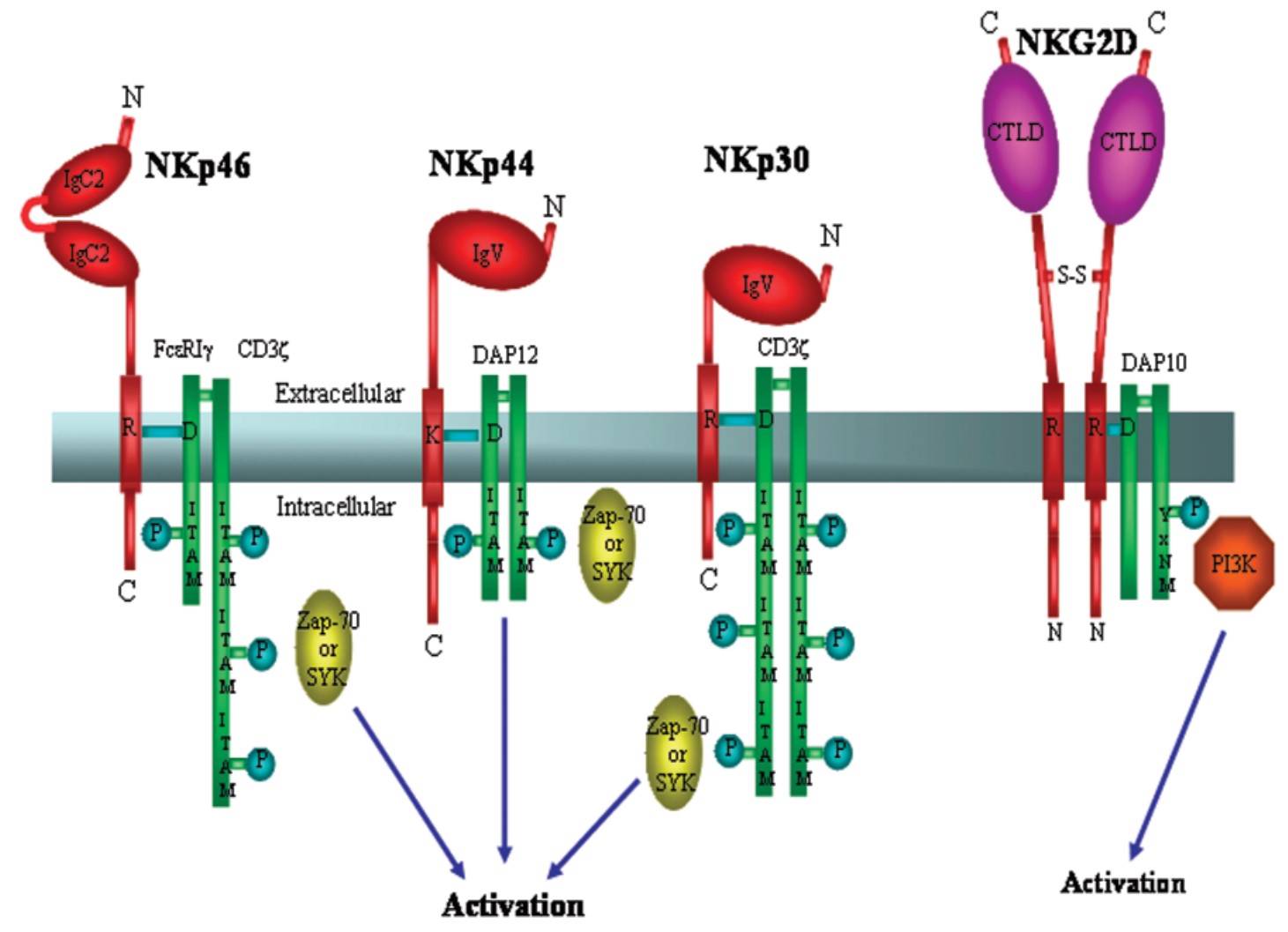
Fig1. NKp46 has an extracellular portion characterized by two Ig-C2 like domains. (R Biassoni, 2003)
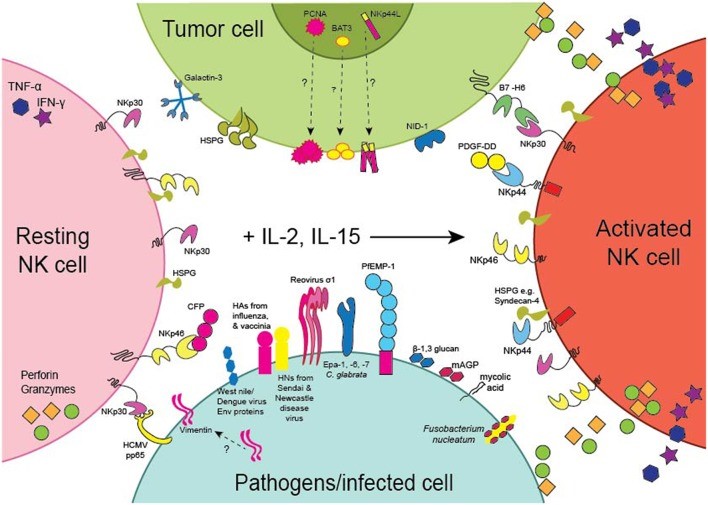
Fig2. Expression of the NCRs and their Ligands. NKp30 and NKp46 are expressed by resting (pink) as well as activated (orange) NK cells. (Alexander David Barrow, 2019)
Protein Function
NCR1 has several biochemical functions, for example, receptor signaling protein activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NCR1 itself. We selected most functions NCR1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NCR1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| receptor signaling protein activity | RAF1A,DOK1,FLRT2,RGS14A,cgr2b,ARAF,DOK5,KLK1B3,DCLK1,PLCG1 |
Interacting Protein
NCR1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NCR1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NCR1.
Resources
Research Area
ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related MoleculesNatural Killer Cells (NK Cells) Markers
Natural Killer T (NKT) Cells
Lymphoid Lineage Markers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Grondahl-Rosado, C; Bonsdorff, TB; et al. NCR1(+) cells in dogs show phenotypic characteristics of natural killer cells. VETERINARY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 39:19-30(2015).
- Olsen, L; Boysen, P; et al. Characterization of NCR1+cells residing in lymphoid tissues in the gut of lambs indicates that the majority are NK cells. VETERINARY RESEARCH 44:-(2013).


