ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules
Related Symbol Search List
- BTLA
- CD22
- CD226
- CD244
- CD28
- CD300A
- CD300C
- CD300E
- CD300LB
- CD300LF
- CD33
- CD3e
- CD3G
- CD5
- CD6
- CD72
- CD84
- CEACAM1
- CEACAM3
- CLEC12A
- CLEC1A
- CLEC1B
- CLEC4A
- CLEC5A
- Dectin-1
- Ctla4
- CD89
- FCER2
- CD32A
- Fcgr2b
- CD16a
- FCGR3B
- FCRL1
- FCRL3
- FCRL4
- FCRL6
- ITGA2B/CD41
- Integrin beta 3
- KIR2DL1
- KIR2DL3
- KIR2DL4
- KIR2DL5A
- KIR3DL1
- KIR3DL3
- KIR3DS1
- KLRF1
- KLRG1
- LAIR1
- LAIR2
- LILRA3
- LILRA4
- LILRA5
- LILRB1
- ILT4
- LILRB3
- LY9
- MS4A2
- NCR1
- NCR2
- NCR3
- PDCD1
- PDCD6
- CD31
- PILRA
- PTPN11
- SIRPA
- SIGLEC10
- SIGLEC5
- SIGLEC6
- SIRPB1
- SLAMF6
- SLAMF7
- SLAMF8
- TIGIT
- TREML1
- TREML2
Immunology Background
About ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules
ITIM (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif) and ITAM (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activating motif) are short amino acid sequences in the cytoplasmic domains of various immune receptors and immune-related molecules. These motifs provide docking sites for specific signaling proteins, allowing signal transmission upon receptor activation. The ITIM motif (S/I/V/LxYxxI/V/L) is primarily associated with inhibitory receptors, whereas the ITAM motif (YxxL/I -x6-8 - YxxL/I (where X denotes any amino acid)) is associated with activating receptors. The balance between ITIM and ITAM signaling plays a critical role in regulating immune cell activation and tolerance.
Phosphorylated ITAMs serve as docking sites for tandem SH2 domains of Syk family kinases, whereas phosphorylated ITIMs recruit tyrosine phosphatases. Signaling through ITAM-bearing receptors usually results in cell activation, while engagement of ITIM-bearing receptors is usually inhibitory, although exceptions have been described. The majority of these receptors are involved in tumor development and regulation of the immune system, although some also function in tissues such as bone and brain.
Understanding the functions and mechanisms of ITIM/ITAM immune receptors and related molecules is critical to deciphering the complexity of immune signaling and exploring their potential therapeutic applications.
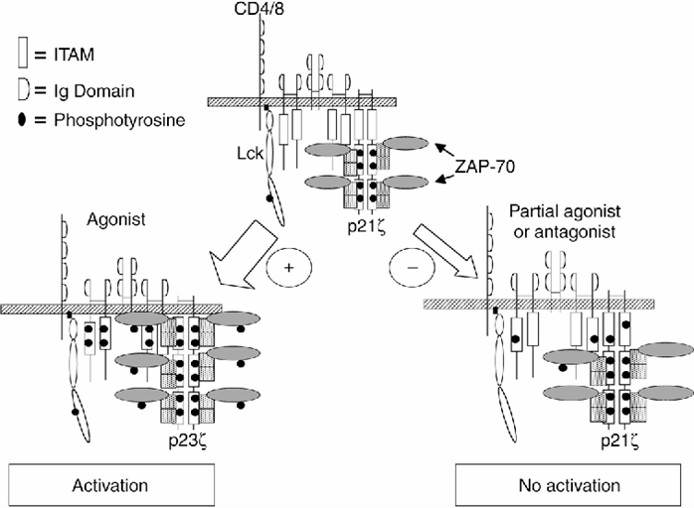 Fig.1 A model depicting TCR-mediated ζ chain phosphorylation. (Billadeau DD, et al., 2002)
Fig.1 A model depicting TCR-mediated ζ chain phosphorylation. (Billadeau DD, et al., 2002)
Mechanism of ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules
ITIM-containing receptors typically signal through inhibitory pathways upon ligand binding. Upon ligand binding, inhibitory receptors with ITIM motifs are recruited to their ligands, resulting in the recruitment of protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) to the ITIM motif. PTP dephosphorylates key signaling molecules, thereby inhibiting downstream signaling pathways and attenuating immune responses.
In contrast, ITAM-containing receptors are associated with activating signaling pathways. Upon ligand binding, ITAM-containing receptors are phosphorylated, leading to the recruitment and activation of various signaling proteins, including kinases and adapter molecules. Recruited signaling proteins initiate downstream signaling cascades leading to immune cell activation, proliferation, and effector functions.
ITIM/ITAM immune receptors and related molecules work together to finely regulate immune responses and maintain a delicate balance between activation and suppression.
Functions of ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules
ITIM/ITAM immunoreceptors and related molecules have diverse functions in immune signaling. Here are some examples of their functions:
- Immune Cell Activation and Inhibition
ITIM/ITAM immunoreceptors contribute to the regulation of immune cell activation and inhibition. Inhibitory receptors with ITIM motifs, such as inhibitory receptors on natural killer (NK) cells and T cells, help maintain immune tolerance by inhibiting excessive immune responses. Activating receptors with ITAM motifs, such as various immune cell receptors, promote immune cell activation and effector functions.
- Phagocytosis and Cytotoxicity
ITIM/ITAM immunoreceptors are involved in phagocytosis and cytotoxicity. For example, Fc receptors on phagocytic cells contain ITAM motifs and mediate the internalization of antibody-coated pathogens. NK cell receptors, including killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs), contain ITIM motifs and regulate NK cell cytotoxicity against target cells.
- Immune Cell Communication
ITIM/ITAM immunoreceptors and related molecules facilitate immune cell communication. Co-receptors on T cells, such as CTLA-4 and PD-1, contain ITIM motifs and modulate T cell activation and responses to antigen presentation. ITAM-containing receptors on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) facilitate interactions with T cells and promote immune synapse formation.
- Autoimmunity and Allergy
Dysregulation of ITIM/ITAM signaling can contribute to autoimmune diseases and allergic reactions. Imbalances in inhibitory and activating receptor signaling can disrupt immune tolerance and lead to aberrant immune responses against self-antigens or harmless allergens.
Research Tools for ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules
Understanding the role of ITIM/ITAM immunoreceptors and related molecules in immune signaling is crucial for deciphering immune responses and developing targeted immunotherapies. At Creative BioMart, we offer a wide range of research tools and services to support studies related to ITIM/ITAM immunoreceptors, including recombinant proteins, antibodies, custom assay development, etc. Click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. Please get in touch with us with any questions or requests.
Our Advantages
Reference:
- Billadeau DD, Leibson PJ. ITAMs versus ITIMs: striking a balance during cell regulation. J Clin Invest. 2002;109(2):161-168.

