PIN1
-
Official Full Name
peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1 -
Overview
The enzyme Peptidylprolyl isomerase (Pin1) is responsible for flipping the proline ring from the cis to trans conformation. This enzyme regulates mitosis presumably by interacting with NIMA and attenuating its mitosis-promoting activity. Pin1 is concentra -
Synonyms
PIN1;peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1;protein (peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase) NIMA interacting 1;peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1;dod;PPIase Pin1;rotamase Pin1;protein (peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans iso
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- T7
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is PIN1 protein?
PIN1 (peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. The protein encoded by this gene is human PIN1 , a peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase) that interacts with NIMA and essential for cell cycle regulation. PIN1 is thus an essential PPIase that regulates mitosis presumably by interacting with NIMA and attenuating its mitosis-promoting activity. Substrates of PIN1 include the mitotic regulators (Cdc25 phosphatase and NIMA ,PLK I, Wee, and Myt1 kinases), several transcription factors like Catenin, c-Jun, and the tumor suppressor protein p53 , and some specific proteins like the RNA Pol II, the cytoskeleton protein tau, and the G1/S protein Cyclin D1. The PIN1 protein is consisted of 163 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 18.2 kDa.
What is the function of PIN1 protein?
The conformational regulation catalyzed by this PPIase has a profound impact on key proteins involved in the regulation of cell growth, genotoxic and other stress responses, the immune response, induction and maintenance of pluripotency, germ cell development, neuronal differentiation, and survival.
PIN1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathway involved in PIN1 protein is mainly involved in regulating protein phosphorylation and conformational change, thus affecting cell signal transduction and regulating a variety of biological processes, including NMP signaling pathway, cell growth factor signaling pathway, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, etc. For example, PIN1 is involved in the regulation of cell growth, survival and metabolism by regulating the phosphorylation of Akt and mTOR and the stability of transcription factors.
PIN1 Related Diseases
The abnormal function of PIN1 protein is closely related to the occurrence and development of many diseases, including cancer, nervous system diseases, cardiovascular diseases and so on. PIN1 is also associated with a number of other diseases, such as diabetes, liver disease, kidney disease, etc.
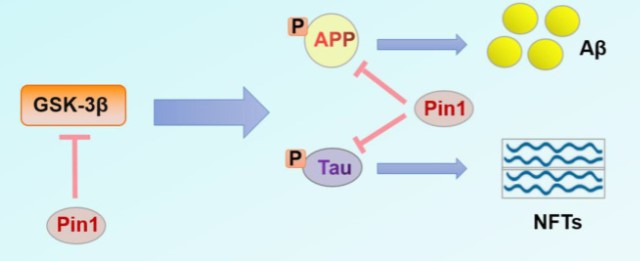
Fig1. Accumulation of NFTs and Aβ is one of the pathogenic factors of AD. NFTs and Aβ are products of Tau and APP processing, respectively.
Bioapplications of PIN1
At present, the biological application of PIN1 protein is mainly in the field of cancer therapy. The high expression of PIN1 in cancer cells is associated with the enhancement of drug resistance, proliferation and invasion ability. Therefore, the development of anti-cancer drugs targeting PIN1 has become a hot research direction.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Juan Long, 2024
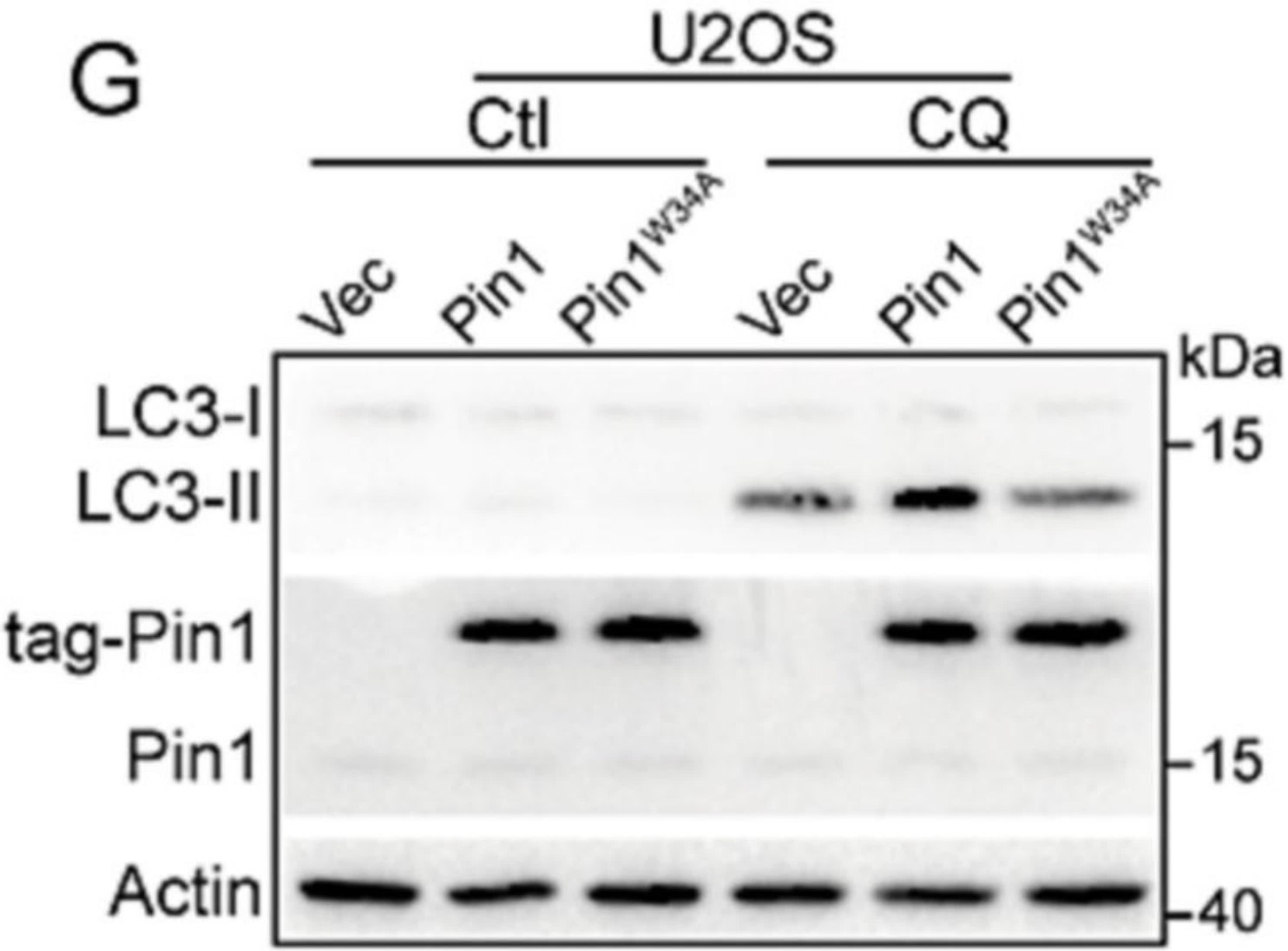
Fig1. Western blot analysis for LC3 in chloroquine (CQ) treated U2OS cells with stable expression of tagged Pin1 or Pin1W34A.
Case Study 2: Qiaoxia Zhou, 2021
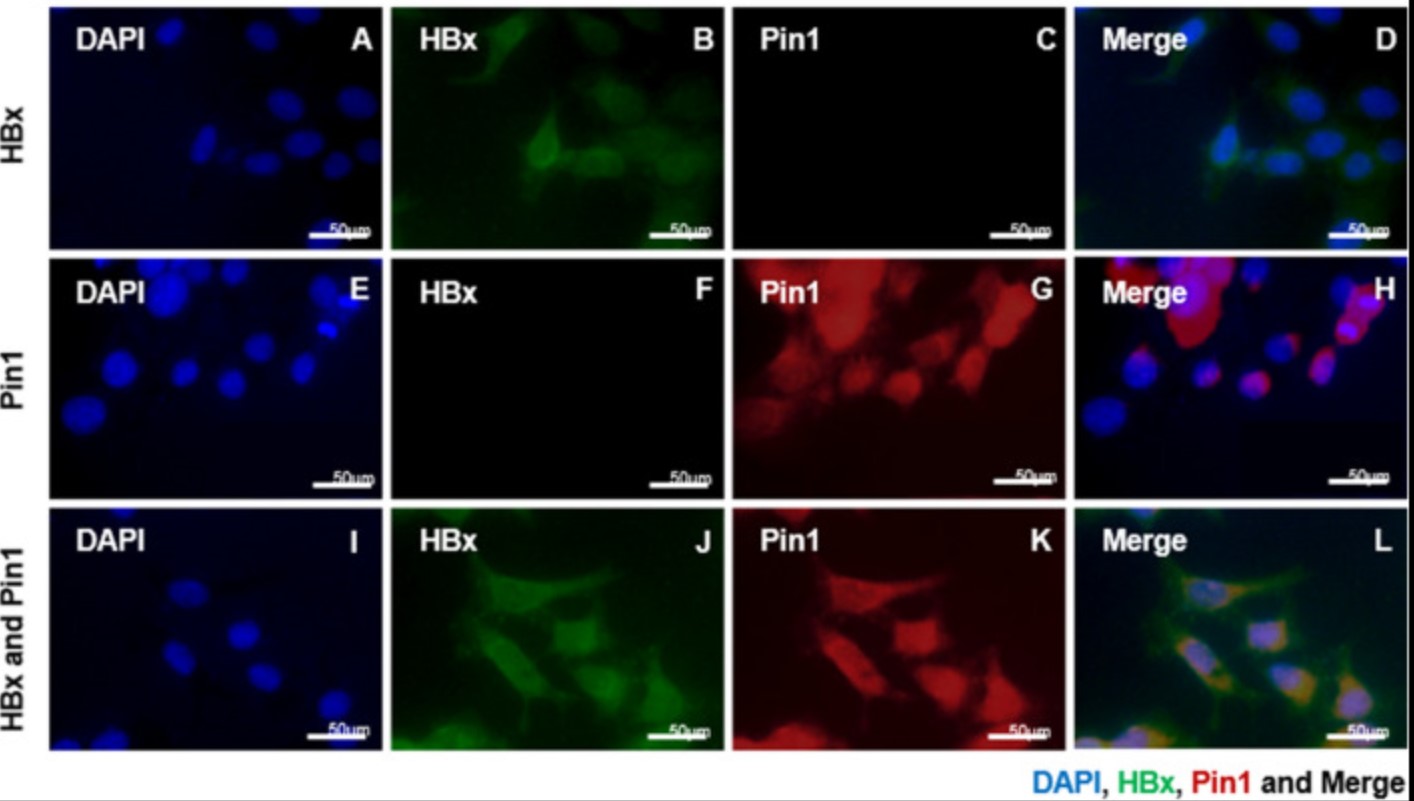
Fig2. Immunofluorescence microscopy shows the common position of Pin1 and HBx in both cytoplasm and nucleus.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
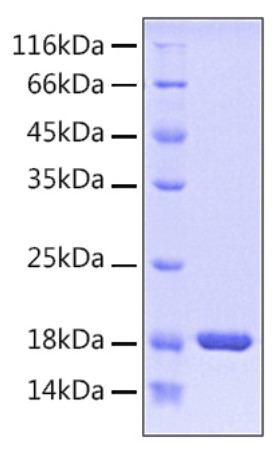
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PIN1-2569H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
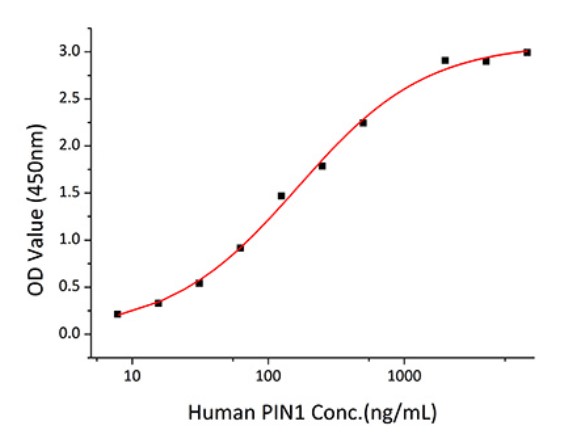
Fig2. Activity Data. (PIN1-2569H)
Involved Pathway
PIN1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PIN1 participated on our site, such as RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PIN1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | IFNA13,MAPK10,NFKBIB,OTUD5,IFNA6,MAPK8B,IL12B,MAP3K1,IFNA2,MAPK12A |
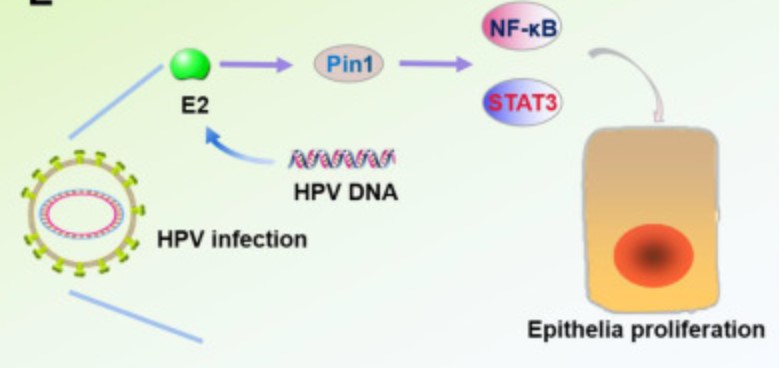
Fig2. In HPV-infected cells, overexpression of Pin1 causes NF-κB nuclear retention and activation of STAT3. (Jingyi Li, 2021)
Protein Function
PIN1 has several biochemical functions, for example, GTPase activating protein binding,mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding,peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PIN1 itself. We selected most functions PIN1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PIN1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| phosphoserine binding | YWHAB,NEDD4,YWHAE |
| peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity | FKBP1B,FKBP10,PPIF,FKBP4,PPWD1,PPIL1,FKBP2,FKBP1A,PPP2R4,CWC27 |
| protein binding | ZZZ3,RAB26,BNIP3L,FREM2,MARVELD2,KCNJ5,HPGDS,PAGE5,SP100,CUL4B |
| phosphothreonine binding | NEDD4 |
| GTPase activating protein binding | GNAI3,FMNL1,CDH1,GNAI1,TSC1,PLCD1,RGS14,GNAO1,TUBB,PTBP3 |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding | TRIB2,TRIB1,BRAF,MAP3K11,ACE,MAPK8IP3,KSR1,TRIB3,TAOK2,ARRB1 |
Interacting Protein
PIN1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PIN1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PIN1.
TP53;ARHGAP8
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Yun, HJ; Kim, JY; et al. Prolyl-isomerase Pin1 Impairs Trastuzumab Sensitivity by Up-regulating Fatty Acid Synthase Expression. ANTICANCER RESEARCH 34:1409-1416(2014).
- Driver, JA; Zhou, XZ; et al. Regulation of Protein Conformation by Pin1 Offers Novel Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches in Alzheimer's Disease. DISCOVERY MEDICINE 92:93-99(2014).



