MLH1
-
Official Full Name
mutL homolog 1 -
Overview
This gene was identified as a locus frequently mutated in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC). It is a human homolog of the E. coli DNA mismatch repair gene mutL, consistent with the characteristic alterations in microsatellite sequences (RER+phenotype) found in HNPCC. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Additional transcript variants have been described, but their full-length natures have not been determined.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009] -
Synonyms
MLH1;mutL homolog 1;FCC2;COCA2;HNPCC;hMLH1;HNPCC2;DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1;mutL homolog 1, colon cancer, nonpolyposis type 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Zebrafish
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- E. coli
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- Flag
Background
What is MLH1 protein?
MLH1 (mutL homolog 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3p22. The protein encoded by this gene can heterodimerize with mismatch repair endonuclease PMS2 to form MutL alpha, part of the DNA mismatch repair system. When MutL alpha is bound by MutS beta and some accessory proteins, the PMS2 subunit of MutL alpha introduces a single-strand break near DNA mismatches, providing an entry point for exonuclease degradation. The encoded protein is also involved in DNA damage signaling and can heterodimerize with DNA mismatch repair protein MLH3 to form MutL gamma, which is involved in meiosis. The MLH1 protein is consisted of 756 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 84.6 kDa.
What is the function of MLH1 protein?
Its primary function is to recognize and correct errors that occur during DNA replication, such as base mismatches and small insertions or deletions. MLH1, along with other proteins, forms a complex that scans the newly synthesized DNA strand, identifies the mismatches, and facilitates their removal and the correct nucleotide insertion.
MLH1 Related Signaling Pathway
MLH1 (MutL Homolog 1) protein is mainly involved in DNA Mismatch Repair (MMR) pathway in cells. A key function of this pathway is to identify and repair errors that occur during DNA replication, such as base mismatches and small insertions or deletions. MLH1 interacts with proteins such as MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 to form a complex that recognizes mismatch bases in DNA and initiates the repair process. During meiosis, MLH1 is also involved in the regulation of homologous recombination. The MLH1-MLH3 (MutLγ) complex mediates the formation of Crossovers in meiosis homologous recombination, which is achieved through the endonuclease signaling pathway.
MLH1 Related Diseases
The MMR process involving MLH1 is essential for maintaining genomic stability and preventing mutations that can lead to various diseases, including cancer. Defects or mutations in the MLH1 gene can impair the mismatch repair mechanism, resulting in a higher mutation rate and an increased risk of developing hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), also known as Lynch syndrome. This condition is characterized by an increased susceptibility to colorectal and other types of cancers.
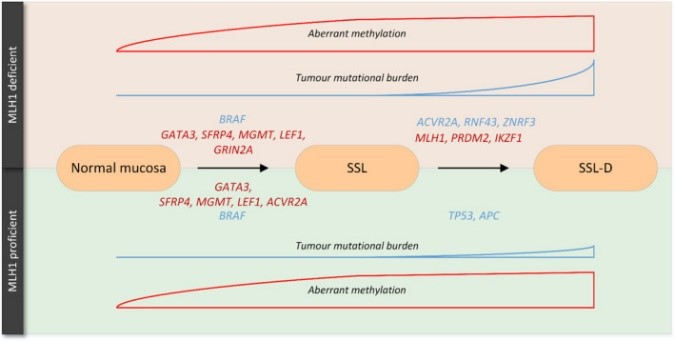
Fig1. Two unique oncogenic routes of sessile serrated lesions. (David Efwm van Toledo, 2024)
Bioapplications of MLH1
Promoter methylation of the MLH1 gene is a common epigenetic alteration in colorectal cancer (CRC) and endometrial cancer (EC) that leads to gene silencing and microsatellite instability (MSI-H). The presence of MLH1 methylation can be used to assess an individual's cancer risk, especially in screening for Lynch syndrome. In some cancer types, the functional status of MLH1 may be related to the tumor's sensitivity to specific chemotherapy drugs.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Berna Somuncu, 2022
The synthetic lethal interaction between the mismatch repair (MMR) protein, MutL homolog 1 (MLH1), and the mitochondrial base excision repair protein, DNA polymerase γ (Pol γ) was used in this study for the selective treatment of MLH1 deficient cancers. Germline mutations in the MLH1 gene and aberrant MLH1 promoter methylation result in an increased risk of developing many cancers, including nonpolyposis colorectal and endometrial cancers. Because the inhibition of Pol γ in MLH1 deficient cancer cells provides the synthetic lethal selectivity, the researchers conducted a comprehensive small molecule screening from various databases and chemical drug library molecules for novel Pol γ inhibitors that selectively kill MLH1 deficient cancer cells. CR reduced the cell proliferation of MLH1 deficient HCT116 human colon cancer cells and suppressed HCT116 xenograft tumor growth whereas it did not affect the MLH1 proficient cell proliferation and xenograft tumor growth. CR caused mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death by inhibiting Pol γ activity and oxidative mtDNA damage repair, increasing the production of reactive oxygen species and oxidative mtDNA damage in MLH1 deficient cells.
.jpg)
Fig1. Real-time dynamic monitoring of the cytotoxic effects of CR on HCT116V1 (MLH1 proficient).
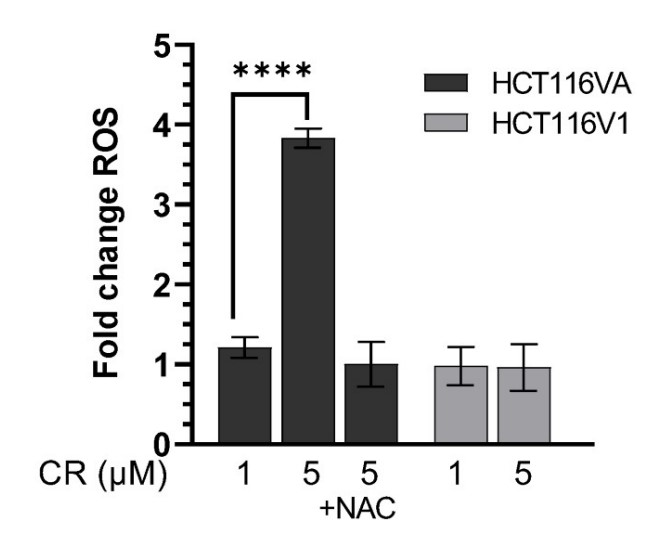
Fig2. CR increases ROS in MLH1 deficient cells.
Case Study 2: Yuling Huang, 2022
Mut L homolog-1 (MLH1) is a key DNA mismatch repair protein which participates in the sensitivity to DNA damaging agents. However, its role in the radiosensitivity of tumor cells is less well characterized. This study investigated the role of MLH1 in cellular responses to ionizing radiation (IR) and explored the signaling molecules involved. The isogenic pair of MLH1 proficient (MLH1+) and deficient (MLH1-) human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells was exposed to IR for 24 h at the dose of 3 cGy. The clonogenic survival was examined by the colony formation assay. Cell cycle distribution was analyzed with flow cytometry. Changes in the protein level of MLH1, DNA damage marker γH2AX, and protein kinase A catalytic subunit (PRKAC), a common target for anti-tumor drugs, were examined with Western blotting. The results showed that the HCT116 (MLH1+) cells demonstrated increased radio-resistance with increased S population, decreased G2 population, a low level of γH2AX, a reduced ratio of phosphorylated PRKACαβ to total PRKAC, and an elevated level of total PRKAC and phosphorylated PRKACβII following IR compared with the HCT116 (MLH1-) cells. Importantly, silencing PRKAC in HCT116 (MLH1+) cells increased the cellular radiosensitivity.
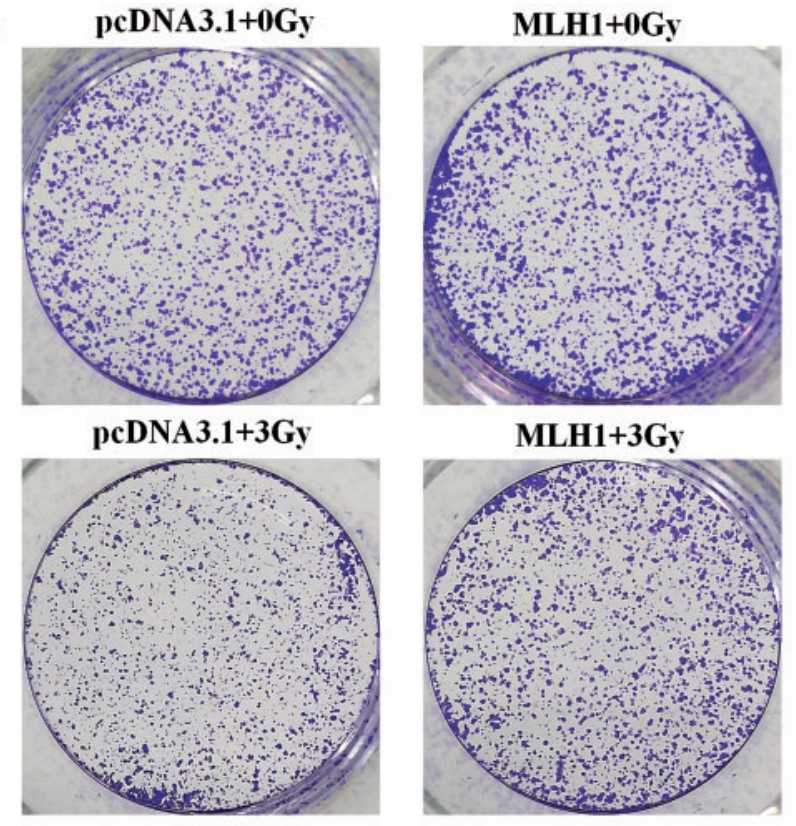
Fig3. The human colon carcinoma cell line HCT116 deficient in the MLH1 gene was used in this study.
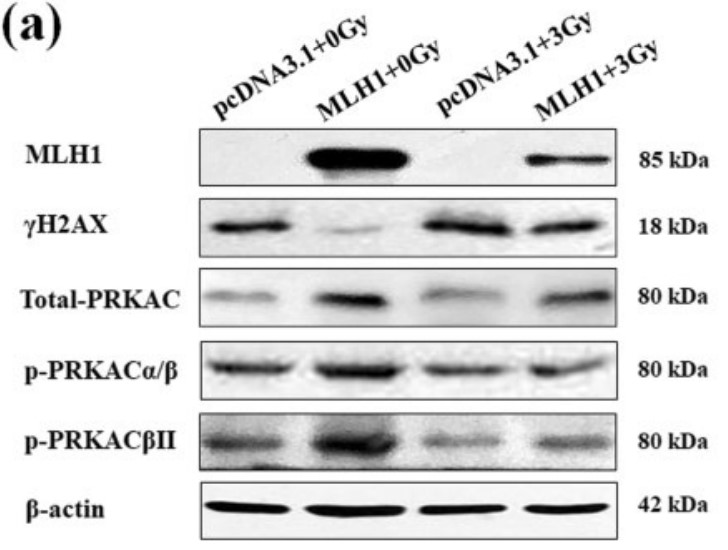
Fig4. The protein levels of MLH1, γH2AX, and PRKAC in the HCT116 cells before and after IR.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MLH1-1290H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MLH1-2320H)
Involved Pathway
MLH1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MLH1 participated on our site, such as Mismatch repair,Fanconi anemia pathway,Pathways in cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MLH1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Mismatch repair | POLD4,SSBP1,LIG1,POLD2,RPA3,MSH3,MSH6,MLH3,RFC5,RFC2 |
| Colorectal cancer | RAC2,TGFBR2,Casp3,TCF7,APC,PIK3CB,MAPK9,TGFB2,BRAF,PIK3CA |
| Pathways in cancer | APC,PTCH1,SUFU,FLT3,RALGDS,HDAC1,BCR,CCNA1,PTK2,MDM2 |
| Fanconi Anemia Pathway | FANCI,RPA1,RAD51,FANCA,REV3L,POLK,RMI2,FAN1,BRCA1,MUS81 |
| Endometrial cancer | MAPK3,ELK1,LEF1,PIK3R2,TP53,TCF7,PIK3R5,PDPK1,GSK3B,TCF7L2 |
Protein Function
MLH1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,ATPase activity,contributes_to MutSalpha complex binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MLH1 itself. We selected most functions MLH1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MLH1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATPase activity | MYH7,ERCC3,KIF2A,KIF4A,PSMC6,ABCD3A,WRNIP1,ATAD2,DDX3X,DNAH11 |
| protein binding | URM1,B3GAT3,MTM1,EFCAB12,CTNNAL1,RTN3,YRDC,YY1,PAM,HJURP |
| ATP binding | MAST4,VMHC,DNAJA2,TWF2,MAPK12A,FER,TIMM44,ATP2A3,TTLL4,UBE2NA |
| contributes_to single-stranded DNA binding | IGJ,MSH3,POLR2D,MSH2,IGHM,PMS2 |
| contributes_to MutSalpha complex binding | PMS2 |
| mismatched DNA binding | MSH5,TDG,MSH6,PMS1,MSH4,MLH3 |
| contributes_to protein binding | INTS10,PAK1,CRY1A,MEF2A,ACVR2A,INHA,CPSF3L,TGFBR3,MSH2,POLR2A |
Interacting Protein
MLH1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MLH1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MLH1.
PMS2;TMSB4X
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Roth, RM; Hampel, H; et al. A Modified Lynch Syndrome Screening Algorithm in Colon Cancer BRAF Immunohistochemistry Is Efficacious and Cost Beneficial. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 143:336-343(2015).
- Bettington, ML; Walker, NI; et al. A clinicopathological and molecular analysis of 200 traditional serrated adenomas. MODERN PATHOLOGY 28:414-427(2015).



