PDPN
-
Official Full Name
Podoplanin -
Overview
This gene encodes a type-I integral membrane glycoprotein with diverse distribution in human tissues. The physiological function of this protein may be related to its mucin-type character. The homologous protein in other species has been described as a differentiation antigen and influenza-virus receptor. The specific function of this protein has not been determined but it has been proposed as a marker of lung injury. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. -
Synonyms
T1A;GP36;GP40;Gp38;OTS8;T1A-2;AGGRUS;HT1A-1;PA2.26;PDPN;podoplanin;T1-alpha;hT1alpha-1;hT1alpha-2;PA2.26 antigen;glycoprotein 36;OTTHUMP00000009639;OTTHUMP00000009640;OTTHUMP00000221492;OTTHUMP00000221493;OTTHUMP00000221495;OTTHUMP00000221496;OTTHUMP00000221498;OTTHUMP00000221499;glycoprotein, 36-KD;lung type I cell membrane associated glycoprotein;lung type-I cell membrane-associated glycoprotein (T1A-2)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Dog
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Human Cells
- Fc
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
Background
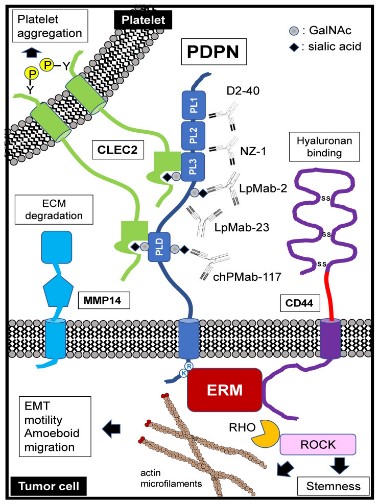
Fig1. Schematic representation of podoplanin (PDPN) structure and functions. (Hiroyuki Suzuki, 2022)
What is PDPN protein?
PDPN (podoplanin) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p36. This gene encodes a type-I integral membrane glycoprotein with diverse distribution in human tissues. The physiological function of this protein may be related to its mucin-type character. The homologous protein in other species has been described as a differentiation antigen and influenza-virus receptor. The PDPN protein is consisted of 162 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 16.7 kDa.
What is the function of PDPN protein?
PDPN is a membrane protein mainly expressed in lymphatic endothelial cells and has multiple functions. First, PDPN plays an important role in maintaining the structure and function of lymphatic vessels, helping to maintain the integrity of lymphatic vessels by regulating the adhesion and migration between lymphatic endothelial cells. Secondly, PDPN participates in the immune response and regulates the activation and chemotaxis of macrophages by binding to CLEC-2.
PDPN Related Signaling Pathway
PDPN interacts with multiple signaling molecules and pathways. For example, it can promote cell growth, migration and invasion by activating C-terminal Src kinase (c-Src). PDPN also activates the downstream PLCγ and Ca² + signaling pathways by binding to its ligand CLEC-2. In addition, PDPN also participates in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. By interacting with Wnt receptors Frizzled and LRP5/6, PDPN can regulate β-catenin stability and nuclear translocation, thereby affecting gene expression.
PDPN Related Diseases
PDPN is a protein closely related to nerve growth and regeneration. Its dysfunction or abnormality is associated with a variety of neurological diseases, such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease, and lateral sclerosis. Due to the role of PDPN in neurodevelopment, its abnormal function may lead to certain congenital or acquired neurodevelopmental disorders.
Bioapplications of PDPN
PDPN may serve as a potential biomarker in the diagnosis of certain types of cancer. Because of its specific expression on cancer cells, the detection of PDPN can help identify and distinguish certain tumor types, thus providing patients with more precise diagnosis and treatment options.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Justyna Sikorska, 2019
Podoplanin (PDPN) is a mucin-type transmembrane glycoprotein specific to the lymphatic system. PDPN expression has been found in various human tumors and is considered to be a marker of cancer. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of PDPN down-regulation in another thyroid cancer-derived cell line: BcPAP.
The efficacy of PDPN silencing was confirmed by qRT-PCR and Western blotting. Then, the researchers tested the motility and invasiveness of these cells (using scratch test and Transwell assay), their growth capacities F(cell cycle analysis, viability, clonogenic activity) and apoptosis assays), adhesion-independent colony-formation capacities, as well as the effect of PDPN silencing on MMPs expression and activity (zymography). PDPN down-regulation in BcPAP cells was negatively correlated with the migration and invasion, in contrast to TPC1 cells in which PDPN depletion resulted in enhanced migration and invasiveness. They also demonstrated that PDPN expression is associated with the MAPK signaling pathway. The inhibition of the MAPK pathway resulted in a decreased PDPN expression, increased E/R/M phosphorylation and reduced cell migration.
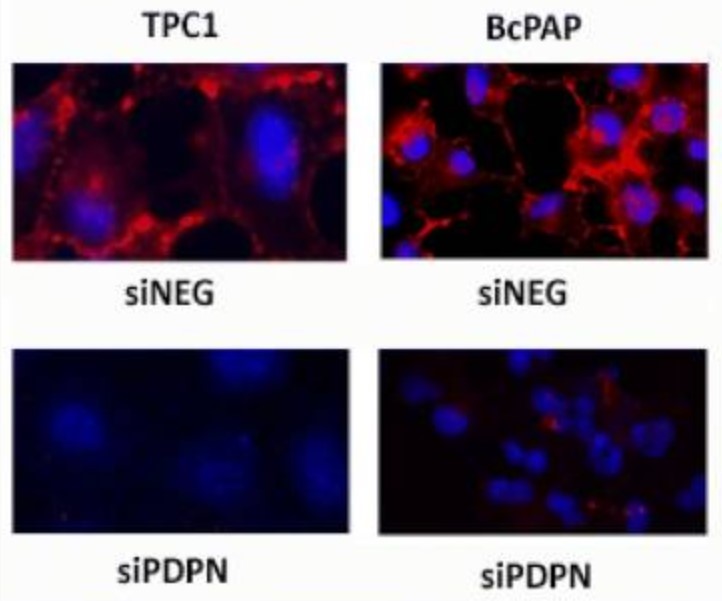
Fig1. Immunofluorescent staining of podoplanin in BcPAP cells transfected with siPDPN or control siNeg.

Case Study 2: Satoshi Takagi, 2014
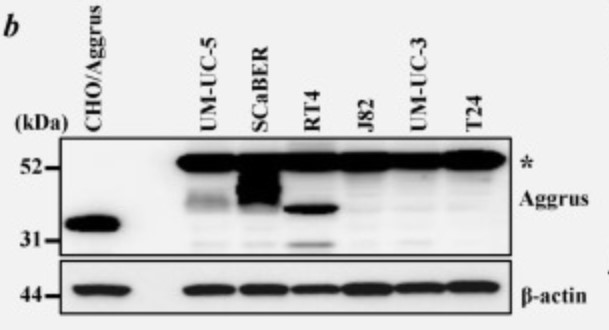
Platelet aggregation-inducing factor Aggrus, also known as podoplanin, is associated with tumor malignancy by promoting hematogenous metastasis. Aggrus overexpression has been reported in some tumor tissues including lung, esophagus, head and neck and brain. The researchers here found the frequent upregulation of aggrus mRNA in urinary bladder cancers using cancer tissue panels from various organs. Immunohistochemical analysis confirmed Aggrus protein expression in urinary bladder cancers and suggested a positive correlation between Aggrus expression and metastatic tendency in bladder cancers. Endogenous expression of Aggrus protein on the cell surface was found in the mouse bladder cancer MBT-2 cell line and human bladder cancer SCaBER cell lines. Knockdown of Aggrus expression in MBT-2 cells decreased their ability to induce platelet aggregation and form pulmonary metastasis in syngeneic mouse models. Knockdown of Aggrus expression in the human bladder cancer SCaBER cells also attenuated their ability to induce platelet aggregation and form pulmonary metastasis in mice. Moreover, pulmonary metastasis of SCaBER cells was prevented by prior administration of our generated anti-Aggrus neutralizing monoclonal antibodies by attenuating their retention in lung.
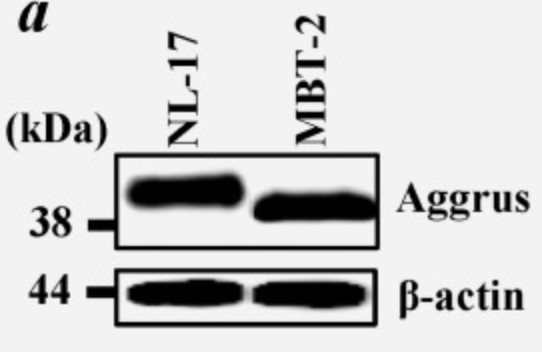
Fig3. Aliquots of cell lysates were immunoblotted with the anti-mouse Aggrus mAb.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PDPN-42H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
High Bioactivity
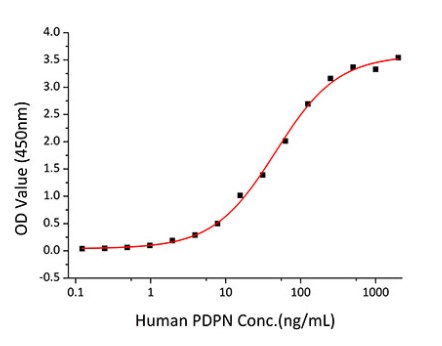
Fig2. Activity Data. (PDPN-2706H)
Involved Pathway
PDPN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PDPN participated on our site, such as GPVI-mediated activation cascade,Hemostasis,Platelet activation, signaling and aggregation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PDPN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GPVI-mediated activation cascade | LCP2A,PIK3R6,RHOB,G6b,FCER1GL,C6orf25,CLEC1B,RHOGA |
| Hemostasis | GNA13,APOER2,MFN1,DGKQ,DOCK7,MERTK,PRTN3,DOCK8,DOCK11,ZFPM2A |
| Platelet activation, signaling and aggregation | MMRN1,GNA13B,SCG3,STXBP3,FCER1GL,GAS6,CLU,AASS,G6b,SERPINF2B |
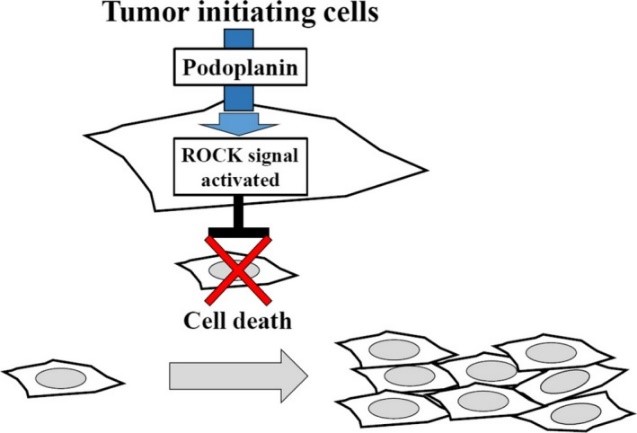
Fig1. Podoplanin (PDPN) expression induces Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK) activity to promote squamous cell carcinoma survival and colony expansion. (Harini Krishnan, 2018)
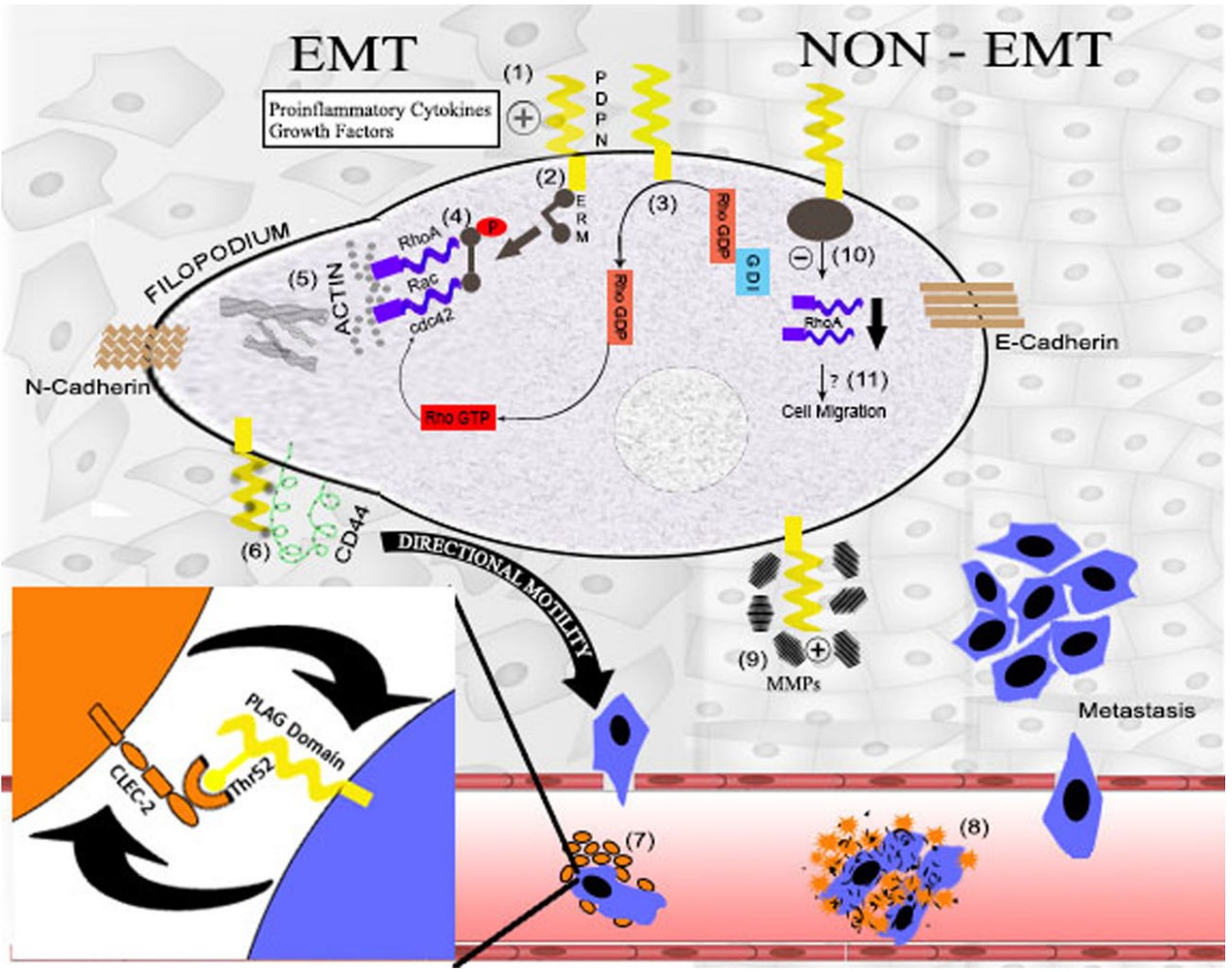
Fig2. Podoplanin in tumorogenesis and metastasis. (Niharika Swain, 2014)
Protein Function
PDPN has several biochemical functions, for example, NOT amino acid transmembrane transporter activity,NOT folic acid transporter activity,NOT water channel activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PDPN itself. We selected most functions PDPN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PDPN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NOT water channel activity | MIPB |
Interacting Protein
PDPN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PDPN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PDPN.
TOM1L1
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Li, JC; Li, Y; et al. Podoplanin-positive cancer cells at the edge of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas are involved in invasion. MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10:1513-1518(2014).
- Kato, Y; Kaneko, MK; et al. A Cancer-specific Monoclonal Antibody Recognizes the Aberrantly Glycosylated Podoplanin. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4:-(2014).



