S100A11
-
Official Full Name
S100 calcium binding protein A11 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein may function in motility, invasion, and tubulin polymerization. Chromosomal rearrangements and altered expression of this gene have been implicated in tumor metastasis. -
Synonyms
S100A11;S100 calcium binding protein A11;S100 calcium binding protein A11 (calgizzarin) , S100 calcium binding protein A11 (calgizzarin);protein S100-A11;S100C;MLN 70;calgizzarin;protein S100-C;metastatic lymph node gene 70 protein;S100 calcium-
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Pig
- Rat
- Rabbit
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- Non
- His
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
Background
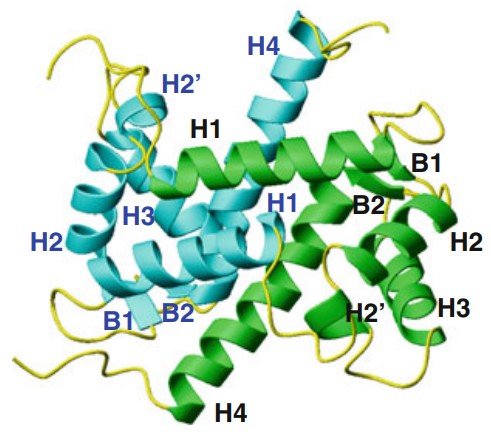
Fig1. Ribbon representation of the tertiary structure of human holo S100A11 dimer. The secondary structure elements of monomers in green and cyan are labeled in black and blue, respectively. (Kuo-Wei Hung, 2012)
What is S100A11 protein?
S100A11 (S100 calcium binding protein A11) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. The S100A11 protein is consisted of 105 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 11.7 kDa.
What is the function of S100A11 protein?
S100A11 is a multifunctional protein that plays a role in cell differentiation, inflammation, cell proliferation/apoptosis, and tumourgenesis. S100A11 is involved in promoting the differentiation of epithelial cells. S100A11 can affect the course of the cell cycle, inhibit or promote cell proliferation, and regulate apoptosis. It can also promote the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines by activating receptors, thus playing an important role in the inflammatory process.
S100A11 Related Signaling Pathway
When S100A11 binds to RAGE on the cell surface, it activates the NF-κB pathway, which promotes the expression of genes related to inflammation and cell survival. In addition, the S100A11-RAGE interaction activates MAPK pathways, including extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK, all of which influence cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. In addition, S100A11 can further regulate cytoskeletal recombination and cellular function by activating the PKC pathway.
S100A11 Related Diseases
In cancer, it is associated with lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, liver cancer and other cancers, and may participate in the process of cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis. In inflammatory diseases, S100A11 may be involved in the regulation of inflammatory response and immune mechanisms, and is associated with rheumatoid arthritis, campylobacter infection and other diseases. In addition, S100A11 has been found to be involved in fibrotic processes such as liver fibrosis and nephropathy. Meanwhile, its abnormal expression is closely related to the occurrence and development of nervous system diseases.
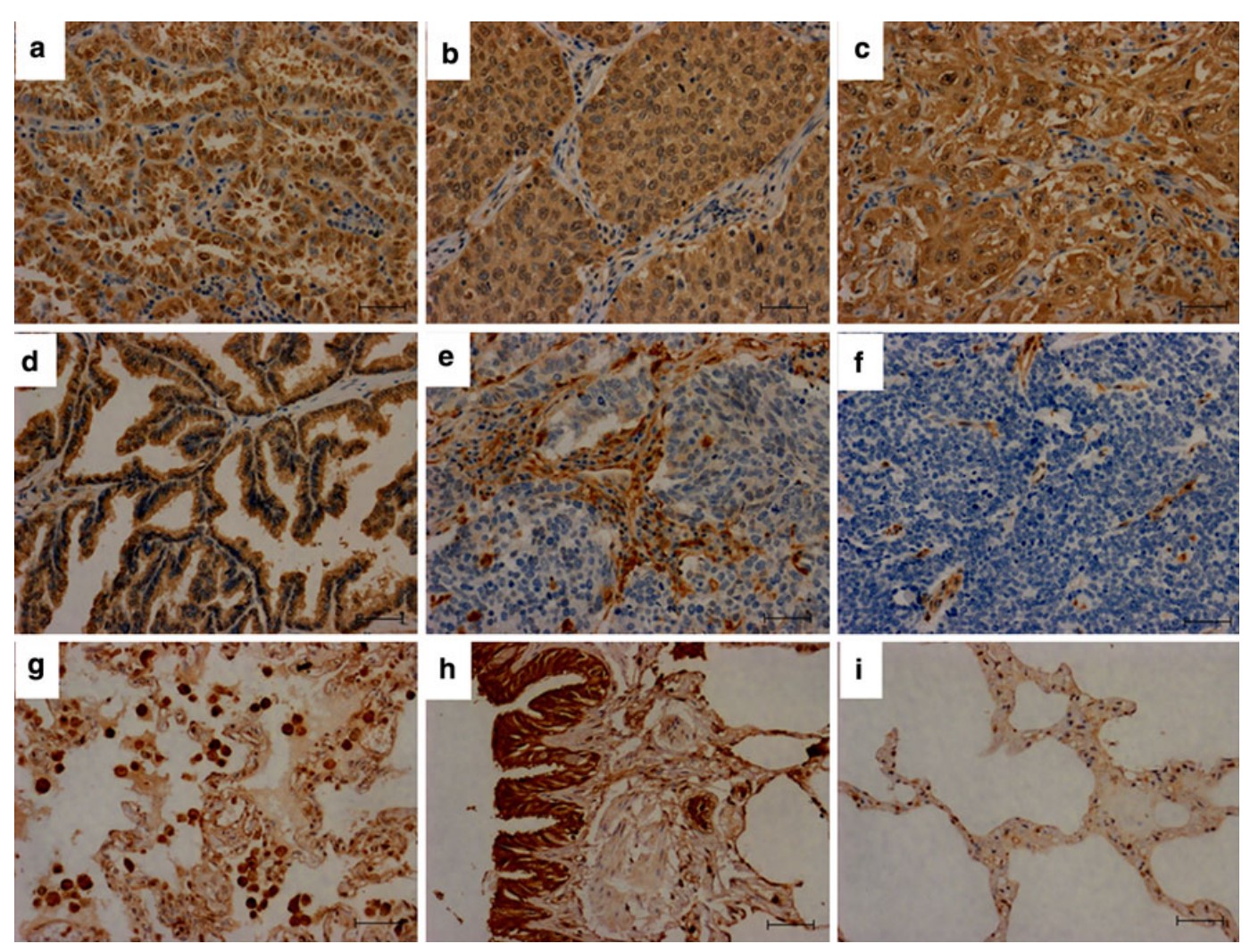
Fig2. Immunohistochemical analysis of S100A11 protein expression in subtypes of lung cancer tissues, benign lung diseases, and normal lung tissues. a Adenocarcinoma; b squamous cell carcinoma; c large cell carcinoma; d papilla carcinoma; e–f small cell lung cancer; g pneumonia; h–i normal lung tissue. (Juanting Hao, 2012)
Bioapplications of S100A11
S100A11 currently has no specific clinical applications, but several studies are underway to explore its potential applications in disease diagnosis and treatment, including inhibitor development, biomarker studies.
Case Study
Case study 1: Mei Zheng, 2023
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common and malignant liver tumor worldwide, although the treatment approaches for HCC continue to evolve, metastasis is the main reason for high mortality rates. S100A11 is overexpressed in various cells and regulates tumor development and metastasis. However, few studies report the role and underlying regulatory mechanisms of S100A11 in HCC development and metastasis.
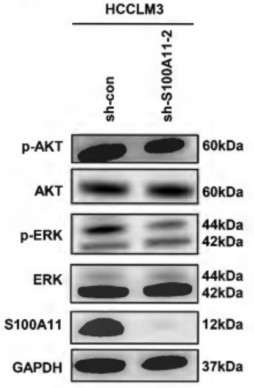
This study provided the first demonstration that S100A11 could serve as a novel diagnostic biomarker used in conjunction with AFP for HCC. Using in vitro cell culture model, we demonstrated that S100A11 is overexpressed in metastatic hepatoma cells, knockdown of S100A11 decreases hepatoma cells proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition process by inhibiting AKT and ERK signaling pathways.
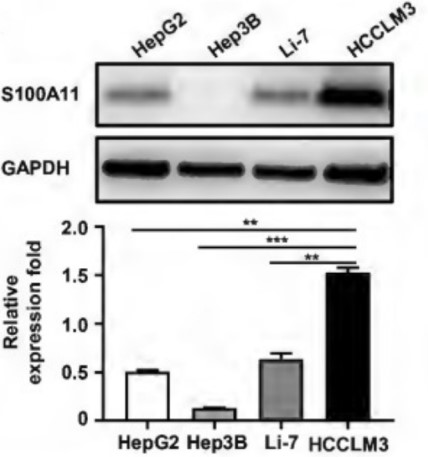
Fig1. The protein expression level of S100A11 in HepG2, Hep3B, Li-7, and HCCLM3 cells was determined by Western Blot assay.
Case study 2: Youquan Chen, 2021
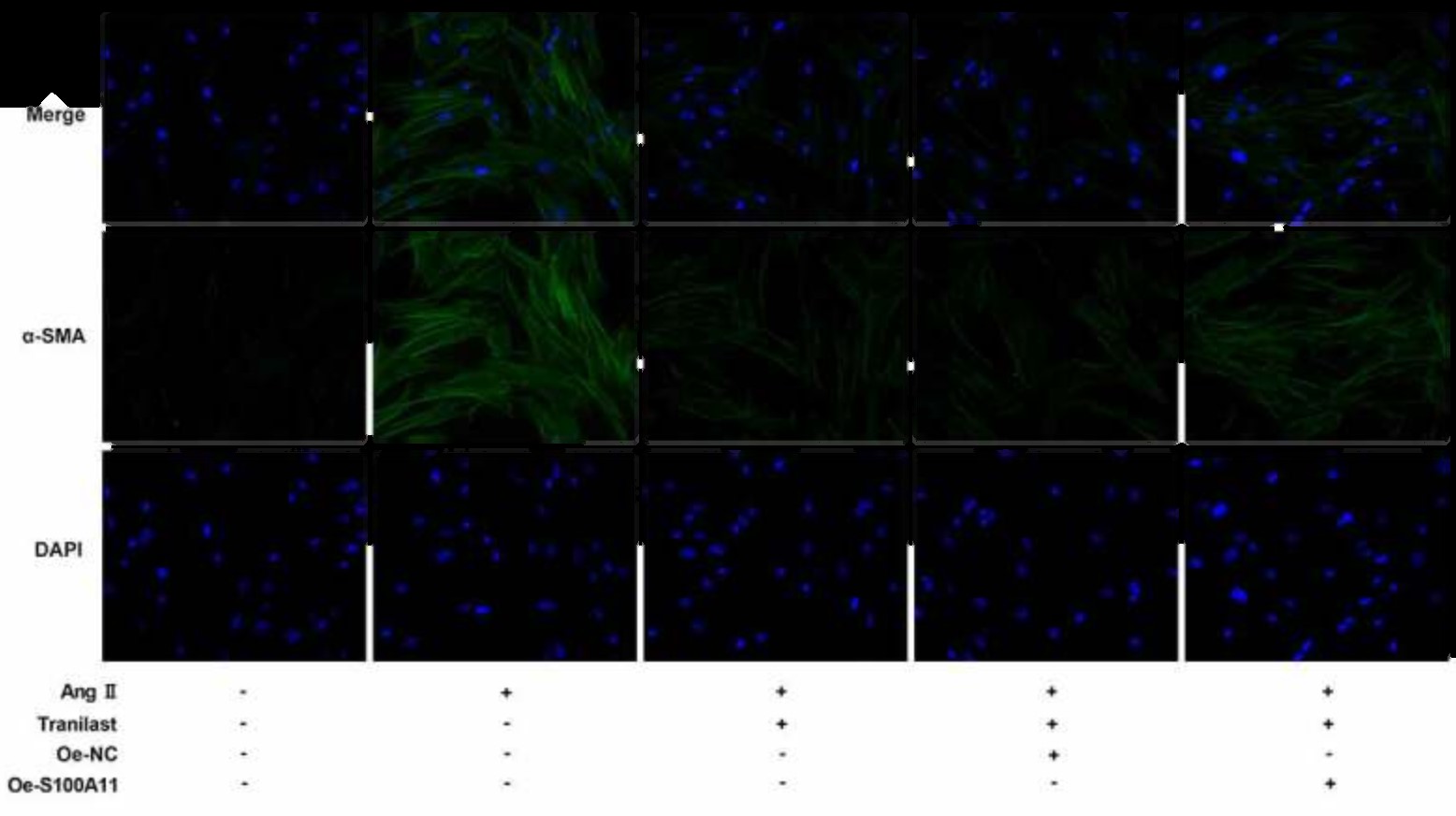
Tranilast has an ameliorative effect on myocardial fibrosis (MF), but the specific mechanism has not been studied. S100A11 is a key regulator of collagen expression in MF. In this paper, the researchers will study the regulatory roles of Tranilast and S100A11 in MF.
After the introduction of angiotensin II (AngII) to Human cardiac fibroblasts (HCF), Tranilast was administered, CCK-8 kit, Wound Healing assay and Western blot was used to detect cell functions. The expression of S100A11 was detected by qPCR and Western blot, and then S100A11 was overexpressed by cell transfection technology, so as to explore the mechanism by which Tranilast regulated MF. Overexpression of S100A11 reversed the inhibition of Tranilast on AngII-induced over-proliferation, migration, and fibrosis in HCF, accompanied by activation of the TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Overall, Tranilast inhibits angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis through S100A11/TGF-β1/Smad axis.
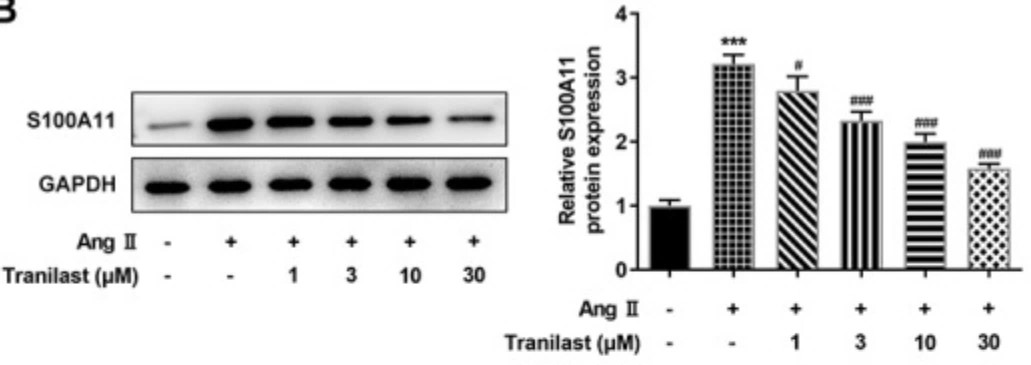
Fig3. Tranilast down-regulated the expression of S100A11. Western blot detected the expression of S100A11.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (S100A11-1178HFL) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
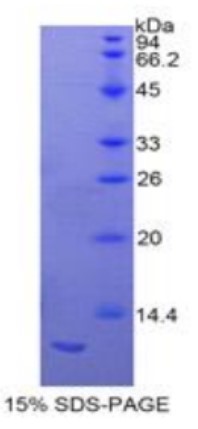
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (S100a11-2582R) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
S100A11 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways S100A11 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with S100A11 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
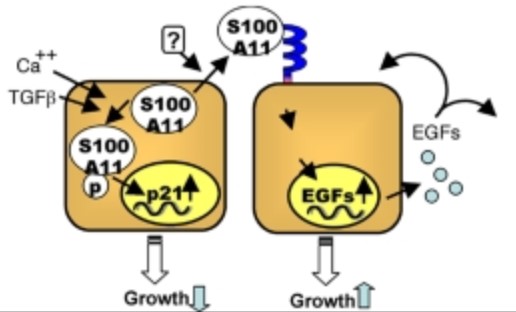
Fig1. Schematic presentation of the ambivalent role of S100A11 in growth regulation of normal human keratinocytes (NHK). (Masakiyo Sakaguchi, 2008)
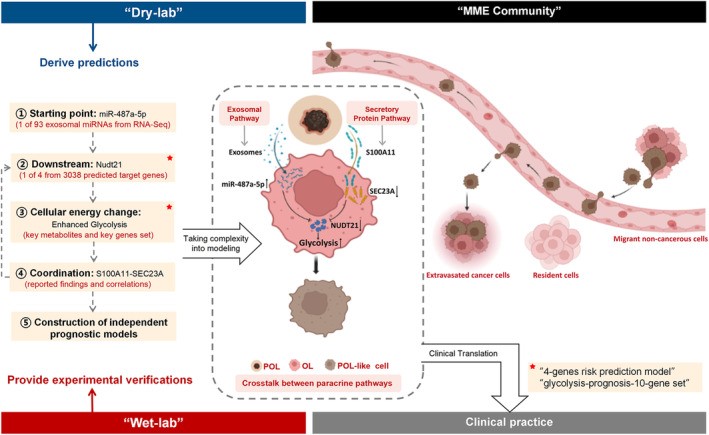
Fig2. Schematic summary of the 'dry-lab discovery/wet-lab validation' approach and key findings. (Bin Zeng, 2023)
Protein Function
S100A11 has several biochemical functions, for example, S100 protein binding,calcium ion binding,calcium-dependent protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by S100A11 itself. We selected most functions S100A11 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with S100A11. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| S100 protein binding | AGER,ANXA11,KCNK3,AHNAK,DDX1,FGF1A,ATP2A2,FGF1,ANXA2,EZR |
| protein homodimerization activity | ACTN2,TENM2,PRPS2,BCL11A,CADM4,CUBN,NPPC,FGFR1,USF2,TRIM9 |
| protein binding | TERF1,CD46,CSTF1,UNC119B,KLF10,RBM14,UNC45A,SOST,SIN3A,POU2F1 |
| calcium-dependent protein binding | SLC9A1,ANXA11,TSG101,S100P,CD209A,ALG2,ANXA4,CPNE3,MBL1,SELP |
| calcium ion binding | ICN,CDH18A,DNASE1L2,ASPH,MMP12,LPCAT2,PCDH2AB7,PPEF2,PLCB2,LOC100686744 |
Interacting Protein
S100A11 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with S100A11 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of S100A11.
S100B;EPB41;HLA-B;VHL;TRAF6;q5nfd5_fratt;EGFR;ATF2;ATP6V1A;P;GABARAPL1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Hanaue, M; Miwa, N; et al. Immunohistochemical Characterization of S100A6 in the Murine Ovary. ACTA HISTOCHEMICA ET CYTOCHEMICA 45:9-14(2012).
- Nylandsted, J; Becker, AC; et al. ErbB2-associated changes in the lysosomal proteome. PROTEOMICS 11:2830-2838(2011).



