Calcium-binding Proteins and Related Molecules
Related Symbol Search List
- Iba1
- CALB1
- CALB2
- CALCR
- CALD1
- CALM1
- CALR
- CALR3
- Camk1
- CAMK2A
- CAMK2B
- CaMKII
- CAMK2G
- CAMKK1
- CAMKK2
- CIB1
- CLSTN1
- CLSTN2
- CLSTN3
- DCLK1
- DOC2A
- GPRC6A
- HAX1
- Nucb2
- PCDH12
- PDP1
- PPP3CA
- PPP3R1
- PPP3R2
- PRKD1
- PVALB
- S100A1
- S100A10
- S100A11
- S100A12
- S100A13
- S100A16
- S100A2
- S100A4
- S100A6
- S100A7
- S100A8
- S100A9
- S100B
- S100P
- SMOC1
- SMOC2
- SYT1
- TPT1
- WFS1
Immunology Background
About Calcium-binding Proteins and Related Molecules
Calcium-binding proteins and related molecules are essential components of many biological processes. These proteins can bind calcium ions, which allows them to regulate various cellular functions such as signal transduction, enzyme activation, muscle contraction, and protein-protein interactions. Calcium-binding proteins are classified into several families based on their structural and functional properties. Some notable families include calmodulins, troponins, annexins, and EF-hand proteins. Each family has different calcium-binding motifs and plays specific roles in cellular processes.
Calmodulins are perhaps the most well-known and extensively studied calcium-binding proteins. They consist of a compact structure with four calcium-binding EF-hand motifs. Calmodulins exhibit a high affinity for calcium ions and are involved in regulating numerous cellular activities, including enzyme activity, ion channel gating, and cytoskeletal organization.
Troponins are another group of calcium-binding proteins that play a critical role in muscle contraction. They are composed of three subunits, namely troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T. Troponin C binds calcium ions, leading to conformational changes that activate the contraction machinery in muscle cells.
Annexins are a family of calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins involved in membrane organization and repair. They have a unique structure characterized by a core domain and multiple calcium-binding sites. Annexins interact with phospholipids in a calcium-dependent manner, which enables their participation in membrane remodeling and vesicle trafficking.
EF-hand proteins are a diverse group of calcium-binding proteins that share a common structural motif known as the EF-hand. This motif consists of two helices connected by a short calcium-binding loop. EF-hand proteins are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including calcium signaling, muscle contraction, and neuronal development.
S100 proteins are another family of calcium-binding proteins involved in a wide range of cellular processes. They are mainly found in vertebrates and have diverse functions such as regulation of cell growth, apoptosis, and inflammation. S100 proteins have two calcium-binding EF-hand motifs and exert their effects by interacting with target proteins.
Calsequestrin is a calcium-binding protein primarily found in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. It binds to and releases calcium ions within the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which plays a crucial role in regulating calcium levels during muscle contraction and relaxation.
Osteocalcin is a calcium-binding protein primarily found in bone cells. It is involved in bone mineralization and has been implicated in other physiological functions. Osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation synthesize osteocalcin. Once synthesized, it is incorporated into the bone matrix, where it contributes to the mineralization process.
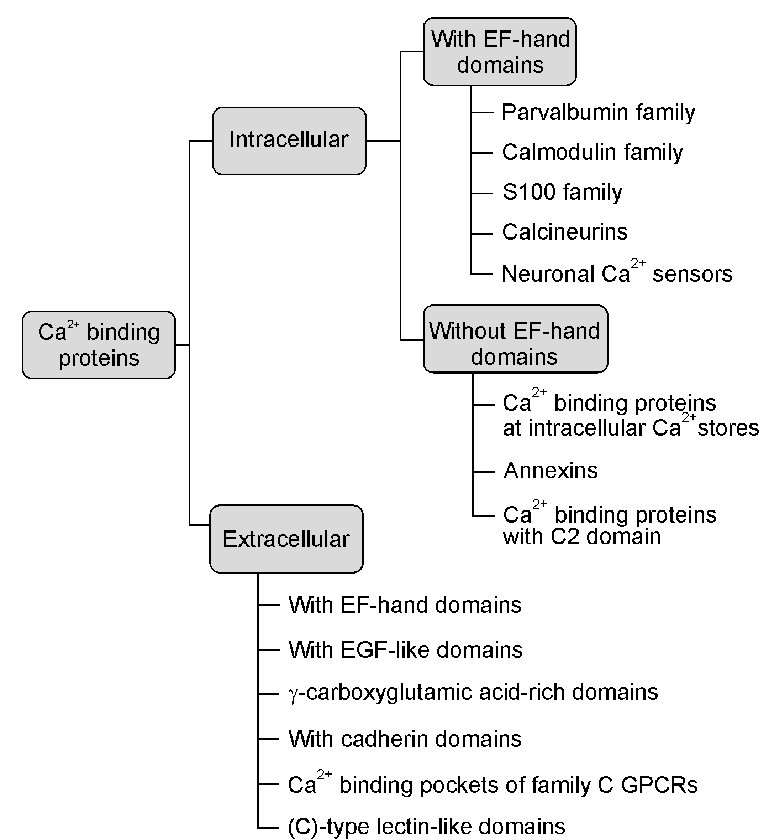 Fig.1 The main types of calcium-binding proteins (CaBPs). (Kelemen K, et al., 2021. Elíes J, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 The main types of calcium-binding proteins (CaBPs). (Kelemen K, et al., 2021. Elíes J, et al., 2020)
Biological Functions of Calcium-binding Proteins and Related Molecules
Calcium-binding proteins and related molecules play important roles in various biological functions. Some of the key functions include:
Cell Signaling: Calcium ions are crucial for intracellular signaling processes. Calcium-binding proteins such as calmodulin, troponin, and S100 proteins help regulate the concentration of calcium ions within cells, which in turn modulates the activity of various signaling pathways. These proteins act as calcium sensors and facilitate the transmission of signals important for cell survival, growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Muscle Contraction: Calcium ions are essential for the contraction of muscle cells. Proteins like troponin C, which binds calcium, are part of the regulatory system in muscle tissues. Troponin C binds calcium and triggers a series of molecular events that ultimately result in muscle contraction. Other calcium-binding proteins, such as calmodulin, regulate the activity of myosin light chains and other contractile proteins.
Blood Clotting: Calcium-binding proteins like factor VII, factor IX, and factor X are crucial for the coagulation cascade, which leads to the formation of blood clots. These proteins bind calcium ions and participate in the activation of clotting factors, which ultimately leads to the formation of fibrin, the protein network that forms the clot.
Bone Mineralization: Calcium-binding proteins like osteocalcin and osteopontin are involved in the regulation of bone mineralization and remodeling. These proteins bind calcium ions and play important roles in the formation and regulation of hydroxyapatite, the mineral component of bones and teeth.
Enzyme Regulation: Calcium-binding proteins like calmodulin and protein S100B can modulate the activity of various enzymes. Calmodulin, for example, can activate or inhibit enzymes such as protein kinases and phosphatases, thereby regulating key cellular processes like signal transduction and gene expression. Protein S100B, on the other hand, has been implicated in the regulation of enzyme activities involved in cell differentiation and proliferation.
Neuronal Signaling: Calcium-binding proteins are involved in various aspects of neuronal signaling. They participate in synaptic transmission by regulating the release of neurotransmitters from vesicles in the presynaptic terminal. They also modulate the sensitivity and activity of ion channels and receptors, thereby influencing neuronal excitability and synaptic plasticity. Calmodulin, for instance, binds to and regulates the activity of calcium channels, contributing to the propagation of electrical signals in neurons.
Cell Proliferation and Differentiation: Calcium-binding proteins have been implicated in regulating cell proliferation and differentiation processes. They interact with various intracellular signaling molecules and transcription factors to modulate gene expression, leading to cell fate determination and tissue development. For example, the protein S100B has been shown to influence the proliferation and differentiation of neuronal cells.
Calcium Homeostasis: Calcium-binding proteins play a crucial role in maintaining calcium homeostasis within cells. They are involved in the uptake, release, and storage of calcium ions in different cell compartments. One example is the calcium-binding protein, calbindin-D28k, which is expressed in the cytosol of many cell types, including neurons, kidney cells, and intestinal epithelial cells. Calbindin-D28k acts as an intracellular calcium buffer, helping to maintain low levels of free calcium ions in the cytosol.Applications of Calcium-binding Proteins and Related Molecules
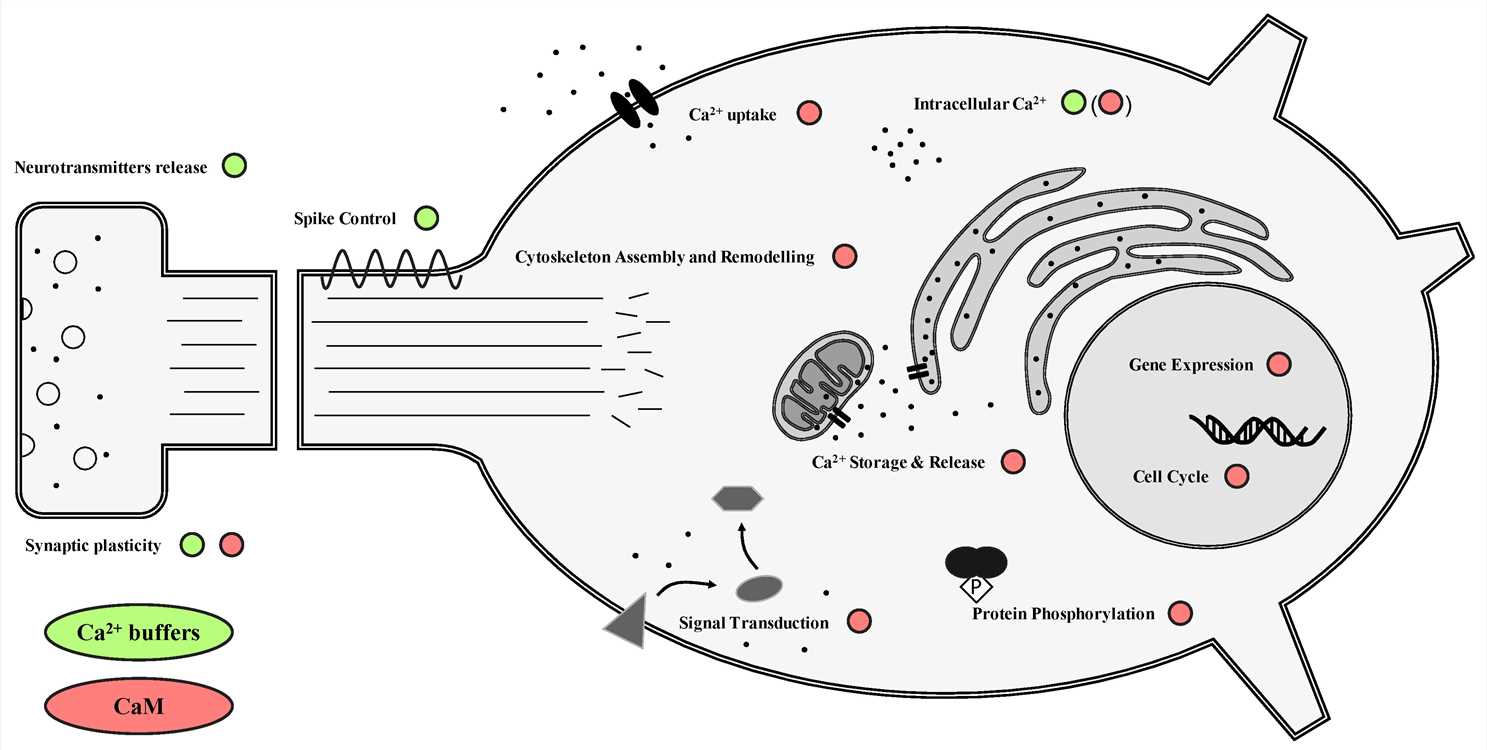 Fig.2 Schematic overview of the functions of buffer and sensor calcium-binding proteins (CBPs) in neurons. (Gattoni G, et al., 2019)
Fig.2 Schematic overview of the functions of buffer and sensor calcium-binding proteins (CBPs) in neurons. (Gattoni G, et al., 2019)
Calcium-binding proteins and related molecules play crucial roles in various biological processes and have diverse applications in medicine, biotechnology, and research. Some of the key applications include:
Calcium signaling: Calcium-binding proteins such as calmodulin and troponin are involved in intracellular calcium signaling pathways. They regulate cellular processes such as muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression. Understanding and manipulating calcium signaling pathways have implications for the treatment of diseases like cardiac arrhythmias, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer.
Bone Health: Calcium-binding proteins like osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein are important for bone mineralization and regulation of bone metabolism. They have applications in diagnosing and monitoring bone diseases like osteoporosis and for the development of therapies to promote bone growth and healing.
Cell Adhesion: Calcium-binding proteins like cadherins and integrins are essential for cell-cell adhesion and cell-matrix interactions. They have applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, where they can be used to promote cell attachment and organize cells into functional structures.
Enzyme Activation: Calcium-binding proteins can act as cofactors or regulators of enzymes. For example, the calcium-binding protein calmodulin activates various enzymes involved in cell signaling pathways. Understanding these interactions can lead to the development of drugs targeting specific enzymes and pathways.
Biomineralization: Calcium-binding proteins are involved in the formation of biological mineral structures such as teeth, shells, and coral skeletons. Understanding the mechanisms of biomineralization has applications in material science, where it can inspire the development of new materials with unique properties.
Biosensors: Calcium-binding proteins can be used in biosensor technology to detect and quantify specific substances. For example, protein-based biosensors can be created using calcium-binding proteins such as calmodulin. Calmodulin can undergo a conformational change upon binding to calcium, which can be detected and measured. This conformational change can be used as a signal to indicate the presence and quantity of a specific substance in the sample being tested.
Available Resources for Calcium-binding Proteins and Related Molecules
Creative BioMart provides a comprehensive range of products, services, and technical resources related to calcium-binding proteins and related molecules. Our product offerings include recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, and protein pre-coupled magnetic beads. These resources serve as high-quality experimental tools for researchers and help facilitate their studies.
The following are calcium-binding proteins and related molecules, click on the molecule/target to view research reagents.
At Creative BioMart, we are committed to supporting researchers in their calcium-binding protein studies. Our products are quality-controlled and backed by extensive technical support. If you have any questions or specific requirements, please feel free to contact us. Our team of experts is always ready to assist you.
References:
- Kelemen K, Szilágyi T. New approach for untangling the role of uncommon calcium-binding proteins in the central nervous system[J]. Brain sciences, 2021, 11(5): 634.
- Elíes J, Yáñez M, Pereira T M C, et al. An update to calcium binding proteins[J]. Calcium Signaling, 2020: 183-213.
- Gattoni G, Bernocchi G. Calcium-Binding Proteins in the Nervous System during Hibernation: Neuroprotective Strategies in Hypometabolic Conditions?. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2364. Published 2019 May 13. doi:10.3390/ijms20092364.

