Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction
Cytoplasmic proteins play fundamental roles in virtually all intracellular processes, including energy metabolism, lipid and nitrogen pathways, heme biosynthesis, signal propagation, and dynamic protein–protein interactions. Accurate extraction of these soluble proteins—while minimizing contamination from membrane-associated or nuclear proteins —is essential for reliable downstream analyses. Creative BioMart provides high-quality, customizable Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction Services tailored to diverse sample types and research goals. With extensive expertise in sequential extraction, advanced solubilization strategies, and proteomic characterization technologies, we deliver highly enriched cytoplasmic fractions suitable for drug discovery, pathway analysis, biomarker identification, and structural or functional studies.
Background: Significance of Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction
The cytoplasm is the dynamic interior environment between the cellular membrane and the nucleus, where countless biochemical activities occur. It contains a heterogeneous mixture of soluble proteins, cytoskeletal elements, metabolic enzymes, signaling mediators, and molecular complexes that collectively govern essential cellular functions. Because the cytoplasm is central to metabolic regulation, stress responses, redox balance, and intracellular trafficking, studying cytoplasmic proteins provides critical insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying health, disease, and drug action.
However, isolating cytoplasmic proteins with high purity poses several technical challenges. Hydrophilic cytoplasmic proteins must be separated from structurally and physicochemically distinct components, including:
- Hydrophobic membrane proteins
- Nuclear proteins and chromatin-associated factors
- Organellar contaminants (ER, mitochondria, lysosomes)
- Membrane-associated signaling complexes
A widely used and effective strategy to meet these challenges is the sequential extraction approach, which leverages differential protein solubility across gradually intensified extraction buffers. This technique employs controlled lysis conditions, chaotropes, detergents, and centrifugation steps to fractionate cytoplasmic proteins away from membranes and nuclei. Subsequent precipitation—often using trichloroacetic acid (TCA)—yields highly enriched cytoplasmic fractions suitable for quantitative or qualitative analysis.
Cytoplasmic protein extraction is crucial across research and industry. In pharmaceutical development, cytoplasmic proteomics facilitates target discovery, mechanism-of-action studies, toxicity prediction, and biomarker identification. In basic research, purified cytoplasmic proteins support enzymatic assays, structural studies, interactome mapping, and post-translational modification profiling. Creative BioMart offers a comprehensive suite of extraction and analysis solutions that streamline these applications with precision and reliability.
What We Offer: Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction Services
Creative BioMart provides a complete portfolio of cytoplasmic protein extraction and proteomic solutions designed to maximize purity, yield, and downstream usability. Our service offerings include:
- Custom cytoplasmic protein isolation using sequential extraction or tailored buffer systems.
- Selective solubilization strategies optimized for diverse cell lines, primary cells, microbial species, and plant tissues.
- Gel-based and gel-free proteomic analysis (2D-PAGE, LC–MS/MS, MALDI-TOF, etc.).
- Protein identification and characterization, including PTM profiling and functional annotation.
- High-purity, ready-to-use cytoplasmic protein preparations from various species.
- Recombinant protein expression, purification, and structural analysis for individual cytoplasmic proteins of interest.
- Consultative method development, ensuring the extraction workflow suits unique experimental needs.
Each project is executed with strict quality control to ensure fraction integrity, reproducibility, and compatibility with downstream assays.
Service Workflow
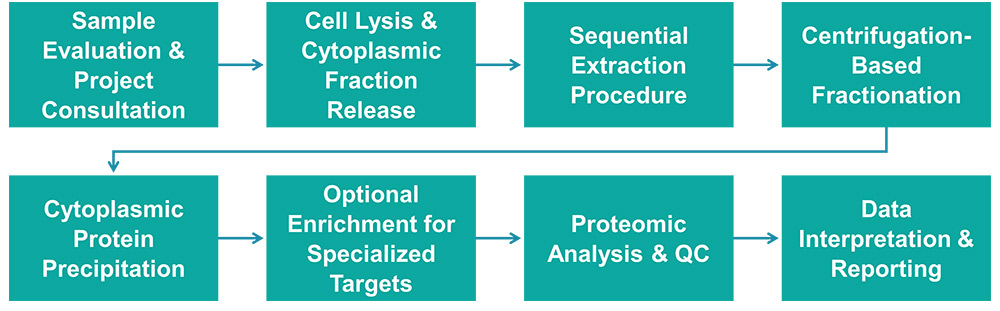
Service Features
-
Sequential Extraction Methodology
Our sequential extraction approach is designed to separate:
- Highly soluble, hydrophilic cytoplasmic proteins
- Membrane-bound or membrane-associated proteins
- Nuclear proteins and chromatin complexes
Each extraction buffer is precisely formulated with optimized concentrations of salts, chaotropes, detergents, and stabilizers. This controlled progression ensures minimal cross-contamination, enabling reliable cytoplasmic proteome profiling.
-
Solubilization Agents
We use a wide spectrum of agents tailored to sample properties, including:
- Triton X-100
- Nonionic/mild detergents (NP-40, digitonin)
- Chaotropes (urea, thiourea)
- Ionic detergents when required (SDS in controlled amounts)
Selection of solubilization agents is crucial for preserving protein function and preventing aggregation.
-
Proteomic Technologies
We support gel-based and gel-free platforms:
- 2D-PAGE for isoform separation and PTM analysis
- High-resolution LC–MS/MS for global proteomics
- MALDI-TOF for rapid profiling
- Native PAGE for complex analysis
-
Quality Control
QC includes:
- Purity verification
- Fraction integrity analysis
- Protein concentration determination
- Mass spectrometry quality checks
- Confirmatory immunoblotting (optional)
Why Choose Creative BioMart
- Proven Expertise in Cytoplasmic Proteomics: Our scientists have extensive experience handling diverse biological materials and designing precise extraction workflows that maximize purity and yield.
- Highly Customizable Extraction Strategies: We tailor buffer systems, solubilization agents, and fractionation techniques to meet unique sample requirements and research objectives.
- Advanced Analytical Capabilities: Our proteomic platforms—gel-based and gel-free—provide deep coverage, high sensitivity, and confident identification of cytoplasmic proteins.
- End-to-End One-Stop Services: From extraction to proteomics, expression, purification, and structural analysis, we support every stage of your project seamlessly.
- Strict Quality Control and Reproducibility: Each stage of the workflow is monitored with rigorous QC assays to ensure consistent, reproducible, and publication-ready results.
- Broad Organism and Sample-Type Coverage: We routinely process mammalian cells, microbial cultures, plant tissues, and specialized cell lines, offering ready-to-use cytoplasmic protein preparations from various species.
Case Studies: Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction
Case 1: Tissue subcellular fractionation and protein extraction
Cox and Emili, 2006. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.273
Subcellular fractionation is a powerful approach to enhance proteome coverage in complex biological samples, such as organs, for mass spectrometry analysis. By separating a tissue into nuclear, cytosolic, mitochondrial, and mixed microsomal fractions using differential centrifugation in density gradients, researchers can obtain detailed molecular information on protein distribution and tissue state. The described method efficiently captures the majority of subcellular fractions with reasonable purity and is scalable from small embryonic tissues to larger organs. Cytosolic proteins can then be extracted from the cytoplasmic fraction, stored, and analyzed later, enabling high-quality proteomic studies within approximately five hours.
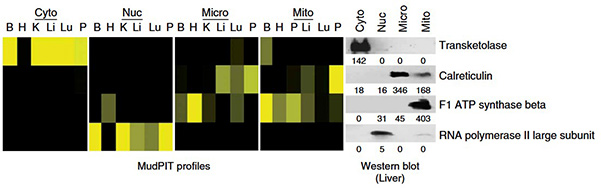
Figure 1. MudPIT profiles and western blot of markers for the four subcellular fractions: nuclei (Nuc), cytosol (Cyto), microsomes (Micro) and mitochondria (Mito). Markers for cytosol (Transketolase), nuclei (RNA polymerase II large subunit), microsomes (Calreticulin) and mitochondria (F1 ATP synthase beta subunit) were blotted against extracts from liver subcellular fractions. B, brain; H, heart; K, kidney; Li, liver; Lu, lung; P, placenta. (Cox and Emili, 2006)
Case 2: Optimized cytoplasmic protein extraction using digitonin
Holden and Horton, 2009. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-2-243
Recombinant protein analysis in mammalian cells is often complicated by contamination from other compartments and solubility challenges. A sequential fractionation protocol using buffers of increasing stringency was developed to isolate cytosolic, organellar, nuclear, and insoluble protein fractions efficiently and cost-effectively. The key step employs digitonin to selectively permeabilize the cholesterol-rich plasma membrane, releasing cytosolic contents while sparing intracellular membranes like the ER and mitochondria. Optimization in HEK293 cells determined that 25 µg/ml digitonin achieves near-complete cytosolic extraction without ER disruption. Subsequent NP40 lysis solubilizes organelle-bound proteins. This method enhances purity and reproducibility of cytoplasmic protein preparations for downstream analyses.
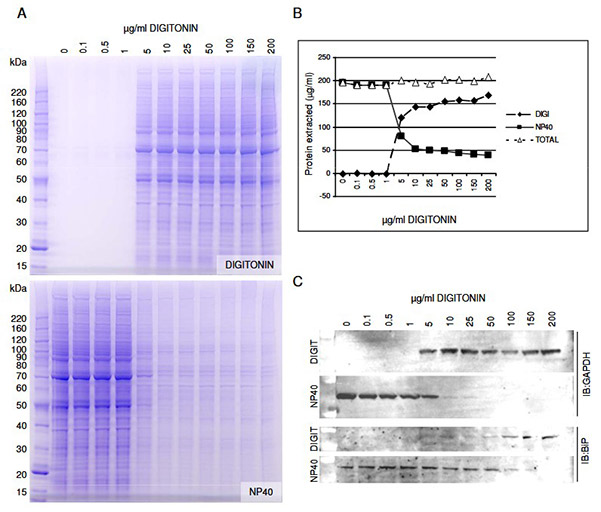
Figure 2. Optimization of digitonin concentration for the extraction of cytosolic proteins. HEK293 cells were lysed with varying digitonin concentrations, followed by NP40 extraction of remaining proteins. (A) SDS-PAGE with Coomassie staining visualized extracted proteins. (B) Protein concentrations confirmed total protein was consistent across digitonin conditions. (C) Western blotting used GAPDH and BiP as markers for cytosol and ER, respectively. (Holden and Horton, 2009)
Customer Testimonials: Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction Services
“Creative BioMart played a pivotal role in our cytoplasmic proteomics project targeting metabolic pathway alterations in a rare disease model. Their sequential extraction workflow delivered exceptionally clean cytoplasmic fractions with negligible nuclear contamination—far better than what we obtained in-house. The downstream LC–MS/MS analysis uncovered low-abundance regulatory proteins we had struggled to detect for months.”
— Director of Translational Research | Global Biopharmaceutical Company
“Our team needed high-purity cytoplasmic proteins from a salt-tolerant plant line to validate stress-responsive metabolic enzymes. Creative BioMart customized the extraction buffers to preserve enzyme activity and metal-binding states, which was essential for our metalloproteomics assays. Their QC documentation and rapid turnaround allowed us to move directly into functional characterization without repeating any prep work.”
— Principal Investigator | Agricultural Biotechnology Institute
“For a large-scale drug target discovery program, we relied on Creative BioMart to isolate cytoplasmic proteins from multiple engineered human cell lines. Their consistency across batches was impressive—the proteomic profiles showed minimal variation, giving our bioinformatics team high-confidence data to compare signal transduction pathways. Their integrated protein structure analysis service was a valuable bonus.”
— Head of Target Discovery | International Pharmaceutical R&D Center
“We partnered with Creative BioMart to obtain cytoplasmic fractions from a pathogenic microbial species with notoriously difficult cell walls. Their scientists optimized the lysis conditions, detergent selection, and precipitation method, producing samples clean enough for both 2D-PAGE and high-resolution MS. Their expertise saved us significant time and helped pinpoint new cytoplasmic virulence factors.”
— Senior Scientist, Infectious Disease Division | Public Health Research Organization
FAQs: Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction Services
-
Q: How do you ensure high purity of cytoplasmic proteins without contamination from membrane or nuclear fractions?
A: We use a carefully optimized sequential extraction workflow, applying buffers of increasing solubilizing strength to separate hydrophilic cytoplasmic proteins from membrane-associated and nuclear components. Each extraction step is followed by controlled centrifugation to remove unwanted fractions. Additional QC—such as marker-based validation and MS profiling—ensures each fraction meets stringent purity standards. -
Q: Can your team handle different sample types, including challenging organisms?
A: Yes. Our experts routinely process mammalian cells, microbial systems, plant tissues, primary cells, and model organisms. Years of hands-on experience allow us to tailor buffer composition, solubilization agents, and workflow modifications to ensure optimal protein recovery from each sample type. -
Q: What analytical methods do you use to evaluate extracted cytoplasmic proteins?
A: We offer a full suite of gel-based and gel-free proteomic analyses, including SDS-PAGE, 2D-PAGE, LC–MS/MS, MALDI-TOF, and native gel methods. Quantitative proteomics, PTM mapping, and protein identification are performed using high-resolution instruments, ensuring deep coverage and reliable detection—even of low-abundance proteins. -
Q: Do you support projects requiring extraction of specialized cytoplasmic proteins, such as metal-binding or redox-sensitive proteins?
A: Absolutely. We design custom workflows for proteins with unique biochemical properties. This includes using chelator-controlled buffers, redox-safe extraction strategies, affinity-based enrichment, and gentle solubilization conditions to preserve protein functionality and native metal-binding or enzymatic states. -
Q: What advantages does Creative BioMart offer over standard cytoplasmic extraction kits or in-house protocols?
A: Our approach is fully tailored, highly reproducible, and supported by advanced proteomics technologies. By combining sequential extraction expertise, optimized solubilization systems, professional QC, and integrated downstream services, we deliver higher purity, higher yield, more reliable proteomic data, and end-to-end project support that off-the-shelf kits cannot match.
Other Resources
Related Services
- Protein Engineering Services
- Metabolism Assays
- Protein Interaction Service
- Drug Discovery Screening
- Protein Pathway Profiling
- Biomarker Service
- Protein Sequence Analysis and Function Prediction
- Protein Extraction Services
- Organelle Protein Extraction
- Nuclear Protein Extraction
- Membrane Protein Extraction
Related Products
References:
- Cox B, Emili A. Tissue subcellular fractionation and protein extraction for use in mass-spectrometry-based proteomics. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(4):1872-1878. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.273
- Holden P, Horton WA. Crude subcellular fractionation of cultured mammalian cell lines. BMC Res Notes. 2009;2(1):243. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-2-243
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

