IkB Kinase (IKK)
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
About IkB Kinase (IKK)
Intracellular Kinases (IKs) are an important class of enzymatic proteins involved in the regulation of intracellular signaling and modulation. Among them, IκB Kinase (IkappaB kinase or IKK), an important member of the IK family, is an enzyme complex that is part of the upstream NF-κB signaling cascade involved in propagating cellular responses to inflammation, particularly in lymphocytes. The IκK complex consists of three subunits: the IkB α kinase (IκKα, IκK1), IκB β kinase (IκKβ, IκK2), and NEMO (NF-κB essential regulator, also known as IKKγ).
IκKα and IκKβ are interrupted subunits, whereas NEMO is an essential regulatory subunit. The IKK complex regulates NF-κB activity by phosphorylating and degrading IκB proteins.
IκBα proteins inactivate NF-κB transcription factors by shielding NF-κB proteins from nuclear localization signals (NLS) and keeping them inactive in the cytoplasm. Specifically, IκK phosphorylates the inhibitory IκBα protein. This phosphorylation results in the dissociation of IκBα from NF-κB. The now free NF-κB migrates to the nucleus and activates the expression of at least 150 genes; some of which have anti-apoptotic effects.
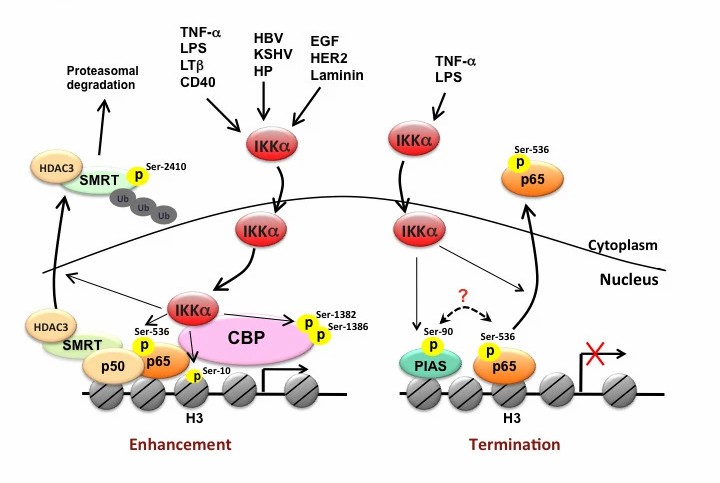 Fig.1 Nuclear IKKα-dependent molecular regulations of NF-κB-mediated gene transcription. (Huang WC, et al., 2013)
Fig.1 Nuclear IKKα-dependent molecular regulations of NF-κB-mediated gene transcription. (Huang WC, et al., 2013)
Mechanism of Action of IKKs
- IκB Phosphorylation and Degradation
The main function of the IκK complex is to regulate the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway. In the inactivated state, IkB proteins form a complex with NF-κB, blocking it in the cytoplasm. When a stimulus (e.g. cytokine, agent infection) activates the IκK complex, IκK phosphorylates the IκB protein, leading to ubiquitination and degradation of IκB. This releases NF-κB, which can enter the nucleus and initiate specific gene regulation.
- Activation of NF-κB
After IκK phosphorylates IκB, NF-κB enters the nucleus and binds to specific DNA sequences that activate the regulation of NF-κB-related genes. These genes encode a variety of inflammatory factors, immunomodulatory molecules, cellular key factors, and others, and thus are involved in critical cellular responses, immune responses, and survival cells.
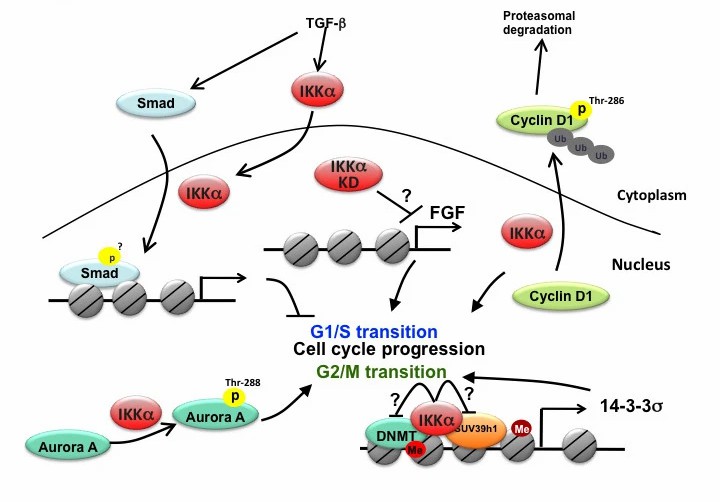 Fig.2 Regulations of cell cycle progression by nuclear IKKα. (Huang WC, et al., 2013)
Fig.2 Regulations of cell cycle progression by nuclear IKKα. (Huang WC, et al., 2013)
Functions of IKKs
The IKK complex exerts important biological functions through the regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and is involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, such as immune responses, inflammatory responses, cell survival and apoptosis, etc. IKK is also involved in other signaling pathways and regulates cellular functions.
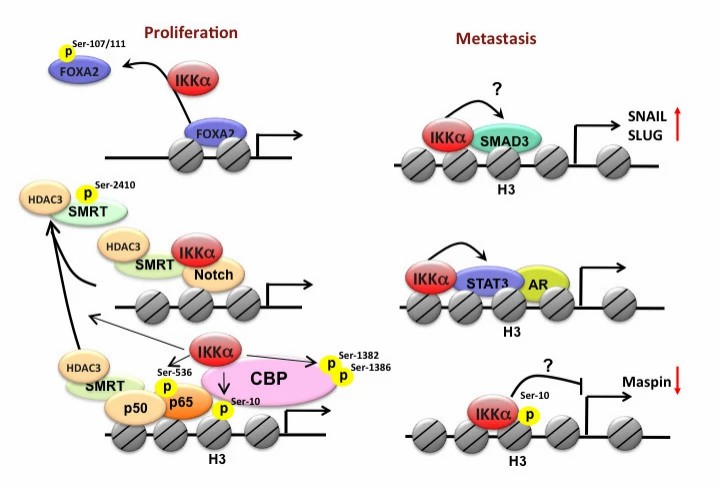 Fig.3 Nuclear IKKα and tumor progression.
Fig.3 Nuclear IKKα and tumor progression.
Nuclear IKKα promotes tumor growth by enhancing NF-κB- and Notch-dependent gene transcriptions and suppressing FOXA2-mediated gene expression. By promoting Smad and STAT3 transcriptional activity and suppressing maspin gene expression, nuclear IKKα contributes to cancer metastasis. (Huang WC, et al., 2013)
IKK can phosphorylate and affect a range of substrates, including ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated), p53 (tumor suppressor), and initiating protein kinase (MAPK). Through these regulatory pathways, IKK is involved in physiological and pathological processes such as apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, and cellular stress.
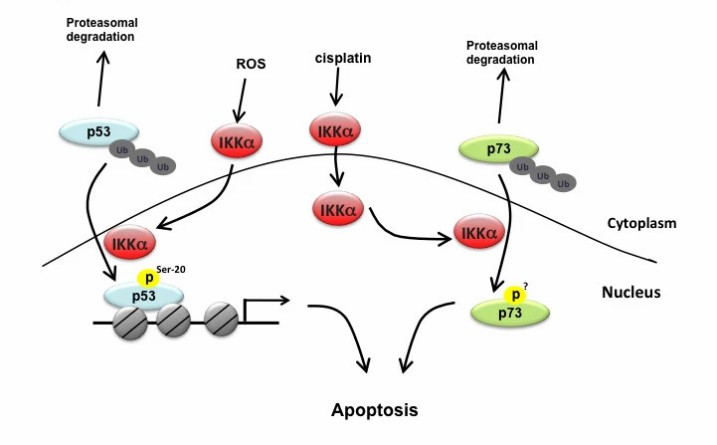 Fig.4 Nuclear IKKα targets p53 and p73 to mediate apoptosis. (Huang WC, et al., 2013)
Fig.4 Nuclear IKKα targets p53 and p73 to mediate apoptosis. (Huang WC, et al., 2013)
Available Resources for IKKs
Investigating the function and regulatory mechanism of IKK helps to gain a deeper understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of cell signaling and provides important clues for the research and treatment of related diseases. Creative BioMart offers a variety of IKK-related research products, such as recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, and protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, as well as customizable services and other resources to support your research in the field of IKKs. The following IKKs are displayed, click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. For further information or to purchase products, please contact us. We are committed to providing the highest quality resources and support for your research to help you succeed.
References:
- Huang WC, Hung MC. Beyond NF-κB activation: nuclear functions of IκB kinase α. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20(1):3.
- Israël A. The IKK complex, a central regulator of NF-kappaB activation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2(3):a000158.

