Inflammatory Disorders Therapeutic Targets
Creative BioMart Inflammatory Disorders Therapeutic Targets Product List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Interleukins & Receptors Research
Creative BioMart provides researchers with products for several families of interleukins and their receptors, such as the common gamma chain family, IL-1 family, IL-10 family, IL-12 family, IL-17 family, IL-6 family, and other interleukin families and receptors. Our wide range of products includes recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, and other essentials. These products have been carefully selected to meet a variety of research needs.
In addition to our diverse range of products and customized services, we offer a wealth of resources for your reference. These resources cover all aspects of interleukins and receptors, including the pathways involved, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, areas of research, and other relevant topics. These resources serve as valuable references that enable researchers to enhance their knowledge of interleukins and receptor function and their role in physiology and disease.
About Interleukins & Receptors
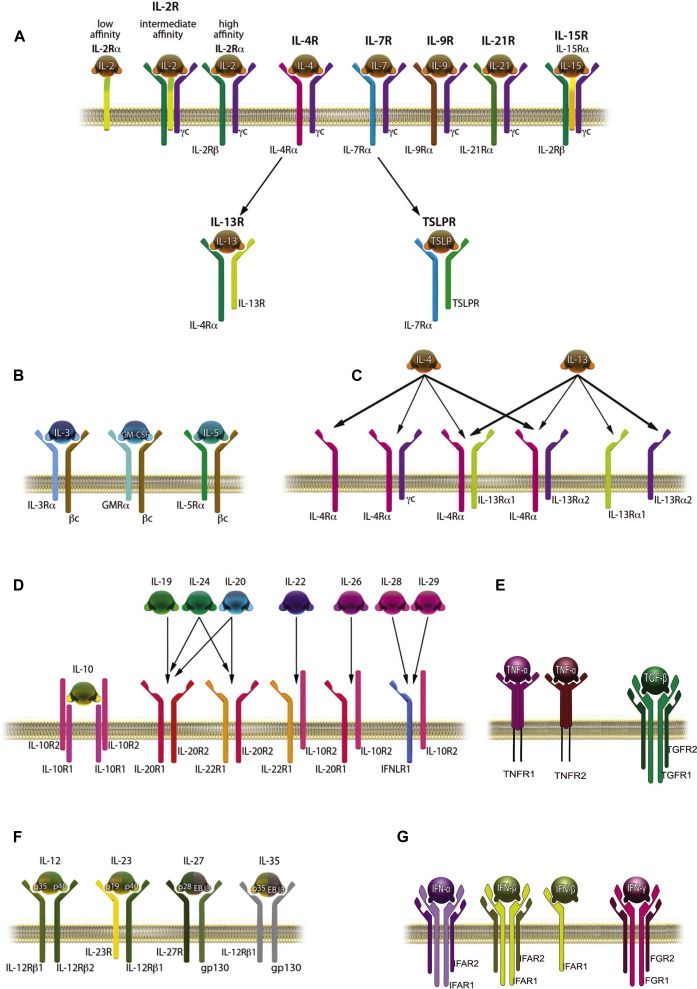
Secreted proteins that bind to their specific receptors and play a role in the communication among leukocytes are named ILs. ILs are assigned to each family based on sequence homology and receptor chain similarities or functional properties (Fig 1).
A. Receptors of the IL-2 family, which is composed of IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21. Receptors contain the common cytokine receptor γ chain (CD132, γc). IL-13R shares IL-4Rα with IL-4, and TSLPR shares IL-7R with IL-7.
B. Receptors for IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF are heterodimers of a unique α chain and the common β chain (βc, CD131) subunit.
C. Receptors for IL-4 and IL-13 consist of 2 receptor chains: IL-4Rα (CD124) and γc. IL-4 and IL-13 bind to IL-4R, which consists of IL-4Rα and the IL-13Rα1 chain. IL-13R consists of 2 subunits, IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2, and signaling occurs through the IL-4R complex type II, which consists of IL-4Rα and IL-13Rα.
D. Based on similarities in their intron-exon structure, conserved secondary protein structures, and similar types of receptors, the following cytokines have been classified as IL-10 family members: IL-10, IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24, IL-26, IL-28, and IL-29. They share common receptor subunits, as shown.
E. TNF-α binds to TNFRI and TNFR2, and TGF-β binds to heterodimer receptor consisting of TGF-βR1 and TGF-βR2.
F. IL-12R consists of 2 subunits: IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ3. A heterodimer of IL-12Rβ1 and IL-23R binds IL-23. IL-12Rβ2 shows homology to the gp130 subunit of IL-27R.
G. IFN-α and IFN-β bind to the heterodimer receptor consisting of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2; in addition, IFN-β binds to IFNAR1, and IFN-γ binds to the IFN-γR1 and IFN-γR2 heterodimer.
Physiological Functions of Interleukins & Receptors
- Immune Cell Development and Differentiation: Interleukins are involved in the development and differentiation of immune cells. For example, IL-7 is essential for lymphocyte development, while IL-3, IL-5, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) promote the differentiation and function of various myeloid cells.
- Inflammatory Response: Interleukins are critical mediators of the inflammatory response. IL-1, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) promote inflammation by stimulating the recruitment and activation of immune cells, inducing the production of acute-phase proteins, and regulating the expression of adhesion molecules.
- Immune Cell Activation and Effector Functions: Interleukins are involved in activating and coordinating immune responses. IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 promote T cell activation and proliferation, while IL-12 and IL-18 enhance natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity. IL-17 and IL-23 play important roles in the activation and recruitment of neutrophils and other effector cells.
- Regulation of Immune Tolerance and Autoimmunity: Interleukins and their receptors contribute to immune tolerance and the prevention of autoimmune diseases. IL-10 and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) have immunosuppressive functions and regulate T cell responses to prevent excessive inflammation and autoimmunity. Dysregulation of these interleukins and their signaling pathways can contribute to autoimmune diseases.
- Hematopoiesis and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Maintenance: Several interleukins are involved in hematopoiesis, the process of blood cell formation. IL-3, IL-6, IL-11, and stem cell factor (SCF) support the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, which give rise to all blood cell lineages.
- Tissue Repair and Regeneration: Interleukins play roles in tissue repair and regeneration processes. IL-4, IL-10, and IL-13 promote tissue remodeling and wound healing by regulating the activation and function of fibroblasts, promoting angiogenesis, and modulating extracellular matrix deposition.
- Neuroimmune Communication: Interleukins and their receptors are involved in the communication between the immune system and the nervous system. They influence neuronal activity, neurogenesis, and synaptic plasticity, contributing to neuroinflammation, neuroprotection, and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Metabolic Regulation: Certain interleukins, such as IL-6, IL-1β, and IL-15, have been implicated in the regulation of energy metabolism, including glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism, and appetite control. Dysregulation of these interleukins may contribute to metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
It's important to note that the physiological functions of interleukins and their receptors are diverse and interconnected. They often work in concert with other immune molecules and signaling pathways to maintain immune homeostasis, regulate immune responses, and coordinate various physiological processes.
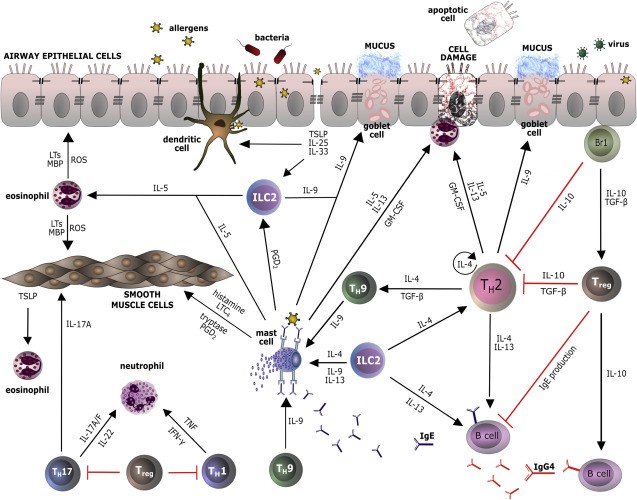 Fig.2 Cytokine and other mediator networks in allergic inflammation. (Akdis M, et al., 2016)
Fig.2 Cytokine and other mediator networks in allergic inflammation. (Akdis M, et al., 2016)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related Reference
- Akdis M, Aab A, Altunbulakli C, et al. Interleukins (from IL-1 to IL-38), interferons, transforming growth factor β, and TNF-α: Receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138(4):984-1010.

