Autoimmune Disease Therapeutic Targets
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Study of Autoimmune Disease Therapeutic Targets
At Creative BioMart, we are dedicated to remaining at the forefront of autoimmune disease research. Our commitment is reflected in our continuous updates of product offerings and resources, ensuring researchers have access to the latest tools and information to drive progress in this critical field of study.
- Our extensive range of products includes recombinant proteins and other essential materials that play a key role in uncovering the mechanisms of autoimmune diseases. We understand that every researcher has unique needs, which is why we provide a wide selection of products tailored to their specific requirements.
- Our team of experienced experts in autoimmune disease research is highly knowledgeable and passionate about their work. They are committed to delivering customized and individualized solutions to meet the specific requirements of each researcher.
- In addition, we offer comprehensive support resources that include involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, and other valuable information. By providing these resources, we aim to empower researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of autoimmune diseases and enhance the impact of their research.
Our Featured Products
- Active Recombinant Human DPP4 protein
- Active Recombinant Human DPP4 Protein (29-766aa), C-hIgG-tagged
- Active Recombinant Human TNFRSF4, MIgG2a Fc-tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Tnfrsf4 Protein, hFc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated
- Active Recombinant Human ICAM1 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human ICAM1 protein(Met1-Glu480)
- Recombinant Rhesus Monkey ICAM1 Protein
- Recombinant Bovine ICAM1 Protein
- Recombinant Human PARP1, His tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Tnfrsf4 Protein
- Recombinant Monkey TNFRSF4 Protein, Fc-tagged, FITC conjugated
- Recombinant Monkey TNFRSF4 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated
- Recombinant Mouse Parp1 Protein, His-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated
- Recombinant Human PARP1 Protein, His-tagged, FITC conjugated
- Recombinant Human IL12A protein, Fc-tagged
- Recombinant Human IL12A, His tagged
Whether you are studying autoimmune disease pathology, drug discovery, or treatment development, Creative BioMart is here to support your research. We are committed to helping you achieve your scientific goals and make meaningful contributions to the field of autoimmune disease research. Contact us today to learn more about our products and resources.
About Autoimmune Disease
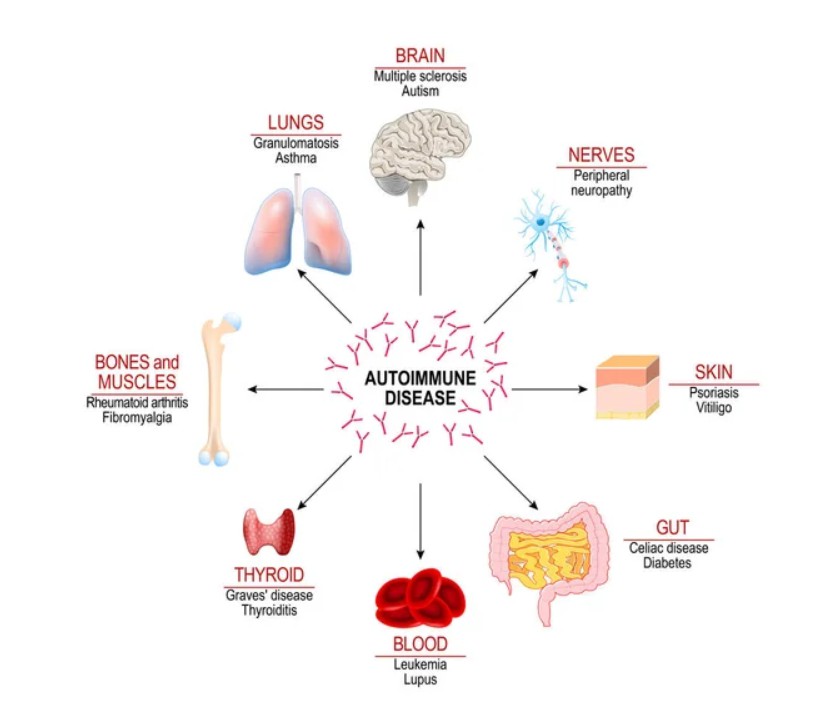
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its healthy tissues and cells. Normally, the immune system acts as a defense mechanism, protecting the body from harmful substances such as bacteria and viruses. However, in the case of autoimmune diseases, the immune system cannot differentiate between these harmful substances and the body's healthy cells, leading to chronic inflammation and damage to various organs and tissues.
There are over 80 known autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, lupus, type 1 diabetes, and celiac disease, among others. These diseases can affect any part of the body, including the skin, joints, muscles, organs, and even the nervous system.
Although the exact cause of autoimmune diseases is still unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genes may increase the risk of developing an autoimmune disease, and various triggers, such as infections, hormonal changes, and exposure to certain chemicals or drugs, can activate the immune system to attack the body.
Symptoms of autoimmune diseases can vary depending on the specific disease and the organs affected. However, common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, muscle weakness, skin rashes, recurring fever, and gastrointestinal issues. Diagnosis of autoimmune diseases can be challenging, as symptoms can be similar to other conditions, and specific diagnostic tests are often required.
Management of autoimmune diseases often involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and self-care strategies. Medications may include anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to reduce inflammation and immune response. Additionally, pain relief medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort.
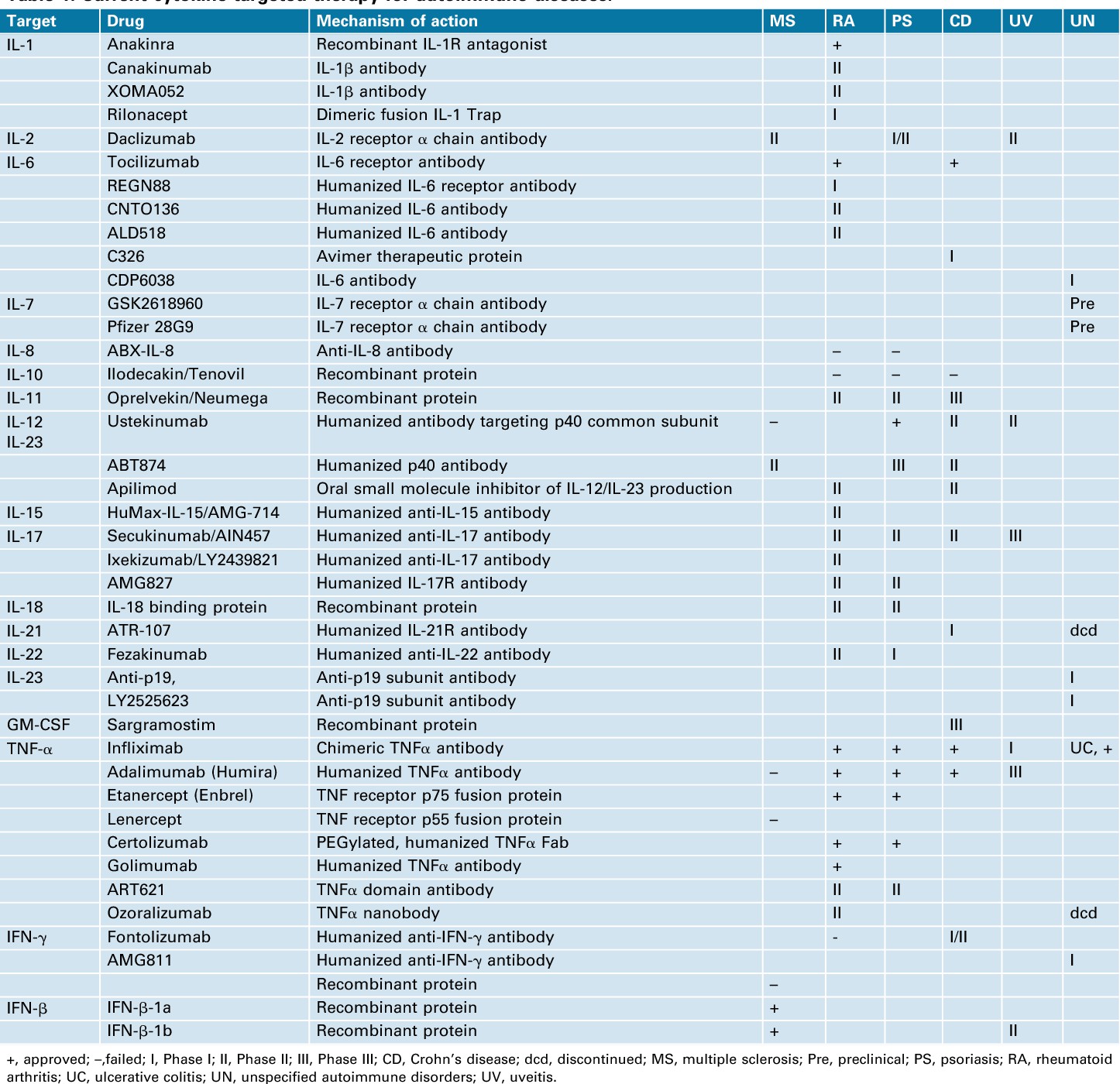
Table 1. Current cytokine-targeted therapy for autoimmune diseases. (Liu X, et al., 2013)
The Treatment Targets of Autoimmune Disease
Research on treatment targets for autoimmune diseases focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms and pathogenic pathways involved in these disorders. While the specific targets vary depending on the autoimmune disease, here are some prominent treatment targets currently being studied:
Cytokines
- Cytokines are small proteins that play a crucial role in immune cell communication and regulation. Abnormal cytokine signaling is often implicated in autoimmune diseases.
- Targeting specific cytokines or their receptors is a common approach. For example, inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) have been developed for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
T-cell Co-stimulation
- T cells are a type of immune cell involved in the immune response. Co-stimulatory molecules on T cells play a role in their activation and function.
- Inhibiting co-stimulatory pathways, such as CD28-B7 or CD40-CD40L, is being explored as a potential treatment strategy for autoimmune diseases. Agents like abatacept and belatacept target these pathways.
B-cell Signaling
- B cells are immune cells that produce antibodies, which can contribute to autoimmune responses.
- Inhibitors of B-cell signaling, such as rituximab (anti-CD20), are being studied for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus to reduce autoantibody production.
Janus Kinase (JAK) Pathway
- The JAK pathway plays a role in cytokine signaling and immune cell activation.
- JAK inhibitors, such as tofacitinib and baricitinib, are being investigated as potential treatments for autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) Pathway
- IL-17 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in autoimmune inflammation.
- Inhibitors of the IL-17 pathway, such as secukinumab and ixekizumab, have shown efficacy in conditions like psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Regulatory T-cell (Treg) Modulation
- Tregs are a subset of T cells that help regulate immune responses and maintain tolerance.
- Strategies to enhance Treg function or induce Treg expansion are being explored for their potential in autoimmune disease treatment.
Interferon Signaling
- Interferons are immune signaling molecules that can contribute to autoimmune inflammation.
- Targeting interferon signaling pathways, such as the type I interferon pathway, is being investigated as a potential treatment approach for conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus.
The choice of treatment target depends on the specific autoimmune disease and its underlying mechanisms. Individualized approaches and combination therapies may be needed to effectively manage autoimmune diseases. Ongoing research aims to identify novel targets and develop more targeted therapies to improve outcomes and minimize side effects in patients with autoimmune diseases.
Reference:
- Liu X, Fang L, Guo TB, Mei H, Zhang JZ. Drug targets in the cytokine universe for autoimmune disease. Trends Immunol. 2013;34(3):120-128. doi:10.1016/j.it.2012.10.003

