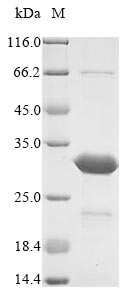
IVD of Vaccinia Virus
🧪 B18R-276V
Source: Insect Cells
Species: VACV
Tag: His
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-351 a.a.

🧪 B19R-174
Source: HEK293
Species: VACV
Tag: Fc
Conjugation: Biotin
Protein Length: His20-Glu351

🧪 B8R-175
Source: CHO
Species: VACV
Tag: His
Conjugation: Biotin
Protein Length: Lys18-Ser272

🧪 E6R-1966V
Source: E.coli
Species: VACV
Tag: His&SUMO
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-567 aa
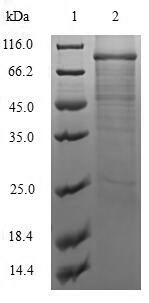
🧪 D8L-2017V
Source: E.coli
Species: VACV
Tag: His&SUMO
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-304 aa
🧪 A27L-2425V
Source: E.coli
Species: VACV
Tag: His&Myc
Conjugation:
Protein Length: 1-110 aa
Vaccinia Virus (VACV)
Vaccinia virus (VACV) is a large and complex DNA virus among animal viruses. Studies have found that VACV can be used as a live virus vaccine against smallpox. Currently, VACV has been used by scientific researchers as a tool to deliver genes into biological tissues in gene therapy and genetic engineering. In addition, VACV is used in recombinant vaccines as a vector to express foreign genes within the host to generate an immune response. VACV infection is usually very mild and usually causes no symptoms in healthy individuals, although it may cause rash and fever.
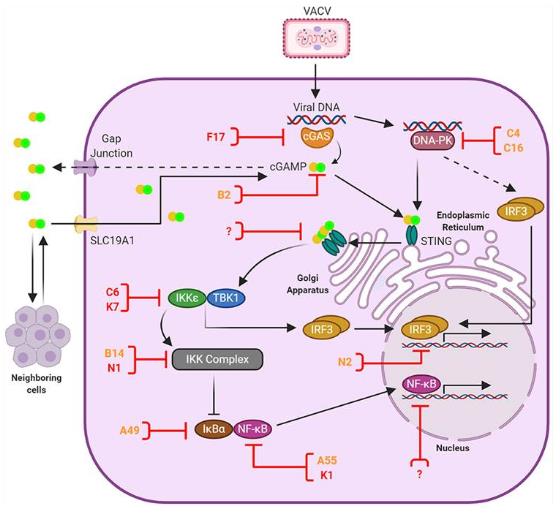 Figure 1. Anti-viral DNA sensing and its antagonism by VACV. (El-Jesr M, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. Anti-viral DNA sensing and its antagonism by VACV. (El-Jesr M, et al., 2020)Main Methods of IVD for Vaccinia Virus
- Antigen testing. VACV has specific antigens, and viral antigens are detected from infected cells or virus particles to determine the infection status.
- Serological testing. Vaccinia virus infection can be indirectly diagnosed by collecting serum samples from infected people and testing for antibodies. The main methods include immunofluorescence, ELISA, WB, etc.
- Nucleic acid amplification testing. The DNA sequence of VACV in the sample is mainly detected by PCR.
- Virus isolation and culture. VACV was inoculated into sensitive cell lines, the pathological characteristics of the cells were observed, and the virus was isolated and identified.
Creative BioMart can provide a range of vaccinia viruses for IVD, including ELISA, lateral flow assays, western blots, and other immunoassays.
Highlights of Our Products
- High sensitivity, high specificity, and high purity.
- Outstanding success rate and fast development speed.
- Completed biological functions and efficient activity.
- A wide range of immune tests are available, such as ELISA, lateral flow, WB, and others.
- Easy to store and transport, conducive to large-scale production and use of vaccines.
Our Outstanding Advantages
- IVD proteins can be used to test for a variety of diseases and conditions, making them valuable tools for diagnosing and monitoring health.
- Guarantee high performance, high reliability, and high consistency of protein quality, leading the industry.
- A complete IVD protein platform can provide customized services to meet different scientific research needs.
- High-quality service, high-level experiments, and reliable analysis.
In addition, Creative BioMart also offers a series of viral proteins and protein-related services to provide customers with high-quality, low-cost active recombinant proteins to meet different needs and assist in preclinical drug development.
Application
1. Vaccine Development:
Smallpox Vaccine: Vaccinia virus was historically used as the immunizing agent in the smallpox vaccine, leading to the eradication of the disease.
Vaccine Vectors: Recombinant vaccinia viruses are used as vectors to develop vaccines against other infectious diseases, such as HIV, influenza, and Ebola. By incorporating genes from these pathogens, they stimulate an immune response without causing the disease.
2. Oncolytic Virotherapy:
Cancer Treatment: Modified vaccinia viruses can selectively infect and destroy cancer cells. They can also be engineered to express therapeutic genes that enhance anti-tumor immune responses.
3. Gene Delivery Systems:
Transgene Expression: Vaccinia virus is engineered to deliver and express foreign genes within host cells. This is useful for both research purposes and potential therapeutic applications, such as gene therapy.
4. Immunotherapy:
Immune Modulation: Certain vaccinia proteins can modulate the immune response. These properties are exploited to enhance the efficacy of vaccines or to modify immune responses in various therapeutic contexts.
5. Molecular Biology and Research Tools:
Protein Expression: Vaccinia virus promoters and other regulatory elements are used in molecular biology for high-level protein expression in mammalian cells.
Study of Host-Pathogen Interactions: VACV proteins are studied to understand viral replication, host immune evasion, and the mechanics of viral life cycles. This can lead to broader insights into virology and host immunity.
6. Bioreactors and Biotechnology:
Protein Production: Recombinant vaccinia virus systems are used to produce proteins of interest in bioreactor settings, aiding in the large-scale production of therapeutic proteins or enzymes.
7. Diagnostic Tools:
Antibody Production: Vaccinia proteins can be used to produce monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies, which are essential for various diagnostic tests and research applications.
Assay Development: Vaccinia virus components can be used in the development of diagnostic assays for detecting viral infections or measuring immune responses.
8. Study of Antiviral Immunity:
Immune Response: The immune response to vaccinia virus infection provides a model for understanding antiviral immunity and for designing better immunotherapeutic interventions.
Case Study
Case 1: Xu L, Sun H, Lemoine NR, Xuan Y, Wang P. Oncolytic vaccinia virus and cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 12;14:1324744. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1324744. PMID: 38283361; PMCID: PMC10811104.
Oncolytic virotherapy (OVT) is a promising form of cancer treatment that uses genetically engineered viruses to replicate within cancer cells and trigger anti-tumor immune response. In addition to killing cancer cells, oncolytic viruses can also remodel the tumor microenvironment and stimulate a long-term anti-tumor immune response. Vaccinia virus (VACV) has emerged as a potential candidate due to its ability to infect a wide range of cancer cells. This review discusses the mechanisms, benefits, and clinical trials of oncolytic VACVs.
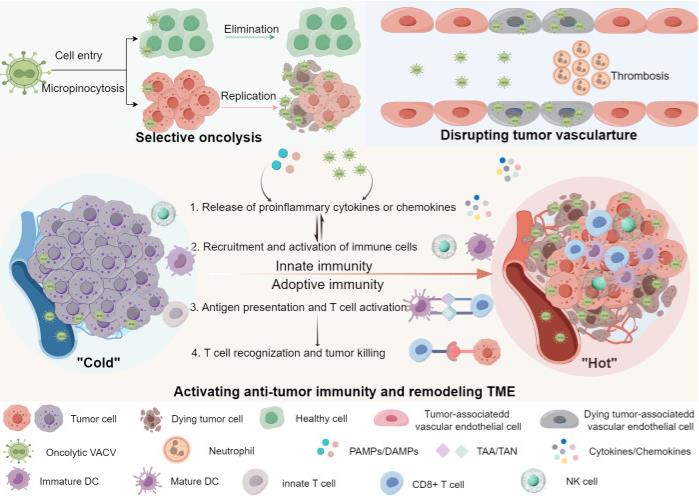 Fig2. Anti-tumor mechanisms of oncolytic VACVs. Oncolytic VACVs can kill cancer cells via a variety of mechanisms. First, they directly infect, replicate and lyse tumor cells sparing normal cells. Released virions can infect neighbor tumor cells and so forth. Second, oncolytic VACVs can infect and lyse tumor associated vascular endothelial cells, meanwhile recruiting neutrophile cells and inducing thrombosis. Third, they can remodel the "cold" TME to "hot" by activating innate and adoptive anti-tumor immunity. The release of progeny viruses and PAMPs/DAMPs can promote the innate immune cells to produce proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which in turn lead to the recruitment and activation of more immune cells, thus innate immune responses are activated. With the activation of antigen presentation cells, DCs can present the released TAA/TAN to T-cells, enhancing the tumor recognition and killing ability of CD8+ T-cells, inducing a tumor-specific adoptive immune response. PAMPs, Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs, Damage-associated molecular pattern; TAA, Tumor-associated antigens; TAN, Tumor-associated neoantigens; DC, Dendritic cell; NK cell, Natural killer cell.
Fig2. Anti-tumor mechanisms of oncolytic VACVs. Oncolytic VACVs can kill cancer cells via a variety of mechanisms. First, they directly infect, replicate and lyse tumor cells sparing normal cells. Released virions can infect neighbor tumor cells and so forth. Second, oncolytic VACVs can infect and lyse tumor associated vascular endothelial cells, meanwhile recruiting neutrophile cells and inducing thrombosis. Third, they can remodel the "cold" TME to "hot" by activating innate and adoptive anti-tumor immunity. The release of progeny viruses and PAMPs/DAMPs can promote the innate immune cells to produce proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which in turn lead to the recruitment and activation of more immune cells, thus innate immune responses are activated. With the activation of antigen presentation cells, DCs can present the released TAA/TAN to T-cells, enhancing the tumor recognition and killing ability of CD8+ T-cells, inducing a tumor-specific adoptive immune response. PAMPs, Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs, Damage-associated molecular pattern; TAA, Tumor-associated antigens; TAN, Tumor-associated neoantigens; DC, Dendritic cell; NK cell, Natural killer cell.Case 2: Zhu J, Gao X, Li Y, Zhang Z, Xie S, Ren S, Li Y, Li H, Niu K, Fu S, Deng Y, Li Y, Moss B, Wu W, Peng C. Human FAM111A inhibits vaccinia virus replication by degrading viral protein I3 and is antagonized by poxvirus host range factor SPI-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 29;120(35):e2304242120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2304242120. Epub 2023 Aug 22. PMID: 37607234; PMCID: PMC10469034.
Vaccinia virus (VACV), the prototypic poxvirus used as the vaccine strain for smallpox eradication, is the best-characterized member of the poxvirus family. VACV encodes a serine protease inhibitor 1 (SPI-1) conserved in all orthopoxviruses, which has been recognized as a host range factor for modified VACV Ankara (MVA), an approved smallpox vaccine and a promising vaccine vector. FAM111A (family with sequence similarity 111 member A), a nuclear protein that regulates host DNA replication, was shown to restrict the replication of a VACV SPI-1 deletion mutant (VACV-ΔSPI-1) in human cells. Nevertheless, the detailed antiviral mechanisms of FAM111A were unresolved. Here, the authors show that FAM111A is a potent restriction factor for VACV-ΔSPI-1 and MVA. Their findings reveal the detailed mechanism by which FAM111A inhibits VACV and provide explanations for the immune evasive function of VACV SPI-1.
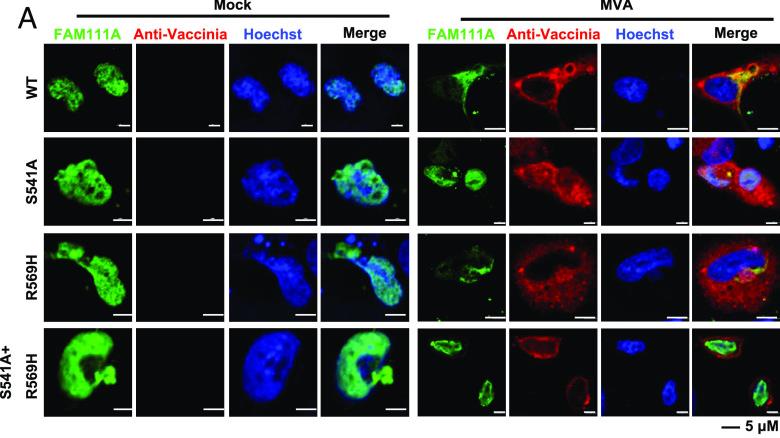 Fig3. MVA infection prompts protease-dependent relocalization of FAM111A. (A and B) Human A549 cells plated on coverslips were transfected with FAM111AWT, FAM111AS541A, FAM111AR569H, or FAM111AS541A+R569H for 24 h and then infected with MVA at 3 PFU/cell. After 12 h, cells were fixed, permeabilized, blocked, and stained with primary antibodies to FAM111A and rabbit antiserum to VACV followed by fluorescent conjugated secondary antibodies. Hoechst was used to stain DNA (A).
Fig3. MVA infection prompts protease-dependent relocalization of FAM111A. (A and B) Human A549 cells plated on coverslips were transfected with FAM111AWT, FAM111AS541A, FAM111AR569H, or FAM111AS541A+R569H for 24 h and then infected with MVA at 3 PFU/cell. After 12 h, cells were fixed, permeabilized, blocked, and stained with primary antibodies to FAM111A and rabbit antiserum to VACV followed by fluorescent conjugated secondary antibodies. Hoechst was used to stain DNA (A).Case 3: Hou F, Zhang Y, Liu X, Murad YM, Xu J, Yu Z, Hua X, Song Y, Ding J, Huang H, Zhao R, Jia W, Yang X. mRNA vaccines encoding fusion proteins of monkeypox virus antigens protect mice from vaccinia virus challenge. Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 22;14(1):5925. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41628-5. PMID: 37739969; PMCID: PMC10516993.
mRNA vaccines, which have shown high efficacy and safety against SARS-CoV-2 infection, are a promising alternative. In this study, three mRNA vaccines are developed that encode monkeypox virus (MPXV) proteins A35R and M1R, including A35R extracellular domain -M1R fusions (VGPox 1 and VGPox 2) and a mixture of encapsulated full-length mRNAs for A35R and M1R (VGPox 3). all three mRNA vaccine groups completely protect mice from a lethal dose of vaccinia virus (VACV) challenge. These results suggest that the VGPox series vaccines enhance immunogenicity and can be a viable alternative to current whole-virus vaccines to defend against mpox.
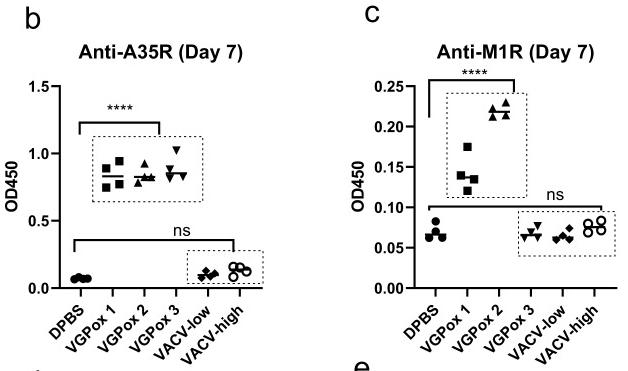 Fig4. Single-dose vaccination, immune responses, and virus challenge. b Anti-A35R and c anti-M1R antibody levels were analyzed by ELISA. All serum samples were diluted 1 in 20. n = 4 biologically independent mice.
Fig4. Single-dose vaccination, immune responses, and virus challenge. b Anti-A35R and c anti-M1R antibody levels were analyzed by ELISA. All serum samples were diluted 1 in 20. n = 4 biologically independent mice.Reference
- El-Jesr M, Teir M, Maluquer de Motes C. (2020). Vaccinia virus activation and antagonism of cytosolic DNA sensing[J]. Frontiers in Immunology. 11: 568412.