What is CD40LG Protein?
The CD40LG protein, otherwise known as Cluster of Differentiation 40 Ligand, is a critical component of the immune system. This protein, encoded by the CD40LG gene, is amongst the numerous extracellular factors that regulate the immune response. It is mainly expressed on the surface of T cells and is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily.
Background and Discovery of CD40LG Protein
The observation of CD40LG protein transpired in the early 1990s. The discovery was made during studies aimed at understanding the nature of helper T cells' interaction with B cells. Scientists detected that the membrane-bound molecule, which was initially known as gp39 and later renamed CD40LG, was central to the delivery of "help" from T cells to B cells. The gene encoding the CD40LG protein is located on the X-chromosome, at locus Xq26.
What Is The Structure of CD40LG Protein?
The structure of the CD40LG protein is similar to that of other TNF superfamily members. It comprises a 'TNF homology domain' identified by two antiparallel β-pleated sheets, a stalk region, and a transmembrane domain that anchors the protein to the cell membrane.
What Is The Function of CD40LG Protein?
CD40LG plays a pivotal role in orchestrating immune responses. It binds to the CD40 receptor predominantly found on antigen-presenting cells (such as B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages) enabling their interaction with CD40LG expressing cells (like activated T cells or natural killer cells). This interaction initiates various signaling pathways that regulate the growth, activation, differentiation, and survival of these immune cells. Its expression consequently leads to the production of antibodies and memory B cells by B cells, the activation of cytotoxic T cells, and the inflammasome activation in dendritic cells and macrophages, which release proinflammatory cytokines.
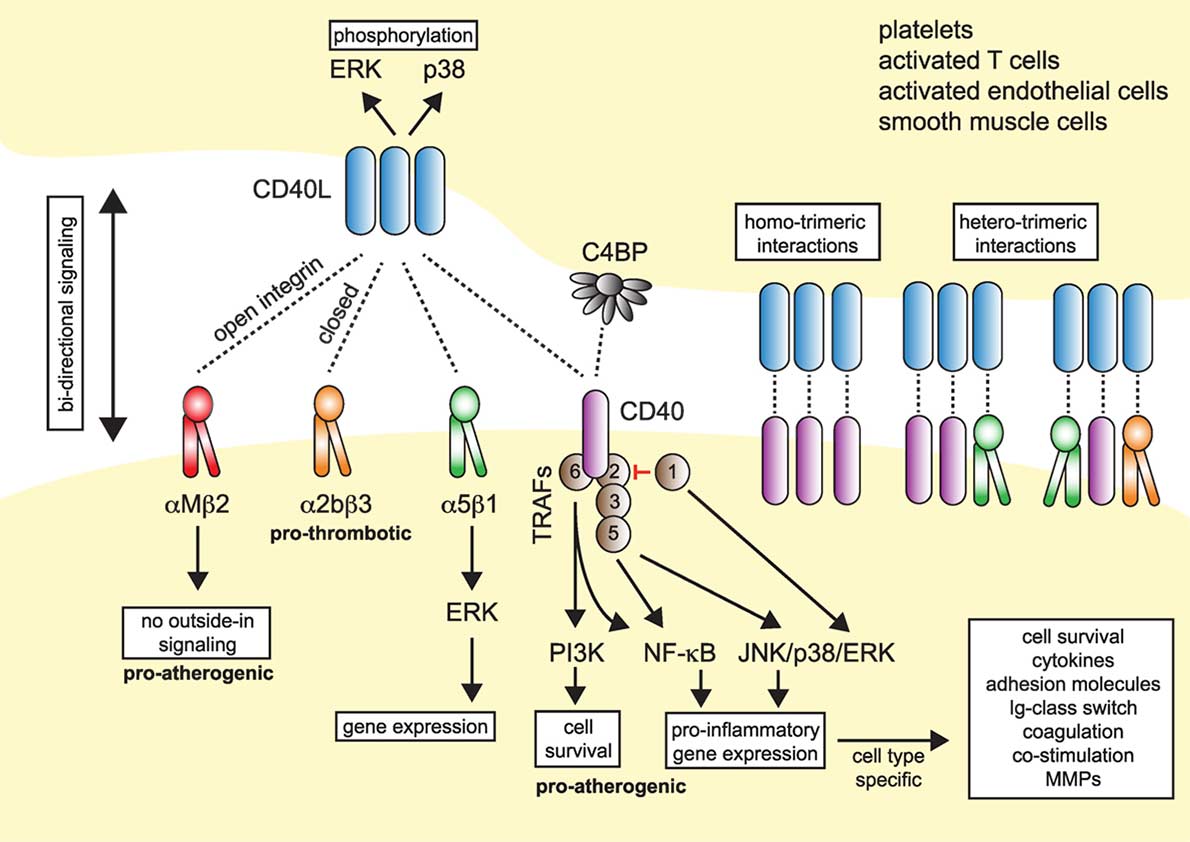
Fig1. CD40L and Its Receptors
CD40LG protein related diseases
Disruptions in this receptor-ligand system have been implicated in several diseases. For instance, mutations in the CD40LG gene are associated with Hyper IgM Syndrome (HIGM), a rare primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a severe reduction in IgG antibodies and an excessive production of IgM antibodies, resulting in severe infections. Besides, abnormal CD40LG expression has been reported in multiple autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and in certain cancers. High levels of soluble CD40LG have been observed in the blood and tumors of cancer patients, often associated with poor prognosis.
CD40LG protein's applications in biomedical
In addition to its role in health and disease, the CD40LG protein holds a vast potential for therapeutic applications. Given its significant role in the immune response, manipulating the CD40-CD40L interaction is an emerging strategy in combating diseases. In cancer therapeutics, CD40 agonists, which are drugs that stimulate the CD40 receptor, are being explored for their capacity to enhance anti-tumor immunity.
Moreover, inhibition of CD40LG has also shown promise in ameliorating autoimmune diseases. Several experimental therapeutics, such as monoclonal antibodies targeting CD40L, are under development and have demonstrated promising results in early-phase clinical trials to treat SLE and prevent organ transplant rejection.
Additionally, in the treatment of HIGM syndrome caused by CD40LG mutations, gene therapy is being studied as a potential option. This approach involves the insertion of a correct copy of the CD40LG gene into patients' cells, compensating for the defective gene and leading to functional protein expression.
In conclusion, the CD40LG protein is critically vital for immune regulation. Any aberrations in its expression or function can gravely impact immune responses, resulting in severe disease states. Given its central role in immunity, it offers a promising target for developing novel therapeutic strategies for several diseases, particularly those of immune origin. Current biomedical research dedicated to understanding CD40LG protein better and harnessing its potential could further contribute to breakthroughs in medical science. Despite the challenges, the prospect of improving and saving lives makes studying CD40LG worthwhile for the biomedical community.
Our Featured Products
Reference
- Michel, N. A., Zirlik, A., & Wolf, D. (2017). CD40L and Its Receptors in Atherothrombosis—An Update. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 4, 268622. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2017.00040

