What is HBSAG Protein
The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBSAG) protein, a glycoprotein prominently displayed on the surface of the Hepatitis B virus (HBV), has emerged as a focal point in both virology and biomedical research.
What is HBSAG Protein?
HBSAG, an integral component of the HBV, is a glycoprotein characterized by a unique structural arrangement. The protein's glycosylation plays a pivotal role in its function, contributing to its antigenic properties. Understanding the molecular architecture of HBSAG is fundamental to unraveling its multifaceted roles within the context of viral infection and host interactions.
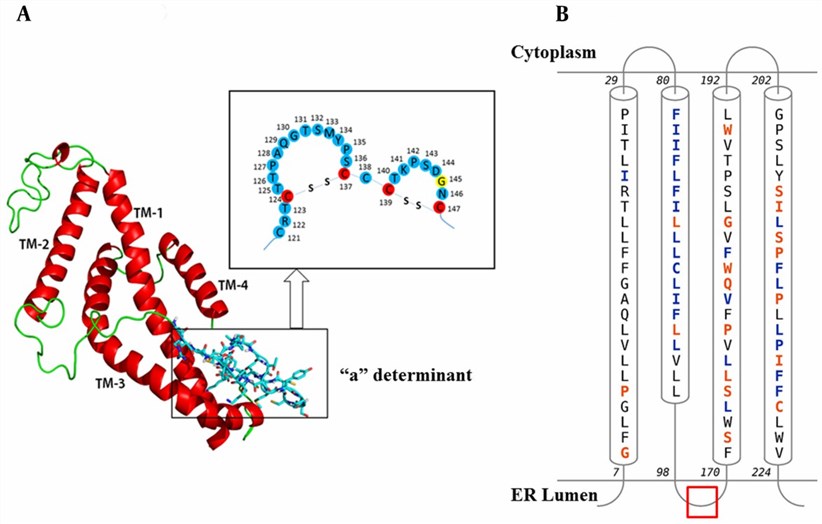
Figure 1. Predicted 3D structure of HBsAg with schematic representation of the "a" determining region and topology of the HBsAg helices within the ER Membrane. (Rezaee, R., et al. 2016)
The Function of HBSAG Protein
HBSAG's primary function is deeply intertwined with the Hepatitis B virus's survival and propagation strategies. Acting as a key player in viral entry, HBSAG facilitates the interaction between the virus and host cell receptors. Once inside the host cell, HBSAG takes center stage in orchestrating the assembly and release of new viral particles, a critical aspect of the viral life cycle.
Beyond facilitating infection, HBSAG exhibits a strategic role in immune evasion. By masking the virus from the host immune system, HBSAG contributes to the establishment of chronic Hepatitis B infections. This evasion mechanism underscores the protein's significance in the long-term health complications associated with persistent viral presence.
HBSAG-Related Diseases
The correlation between HBSAG and Hepatitis B infection is well-established, with chronic infections posing severe risks to liver health. Prolonged exposure to HBSAG in the bloodstream can lead to chronic Hepatitis B, culminating in liver damage, cirrhosis, and an elevated risk of liver cancer. Moreover, HBSAG has been implicated in immune-mediated disorders, such as membranous glomerulonephritis, further highlighting the protein's impact on various physiological systems.
HBSAG Related Signaling Pathways
Examining the signal pathways associated with HBSAG sheds light on the intricate mechanisms governing viral entry and host response. HBSAG recognition by specific receptors on the host cell surface initiates a cascade of events, facilitating viral entry. Additionally, HBSAG manipulates host cell pathways to promote viral replication, showcasing the virus's sophisticated strategies for survival within the host organism.
Ongoing research is unraveling the complexities of HBSAG-related signal pathways, offering potential targets for therapeutic intervention. The identification and modulation of these pathways present promising avenues for the development of antiviral drugs, aiming to disrupt viral replication and enhance the host's immune response.
Applications of HBSAG in Biomedical Research
- Diagnostic Tools
HBSAG's significance extends beyond the realm of virology, finding practical applications in diagnostics. The detection of HBSAG in blood serum serves as a primary indicator of active Hepatitis B replication. Rapid tests and ELISAs targeting HBSAG have become indispensable tools for clinicians, enabling timely and accurate diagnosis of Hepatitis B infections.
- Vaccine Development
In a testament to its versatility, HBSAG has become a cornerstone in the development of Hepatitis B vaccines. Recombinant HBSAG, produced through genetic engineering, forms the core component of these vaccines. The exposure to a harmless form of HBSAG stimulates antibody production, providing immunity against future Hepatitis B virus exposure.
- Therapeutic Approaches
Research endeavors are underway to exploit HBSAG as a therapeutic target for chronic Hepatitis B infections. Inhibitors and modulators targeting HBSAG-related signal pathways are being investigated, holding promise for disrupting viral replication and bolstering the host immune response. While in early stages, these approaches represent a frontier in antiviral therapy development.
- Insights into Host-Pathogen Interactions
The study of HBSAG provides invaluable insights into the intricate interplay between viruses and host cells. The unraveling of molecular mechanisms governing HBSAG interactions informs broader antiviral strategies and enhances our comprehension of viral pathogenesis.
As research endeavors continue, the potential applications of HBSAG in biomedical science remain dynamic, holding promise for innovative solutions in the realms of diagnostics, vaccines, and antiviral therapies.
Recommended Products for HBSAG Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg-258H | HBV | Active Recombinant HBsAg | Yeast | N/A |
| HBsAg-255H | HBV | Recombinant HBsAg | P.pastoris | N/A |
| HBsAg-253H | HBV | Recombinant HBsAg | CHO | N/A |
| HBsAg-270H | HBV | Recombinant HBsAg | E.coli | N/A |
| HBsAg-256H | HBV | Recombinant HBsAg | S.cerevisiae | N/A |
| HBsAg-271H | HBV | Recombinant HBsAg | E.coli | N/A |
| HBsAg-263H | HBV | Recombinant HBsAg | P.pastoris | N/A |
| HBsAg-254H | HBV | Recombinant HBV HBsAg protein | Yeast | N/A |
| HBsAg-268H | HBV | Recombinant HBsAg | S.cerevisiae | N/A |
| HBsAg-267H | HBV | Recombinant HBsAg, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
Reference
- Rezaee, R., et al. Impacts of the G145R Mutation on the Structure and Immunogenic Activity of the Hepatitis B Surface Antigen: A Computational Analysis. Hepat Mon. 2016, 16(7): e39097.

