What is MAPT Protein
Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) stands as a linchpin in cellular biology, orchestrating a symphony of functions within the neurons of the central nervous system.
What is MAPT Protein?
MAPT, encoded by the MAPT gene on chromosome 17, exhibits a sophisticated structure with distinct domains. Its N-terminal projection domain, proline-rich region, and C-terminal microtubule-binding domain collectively orchestrate its pivotal functions.
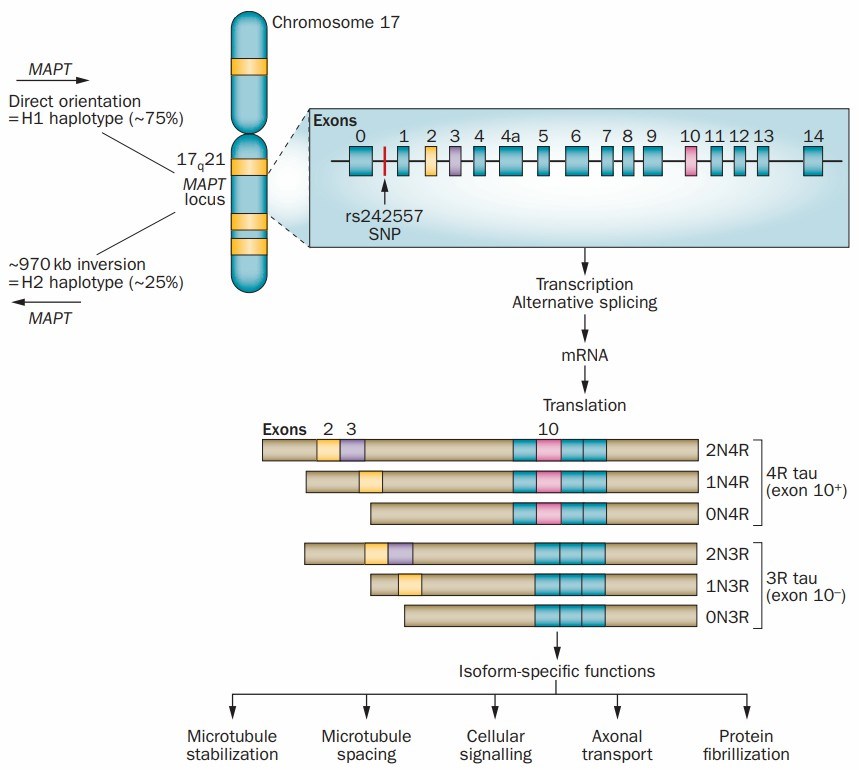
Figure 1. The MAPT gene locus and the tau protein isoforms. (Wade-Martins, R. 2012)
The Function of MAPT Protein
- Microtubule Stabilization
MAPT's primary responsibility is the stabilization of microtubules, the dynamic components of the cytoskeleton. By binding to microtubules, MAPT ensures their proper assembly and disassembly, thereby upholding the structural integrity of cells.
- Axonal Transport
In the intricate network of neurons, MAPT facilitates axonal transport, ensuring the seamless movement of cellular materials along neuronal axons. This function is indispensable for neuronal communication and overall cellular homeostasis.
- Synaptic Plasticity
MAPT's involvement in synaptic plasticity underscores its role in the dynamic modulation of synapses, a crucial aspect of learning and memory processes within the nervous system.
MAPT-Related Diseases
Abnormalities in MAPT pave the way for a spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases collectively known as tauopathies. The most prominent among them is Alzheimer's disease, where the aggregation of MAPT into neurofibrillary tangles is a hallmark pathology.
- Alzheimer's Disease
In Alzheimer's, MAPT undergoes aberrant post-translational modifications, leading to the formation of insoluble tau aggregates. These aggregates disrupt microtubule function, contributing significantly to neurodegeneration and cognitive decline.
- Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
Distinct mutations in the MAPT gene are linked to familial forms of FTD, another tauopathy marked by abnormal tau accumulation in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
- Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) and Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD)
Tauopathies like PSP and CBD exhibit specific regional accumulations of abnormal tau, resulting in motor and cognitive impairments.
MAPT Related Signaling Pathways
Understanding the molecular intricacies of MAPT necessitates a glimpse into the associated signal pathways that regulate its functions and dysregulation in diseases.
- Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) Pathway
GSK-3, a pivotal kinase, phosphorylates MAPT, influencing its microtubule-binding capability. Dysregulation of this pathway is implicated in the hyperphosphorylation of MAPT observed in Alzheimer's disease.
- Cdk5 Pathway
The Cdk5-MAPT pathway, involving cyclin-dependent kinase 5, is crucial for proper neuronal function. Dysregulation of this pathway has been linked to neurodegenerative disorders, emphasizing the delicate balance required for neuronal health.
Applications of MAPT in Biomedical Research
Beyond its implications in disease pathology, MAPT holds promising applications in the domain of biomedical research, opening avenues for diagnostics and therapeutics.
- Biomarker for Neurodegenerative Diseases
MAPT emerges as a potential biomarker for neurodegenerative diseases, with abnormal levels or post-translational modifications serving as indicators in cerebrospinal fluid or blood.
- Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease
Ongoing efforts focus on developing interventions targeting MAPT to disrupt the formation of pathological tau aggregates in Alzheimer's disease. Small molecules, antibodies, and gene therapies are under exploration to modulate MAPT function.
- Neuroprotective Strategies
Leveraging MAPT's role in maintaining neuronal structure, researchers are exploring neuroprotective strategies. Enhancing MAPT stability or promoting its normal function offers promising therapeutic avenues for neurodegenerative disorders.
MAPT, with its pivotal role in microtubule stabilization and neuronal functions, stands as a critical player in cellular biology. As we delve deeper into its intricacies, the potential for targeted interventions in neurodegenerative disorders becomes increasingly apparent. The journey from understanding MAPT's structure and functions to unraveling its involvement in diseases and harnessing its potential in biomedical applications is a testament to the relentless pursuit of knowledge in the realm of cellular biology.
Recommended Products for MAPT Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAPT-2874H | Human | Recombinant Human MAPT, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| MAPT-30090TH | Human | Recombinant Human MAPT | E.coli | N/A |
| MAPT-528H | Human | Recombinant Human MAPT, His tagged | E.coli | His |
| MAPT-21H | Human | Recombinant Human MAPT protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| MAPT-4220HFL | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human MAPT protein, Flag-tagged | Mamanlian cells | Flag |
| MAPT-39H | Human | Recombinant Human MAPT Protein (216-391), N-AVI-tagged, Biotinylated | E.coli | N-AVI |
| Mapt-20M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Mapt protein, His-tagged | Yeast | His |
| Mapt-3953M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Mapt Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| Mapt-2062R | Rat | Recombinant Rat Mapt protein, His & T7-tagged | E.coli | His/T7 |
| MAPT-01C | Cynomolgus | Recombinant Cynomolgus MAPT Protein, His tagged | E.coli | C-His |
Reference
- Wade-Martins, R. The MAPT locus—a genetic paradigm in disease susceptibility. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012, 8: 477–478.

