MAPT
-
Official Full Name
microtubule-associated protein tau -
Overview
This gene encodes the microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) whose transcript undergoes complex, regulated alternative splicing, giving rise to several mRNA species. MAPT transcripts are differentially expressed in the nervous system, depending on stage of neuronal maturation and neuron type. MAPT gene mutations have been associated with several neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimers disease, Picks disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MAPT;microtubule-associated protein tau;TAU;MSTD;PPND;DDPAC;MAPTL;MTBT1;MTBT2;FTDP-17;PHF-tau;paired helical filament-tau;neurofibrillary tangle protein;microtubule-associated protein tau, isoform 4;G protein beta1/gamma2 subunit-interacting factor 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Rat
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Drosophila melanogaster
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Rabbit
- Mouse
- Yeast
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- Non
- His
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Flag
- mCherry
- SUMO
- GST
Background
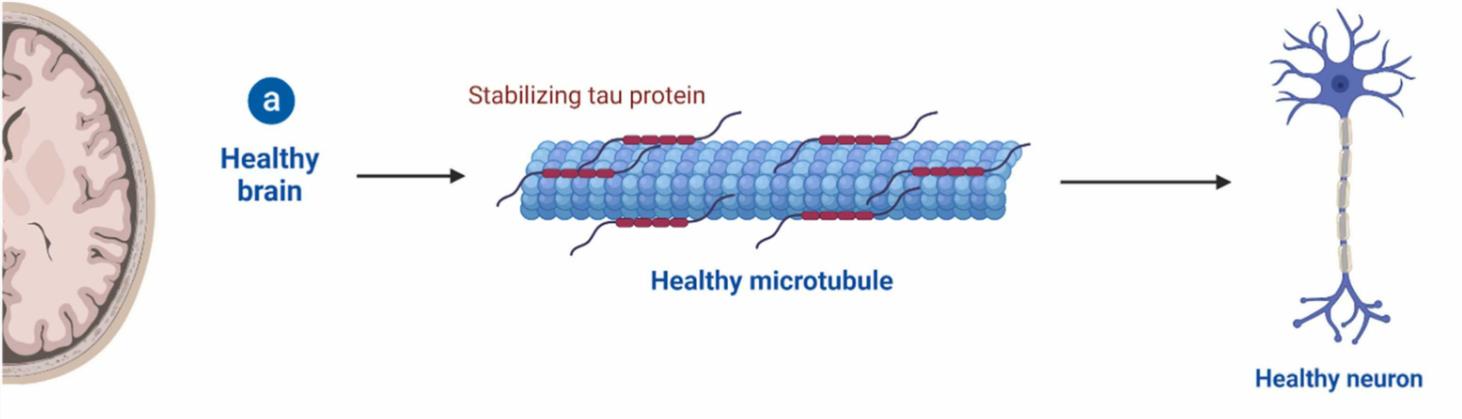
Fig1. Schematic representation of the activity of tau in physiological conditions. (Veera Raghavulu Bitra, 2023)
What is MAPT protein?
MAPT gene (microtubule associated protein tau) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q21. This gene encodes the microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) whose transcript undergoes complex, regulated alternative splicing, giving rise to several mRNA species. MAPT transcripts are differentially expressed in the nervous system, depending on stage of neuronal maturation and neuron type. MAPT gene mutations have been associated with several neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. The MAPT protein is consisted of 758 amino acids and MAPT molecular weight is approximately 78.9 kDa.
What is the function of MAPT protein?
The microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) is a protein that plays a critical role in the nervous system. It is primarily known for its function in binding to and stabilizing microtubules, which are essential for maintaining the structure of neurons and for axonal transport. Abnormalities in MAPT, such as hyperphosphorylation of tau, are associated with the formation of neurofibrillary tangles seen in Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies, leading to neurodegeneration. Mutations in the MAPT gene can result in frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17), further illustrating the protein's importance in maintaining neuronal health.
MAPT related signaling pathway
The protein tau, encoded by the MAPT gene, is essential for stabilizing microtubules in neurons, which are vital for maintaining cell shape and supporting intracellular transport. When tau functions normally, it contributes to the assembly and stability of microtubules, but when it becomes abnormally phosphorylated or misfolded, it can clump together to form neurofibrillary tangles, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies such as frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Mutations in the MAPT gene can lead to these tauopathies, highlighting the importance of tau's normal function for neuronal health.
MAPT related diseases
The protein tau, encoded by the MAPT gene, is a key player in neurodegenerative diseases. It is primarily known for its role in stabilizing microtubules and facilitating axonal transport, which are essential for maintaining neuronal integrity and function. Abnormalities in tau, including hyperphosphorylation and aggregation, are hallmarks of a group of diseases called tauopathies. These include Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), Pick's disease (PiD), and chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Mutations in the MAPT gene can lead to these tauopathies, and research is exploring the potential for tau-directed therapies to treat such conditions.
Bioapplications of MAPT
The microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) is central to several bioapplications, particularly in neurodegenerative disease research. Mutations in the MAPT gene are known to cause frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17), and it is associated with a range of tauopathies, including Alzheimer's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), and Pick's disease (PiD). Research is exploring the use of MAPT as a therapeutic target and the development of inhibitors to counteract tau aggregation and neurodegeneration. Furthermore, MAPT gene expression and tau protein levels are being investigated as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and tracking the progression of these diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ethan D Smith, 2023
This study on tau inclusions in tauopathy patients, using samples from Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP), investigates how phosphorylation affects tau seeding. Here mutating certain sites in the R1-R2 repeat domain, specifically Ser262/Thr263/Ser289/Ser305, to Glu reduced AD-tau seeding efficiency but not PSP-tau. This mutation led to less phosphorylation on key epitopes, suggesting a role for inter-domain cooperativity. Notably, Ser305 emerged as a key regulator of AD-tau seeding, with its phosphorylation potentially influencing disease-specific tau strain formation.
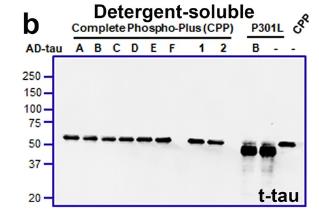
Fig1. Representative immunoblot of the Complete Phospho-Plus (CPP) construct.
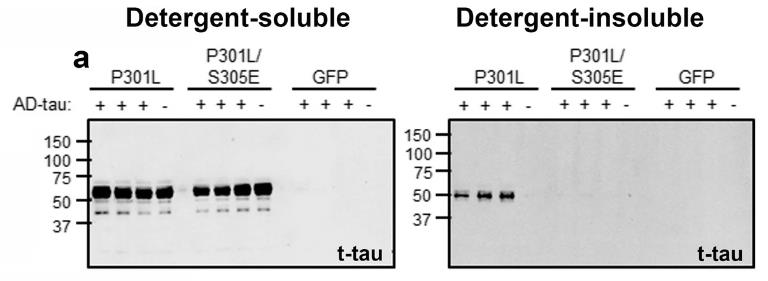
Fig2. Phospho-Plus mutation on Ser305 abrogate seeding by AD-tau.
Case Study 2: Pijush Chakraborty, 2023
This research reveals that tau protein aggregation, a key feature of Alzheimer's and other tauopathies, is influenced by isoform-specific acetylation. Here acetylation reduces aggregation in four-repeat tau but enhances amyloid formation in three-repeat tau. Notably, acetylation at lysine 298 is a key modulator of this isoform-specific aggregation. Structural analysis using solid-state NMR spectroscopy shows that unmodified and acetylated three-repeat tau form different amyloid structures, suggesting that acetylation is a crucial factor in the selective aggregation of three-repeat tau and the development of related neurodegenerative diseases.
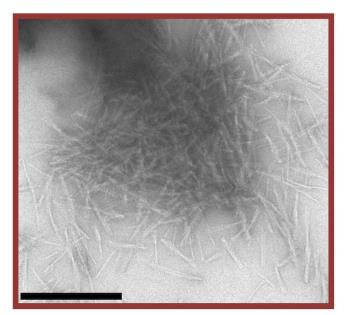
Fig3. Negative-stain electron micrographs of 3R tau fibrils.
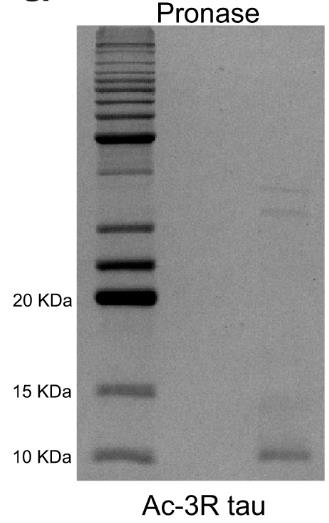
Fig4. SDS-PAGE gel of pronase-digested acetylated 3R tau fibrils.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MAPT-516H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MAPT-51H)
Involved Pathway
MAPT involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MAPT participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Alzheimers disease, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MAPT were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | CASP3A,DUSP3,PLA2G4D,GADD45BB,MAP2K7,RAC3A,MEF2C,MAPK13,MAPK11,FLNA |
| Alzheimers disease | CALM1,COX6B1,SDHC,CAPN2,NDUFC2,IL1B,NDUFS6,CHP,COX7B2,FAS |
Protein Function
MAPT has several biochemical functions, for example, SH3 domain binding,apolipoprotein binding,enzyme binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MAPT itself. We selected most functions MAPT had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MAPT. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| microtubule binding | KLC3,CEP57L1,NME8,MAP2,KIF5B,MAP1LC3B,KIF2A,MID1,MTAP1B,SYBU |
| SH3 domain binding | SH3BGR,ERRFI1,MICAL1,SOS1,ELMO2,SKAP1,DPYSL3,NOXA1,EFS,WAS |
| lipoprotein particle binding | GPIHBP1,APOE,CDH13 |
| enzyme binding | EGFR,PPP1R3B,LGALS9,BRCA1,EIF4E,PTEN,PIAS1,NPM2,MTA1,H2AFX |
| protein binding | CUL4B,STAU2,TOP1,CEP76,TFIP11,HNF1A,MME,CCDC47,PPIA,MCM10 |
| protein phosphatase 2A binding | ENSA,TP53,ARPP19,PTPN1,GRIN3A,CTTNBP2NL,IGBP1,CPD,EIF4EBP1,PPME1 |
| structural constituent of cytoskeleton | TUBA2,YEATS4,TUBGCP5,TUBB2A,DMD,ADD3,TUBA3C,KRT5,KRT71,SORBS3 |
| apolipoprotein binding | SCARB1,LIPC,PLG,VLDLR,LRP1,LPL,CANX,PCSK9,LPA,LRP6 |
| protein kinase binding | TOM1L1,NPM1,TPX2,DNM2,CD8A,GHR,EEF1A1,AXIN1,LAT,PGAM1 |
Interacting Protein
MAPT has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MAPT here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MAPT.
YWHAZ;APP;MARK2;APOE
Resources
-

Unraveling the Mysteries of Tau Protein: Key to Brain Health
-
Tau Protein: The Key to Understanding Alzheimer's
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Xu, H; Rosler, TW; et al. Memory deficits correlate with tau and spine pathology in P301S MAPT transgenic mice. NEUROPATHOLOGY AND APPLIED NEUROBIOLOGY 40:833-843(2014).
- Karageorgiou, E; Miller, BL; et al. Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: A Clinical Approach. SEMINARS IN NEUROLOGY 34:189-201(2014).



