What is OGG1 Protein
The OGG1 protein, officially known as 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1, is a key player in the realm of genomic maintenance. Also recognized by its synonyms such as hOGG1 (human OGG1) and MUTM (MutT homolog), this protein belongs to the family of DNA glycosylases, specifically involved in base excision repair (BER). Structurally, OGG1 harbors an N-terminal proline-rich domain, a central glycosylase domain, and a C-terminal alpha-helical domain, collectively orchestrating its intricate functions.
Recent strides in research have shed light on OGG1's pivotal role in maintaining genomic stability. Scientists have delved deeper into its structural characteristics and classification within the glycosylase family, unraveling the molecular intricacies that underscore its significance.
OGG1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
OGG1 functions as a guardian of genomic integrity. Its primary task is to rectify the DNA damage caused by 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG), a common oxidative lesion. The meticulous process involves recognizing and excising the damaged base, ensuring the subsequent repair of the DNA strand.
Molecular mechanisms governing OGG1's prowess in this repair process involve its interaction with other key players in BER. OGG1 collaborates with downstream enzymes, including apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) and DNA polymerase beta, forming a harmonious ensemble that orchestrates the restoration of the damaged DNA strand.
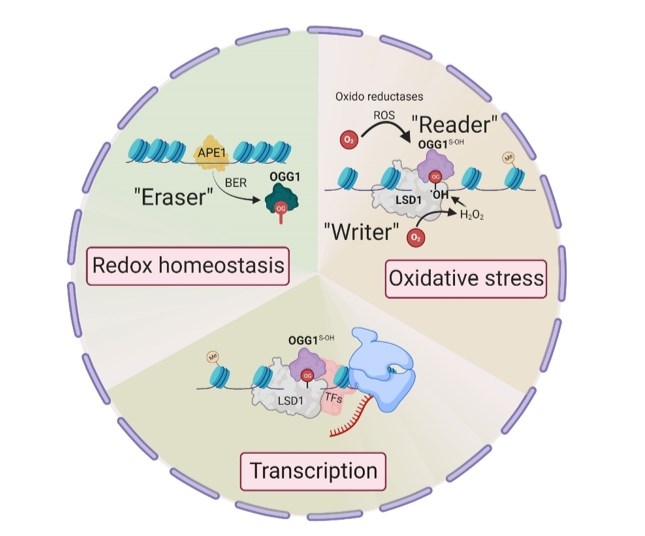
Figure 1. Epigenetic changes in OGG1 dependent gene expression. (Pan L, et al., 2023)
OGG1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signal pathway associated with OGG1 revolves around the intricate dance of molecular signals orchestrating DNA repair. OGG1's involvement in the base excision repair pathway is finely regulated, ensuring timely and accurate responses to DNA damage. The coordination with other proteins, such as APE1 and DNA ligase, adds layers of complexity to the signal pathway, underscoring the meticulous orchestration required for effective genomic maintenance.
OGG1 Related Diseases
The perturbation in OGG1's function is linked to various diseases, marking its significance in human health. Research has illuminated the association between OGG1 polymorphisms and increased susceptibility to cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding these genetic implications not only provides insights into disease etiology but also opens avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions.
OGG1's Applications in Biomedicine
Beyond its fundamental role in DNA repair, OGG1 has found practical applications in biomedical domains. Its utility extends to diagnostic development, where OGG1 polymorphisms serve as potential biomarkers for disease susceptibility. In vaccine development, insights into OGG1's role in genomic stability contribute to the design of targeted vaccines, harnessing the body's immune response for disease prevention.
In the realm of therapeutics, the understanding of OGG1's function opens avenues for novel treatment strategies. Targeting OGG1-related pathways presents a promising approach in combating diseases associated with genomic instability, providing a molecularly precise route for therapeutic interventions.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OGG1-783H | Recombinant Human 8-oxoguanine DNA Glycosylase, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| OGG1-1447H | Recombinant Human OGG1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| OGG1-108H | Recombinant Human OGG1 Protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| OGG1-1448H | Recombinant Human OGG1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E. coli | His |
| OGG1-1846H | Recombinant Human OGG1 Protein (1-345 aa), His-tagged | Human | Yeast | His |
| OGG1-3303H | Recombinant Human OGG1 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | Human | E.coli | His-SUMO |
| OGG1-2119H | Recombinant Human OGG1 Protein (Met1-Gly345), N-GST tagged | Human | E.coli | N-GST |
| OGG1-238H | Recombinant Human OGG1 Protein (Met1-Gly345), C-His tagged, Animal-free, Carrier-free | Human | E.coli | C-His |
| OGG1-4762H | Recombinant Human OGG1 Protein (Ser31-Gly345), His tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| OGG1-4763H | Recombinant Human OGG1 Protein (Ser31-Gly345), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
Reference
- Pan L, et al. Substrate-specific binding of 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1) reprograms mucosal adaptations to chronic airway injury. Frontiers in Immunology. 2023, 14.

