What is PFN1 Protein
PFN1, officially known as Profilin 1, is a vital protein playing a pivotal role in cellular dynamics. This protein, also recognized under the synonyms PFL, PFD, and Profilin I, belongs to the profilin family. Profilins are a group of small actin-binding proteins, crucial for regulating the dynamics of the cellular cytoskeleton. The structural characteristics of PFN1 include a globular shape and a molecular weight of approximately 15 kDa. In terms of classification, PFN1 is a member of the profilin family, alongside PFN2 and PFN3.
Recent research advances in the field of molecular biology have shed light on PFN1's multifaceted roles. Studies have elucidated its involvement in diverse cellular processes, ranging from cell motility and cytokinesis to endocytosis and membrane trafficking.
PFN1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of PFN1 are intricately woven into the fabric of cellular activities. At its core, PFN1 is a regulator of actin dynamics. It binds to monomeric actin, modulating its polymerization and depolymerization, which, in turn, influences cellular processes requiring cytoskeletal rearrangements.
Furthermore, PFN1 is implicated in the regulation of cell motility. By influencing actin filament assembly, it plays a crucial role in cell migration and invasion. PFN1's involvement in cytokinesis is also noteworthy, contributing to the successful completion of cell division.
At the molecular level, PFN1 interacts with various cellular proteins, including formins and VASP (Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein). These interactions further underscore its role in shaping the cellular cytoskeleton and influencing processes like cell adhesion and membrane trafficking.
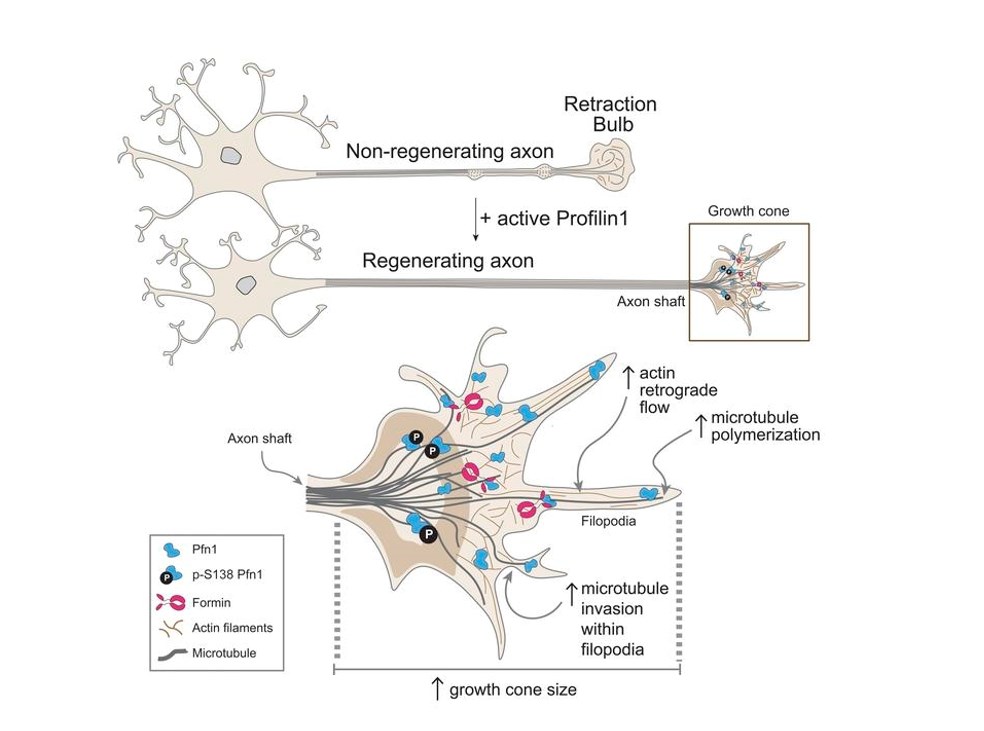
Figure 1. Profilin 1 delivery tunes cytoskeletal dynamics toward CNS axon regeneration. (Pinto-Costa R, et al., 2020)
PFN1 Related Signaling Pathway
PFN1's influence extends to signal pathways crucial for cellular communication. It is intricately involved in the regulation of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, which plays a central role in cell survival, growth, and metabolism. PFN1's impact on this pathway further emphasizes its importance in cellular physiology and its potential as a therapeutic target in diseases where PI3K-Akt signaling is dysregulated.
PFN1 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of PFN1 has been linked to several diseases, highlighting its significance in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a neurodegenerative disorder, is one such condition associated with PFN1 mutations. Research suggests that altered PFN1 function contributes to the pathogenesis of ALS, emphasizing its role in maintaining the health of motor neurons.
PFN1's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of PFN1 have paved the way for its applications in various biomedical domains. In diagnostic development, PFN1 has emerged as a potential biomarker for certain diseases. Its altered expression in conditions such as ALS makes it a promising candidate for diagnostic assays aimed at early disease detection.
Moreover, PFN1 holds promise in vaccine development. As a protein involved in cellular processes critical for pathogen invasion, understanding its interactions with pathogens could inform the design of vaccines that target these interactions, bolstering the immune response.In the realm of therapeutics, researchers are exploring PFN1 as a potential target for drug development. Modulating PFN1 activity could offer a novel approach for treating diseases associated with cytoskeletal dysregulation, such as ALS. Efforts are underway to design small molecules that selectively influence PFN1 function, opening new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFN1-1658H | Recombinant Human PFN1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| PFN1-234H | Recombinant Human PFN1 protein, T7/His-tagged | Human | E.coli | T7/His |
| PFN1-1655H | Recombinant Human PFN1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| PFN1-884H | Recombinant Human PFN1 Protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| PFN1-429H | Recombinant Human PFN1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PFN1-624HFL | Active Recombinant Full Length Human PFN1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| PFN1-3109H | Recombinant Human PFN1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| PFN1-3332H | Recombinant Human PFN1 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| PFN1-90H | Recombinant Human PFN1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PFN1-01H | Recombinant Human PFN1 Protein (mutant C71G) | Human | E.coli |
Reference
- Pinto-Costa R, et al. Profilin 1 delivery tunes cytoskeletal dynamics toward CNS axon regeneration. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2020, 130(4): 2024-2040.

