What is PTPN11 Protein?
Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase, Nonreceptor type 11 (PTPN11), popularly known as SHP-2 (Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2), is an enzyme-encoding gene that plays a vital role in many biological processes. It is a critical hub for signal transduction networks that coordinate myriad cellular processes, encompassing cell survival, proliferation, migration and differentiation.
Discovery and Background
The PTPN11 gene was first recognized in the 1980s using molecular cloning techniques to investigate the Rous sarcoma virus, whose transforming gene was a protein tyrosine kinase (PTK). On analyzing the structure closely, the scientists discovered a novel protein phosphatase containing two SH2 domains - SHP-2 - now known as PTPN11. Thus, PTPN11 became the very first identified non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase, marking a significant breakthrough in understanding crucial cellular functions and molecular mechanisms.
Gene Locus and Protein Structure
PTPN11 gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 12, precisely at position 24.13. The approximate length spans 52.9 kilobases, consisting of 16 exons. This coding gene culminates in 593 amino acids, forming the PTPN11 protein, SHP2. The protein contains two tandem Src homology 2 (SH2) domains in the N-terminus, a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) domain, and a terminus domain for protein-protein interaction.
Function of the PTPN11 Protein
Functioning as a ubiquitous intracellular tyrosine phosphatase, PTPN11/SHP2 catalyzes the addition and removal of phosphate groups from proteins, enabling them to perform various cellular processes. It plays a vital role in transmitting chemical signals from the cell surface to the inner compartments, shaping responses in cellular proliferation, differentiation, survival, and migration. Controlling such important cellular mechanisms has placed PTPN11 at a crucial juncture in understanding cellular and molecular biology mechanisms.
PTPN11 Protein Related Signal Pathway
PTPN11, through SHP-2, predominantly influences the signaling pathways of Ras and Rho family GTPases, which are involved in cell growth and cytoskeletal dynamics. Moreover, it modulates several other signaling pathways, like PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT, and NF-ĸB signaling, helping fine-tune physiological responses.
SHP-2 is crucial in several growth factor-stimulated and cytokine-stimulated signaling events, rendering its function vital for normal development, immune response, and hematopoiesis.
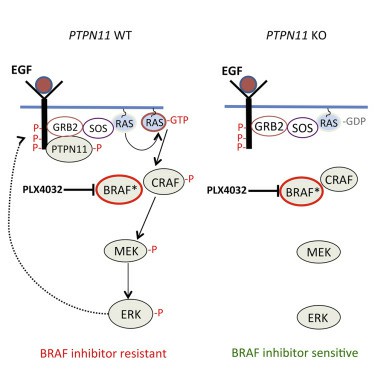
Fig1. Structure of PODXL
PTPN11 Protein Related Diseases
The disruption of the PTPN11 gene can lead to several conditions. Notably, PTPN11 mutations are predominantly related to Noonan Syndrome and LEOPARD syndrome – both are autosomal dominant disorders that involve physical abnormalities and developmental issues.
Aberrant regulation of SHP-2's signaling is also linked to various types of cancer, including leukemia, gastric adenocarcinoma, and lung carcinoma. Understanding the molecular underpinnings of its dysregulation may guide potential therapeutics.
PTPN11 Protein's Applications in Biomedical
Decoding PTPN11 protein's function and its influence on various signal transduction pathways is essential in understanding several diseases and disorders. Thus, it has presented new avenues for the development of therapeutics. Targeting the PTPN11/SHP-2 with specific inhibitors has shown promise in disease models of cancer, making it a potential therapeutic target.
Conclusively, the PTPN11 protein is a keystone in cellular and molecular biology, playing a crucial role in signal transductions that dictate cell responses. Its intrinsic relevance in human disorders delineates the importance of deepening our understanding of this gene and its protein. It may unravel advanced therapeutics avenues that could revolutionize the realm of molecular medicine.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTPN11-461H | Recombinant Human PTPN11, GST-tagged, Active | Human | E.coli | GST |
| PTPN11-519H | Active Recombinant Human PTPN11 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PTPN11-31402TH | Active Recombinant Human PTPN11 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| PTPN11-4830R | Recombinant Rat PTPN11 Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
| PTPN11-4489R | Recombinant Rat PTPN11 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Prahallad, A., Heynen, G. J., Germano, G., Willems, S. M., Evers, B., Vecchione, L., Gambino, V., Lieftink, C., Beijersbergen, R. L., Di Nicolantonio, F., Bardelli, A., & Bernards, R. (2015). PTPN11 Is a Central Node in Intrinsic and Acquired Resistance to Targeted Cancer Drugs. Cell Reports, 12(12), 1978-1985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.037

