What is TCF4 Protein
The TCF4 protein, officially known as Transcription Factor 4, is a vital player in the intricate symphony of cellular processes. Also referred to as ITF-2, SEF2-1, or E2-2, TCF4 belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors. The bHLH family is characterized by conserved structural motifs that contribute to their function as regulators of gene expression. TCF4, with its full name Transcription Factor 4, is encoded by the TCF4 gene, located on human chromosome 18.
Recent research advances have shed light on the dynamic nature of TCF4. Scientists have uncovered its role as a transcription factor, orchestrating the activation or repression of gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences. The protein's modular structure enables interactions with co-factors, adding layers of complexity to its regulatory functions.
TCF4 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
TCF4's biological functions span a wide spectrum, reflecting its influence on diverse cellular processes. This transcription factor is a key player in neurodevelopment, contributing to the formation and maturation of the nervous system. It is notably involved in the differentiation of neuronal cells, emphasizing its significance in brain development.
At the molecular level, TCF4 operates by binding to DNA sequences known as E-boxes, thereby modulating the transcription of target genes. This regulatory role extends beyond neurodevelopment, with TCF4 implicated in the control of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and immune response. The versatility of TCF4 in governing various cellular functions underscores its importance in maintaining homeostasis within the body.
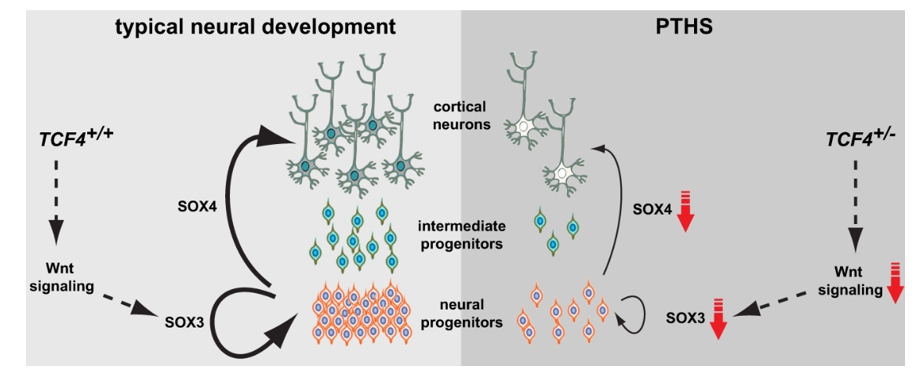
Figure 1. Model of dysregulated pathways underlying PTHS pathophysiology. (Papes F, et al., 2022)
TCF4 Related Signaling Pathway
TCF4 is a key player in the Wnt signaling pathway, a fundamental pathway in embryonic development and tissue homeostasis. In this context, TCF4 interacts with β-catenin, regulating the transcription of Wnt target genes. The dysregulation of the Wnt pathway, often involving TCF4, has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer.
Understanding the TCF4-related signal pathway provides a framework for targeted therapeutic interventions. Researchers are exploring ways to modulate TCF4 activity to influence the Wnt pathway positively, presenting potential avenues for the development of novel treatments.
TCF4 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of TCF4 has been linked to several diseases, highlighting the delicate balance required for proper cellular functioning. Notably, mutations in the TCF4 gene are associated with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, a rare neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by intellectual disability and distinctive facial features. Understanding the link between TCF4 and Pitt-Hopkins syndrome provides critical insights into the molecular basis of this condition.
Moreover, alterations in TCF4 expression have been observed in certain cancers, implicating the protein in tumorigenesis. The intricate interplay between TCF4 and cellular processes underscores the need for further exploration to unravel the complexities of its involvement in disease pathogenesis.
TCF4's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique characteristics of TCF4 make it a promising candidate for applications in the biomedical field. Its involvement in neurodevelopmental disorders positions TCF4 as a potential diagnostic marker. Researchers are exploring the use of TCF4 expression levels as a biomarker for conditions such as Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, offering a non-invasive and efficient means of diagnosis.
In vaccine development, TCF4's role in immune response regulation presents intriguing possibilities. Harnessing its regulatory functions may enhance the efficacy of vaccines by modulating the immune system's response, leading to more targeted and robust immune reactions.
On the therapeutic front, targeting TCF4 holds promise for conditions associated with its dysregulation. Small molecules and gene therapies aimed at restoring proper TCF4 function are being investigated as potential treatments for neurodevelopmental disorders and certain cancers.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCF4-29463TH | Recombinant Human TCF4 protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| TCF4-5109H | Recombinant Human TCF4, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| TCF4-31H | Recombinant Human TCF4 protein, His-tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His |
| TCF4-12H | Recombinant Human TCF4 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| TCF4-580H | Recombinant Human TCF4 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| TCF4-742HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human TCF4 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| TCF4-2168H | Recombinant Human TCF4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| TCF4-30167H | Recombinant Human TCF4 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| TCF4-16563M | Recombinant Mouse TCF4 Protein | Mouse | Mammalian Cell | His |
| TCF4-9081M | Recombinant Mouse TCF4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Papes F, et al. Transcription Factor 4 loss-of-function is associated with deficits in progenitor proliferation and cortical neuron content. Nature Communications. 2022, 13(1): 2387.

