AKT3
-
Official Full Name
v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 3 (protein kinase B, gamma) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the AKT, also called PKB, serine/threonine protein kinase family. AKT kinases are known to be regulators of cell signaling in response to insulin and growth factors. They are involved in a wide variety of biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, tumorigenesis, as well as glycogen synthesis and glucose uptake. This kinase has been shown to be stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), insulin, and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1). Alternatively splice transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. -
Synonyms
AKT3;v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 3 (protein kinase B, gamma);PKBG;PRKBG;STK-2;PKB-GAMMA;RAC-gamma;RAC-PK-gamma;DKFZp434N0250;RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase;PKB gamma;OTTHUMP00000037911;OTTHUMP00000037912;protein kinase Akt-3;protein kinase B gamma;serine threonine protein kinase, Akt-3
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- Flag
- MBP
- Fc
- Avi
- DDK
- Myc
Involved Pathway
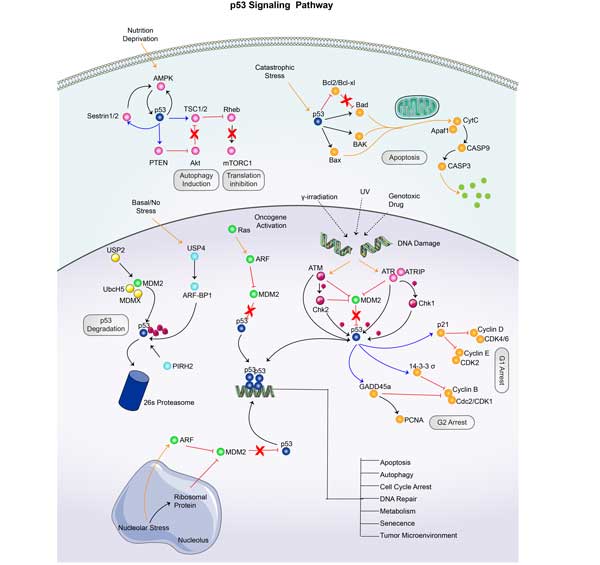
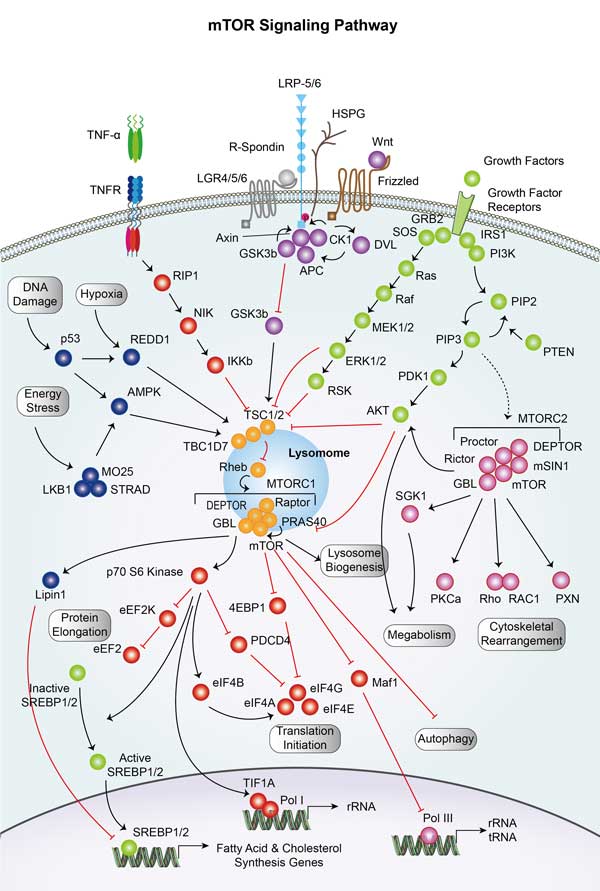
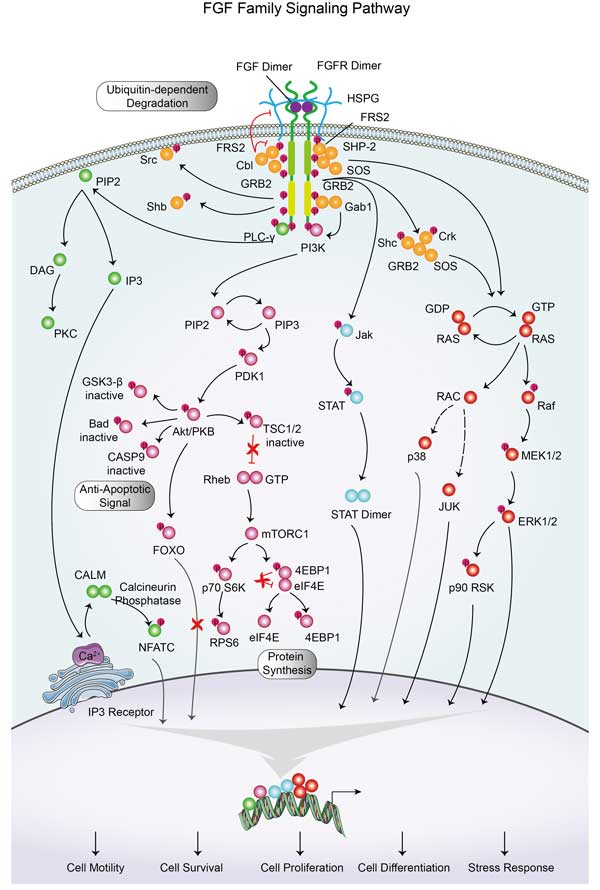
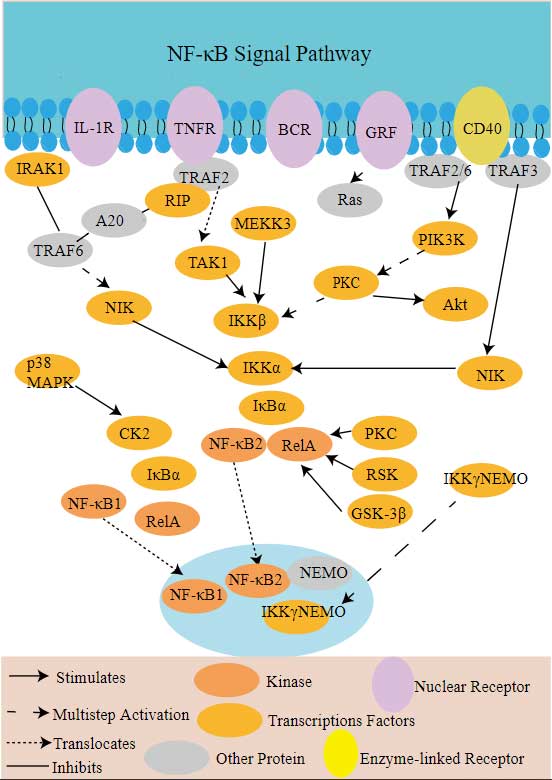
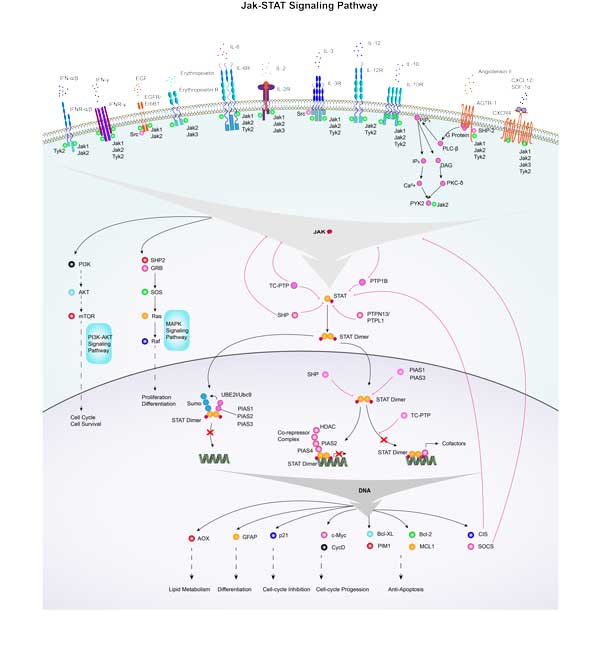
AKT3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways AKT3 participated on our site, such as AKT phosphorylates targets in the cytosol,AKT phosphorylates targets in the nucleus,AKT-mediated inactivation of FOXO1A, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with AKT3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Activation of BAD and translocation to mitochondria | YWHAQ,CDK5RAP2 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | CCND1,STAT5A,SFPI1,PIK3CG,RAF1,SPI1,SOS1,PIK3CD,STAT5B,LEF1 |
| AMPK signaling pathway | AKT1S1,PFKFB3,LIPE,PPP2R2A,PRKAG2,CFTR,ULK1,LEP,PPP2CA,RPTOR |
| Activation of BH3-only proteins | E2F1,CDK5RAP2,DYNLL2,YWHAQ,BCL2L11 |
| AKT phosphorylates targets in the nucleus | CREB1,CREB1B |
| AKT phosphorylates targets in the cytosol | CHUK,CDKN1A,CDKN1B |
| Adaptive Immune System | FGF20A,FRS2B,KIF2B,RNF220,CD200,KIF18A,UFL1,LILRB5,CTSE,GAN |
Protein Function
AKT3 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,protein binding,protein kinase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by AKT3 itself. We selected most functions AKT3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with AKT3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase activity | CASKB,CAMK1DB,CCL8,RPS6KB2,BMPR2B,PTK2,GC2,CHUK,CSF1RA,RPS6KA3 |
| ATP binding | MCM7,KIF15,ABCD2,RTCD1,CDK9,CDK1,ZRANB3,ADRBK2,PKN1,AKT2L |
| protein binding | ABCE1,DOCK4,HELT,EPHB2,PSAP,SLC38A2,PELI3,AKAP17A,PSME3,GMPPB |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | HIPK4,PRKCBA,CAMK2G1,NEK6,MAP3K11,CSNK1D,NEK10,SRPK1A,NUAK2,CAMKK1A |
Interacting Protein
AKT3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with AKT3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of AKT3.
CASP3;CDC37;saicar;PKM;HSP90AA1;PRKCZ;HSP90AB1;NUDCD1
AKT3 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Mias, GI; Chen, R; et al. Specific Plasma Autoantibody Reactivity in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 3:-(2013).
- Marchbank, T; Mahmood, A; et al. Pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor causes autocrine-mediated migration and invasion in bladder cancer and phosphorylates the EGF receptor, Akt2 and Akt3, and ERK1 and ERK2. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY-RENAL PHYSIOLOGY 305:F382-F389(2013).