CD59
-
Official Full Name
CD59 molecule, complement regulatory protein -
Overview
This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein that regulates complement-mediated cell lysis, and it is involved in lymphocyte signal transduction. This protein is a potent inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex, whereby it binds complement C8 and/or C9 during the assembly of this complex, thereby inhibiting the incorporation of multiple copies of C9 into the complex, which is necessary for osmolytic pore formation. This protein also plays a role in signal transduction pathways in the activation of T cells. Mutations in this gene cause CD59 deficiency, a disease resulting in hemolytic anemia and thrombosis, and which causes cerebral infarction. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants, which encode the same protein, have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
CD59;CD59 molecule, complement regulatory protein;1F5;EJ16;EJ30;EL32;G344;MIN1;MIN2;MIN3;MIRL;HRF20;MACIF;MEM43;MIC11;MSK21;16.3A5;HRF-20;MAC-IP;p18-20;CD59 glycoprotein;protectin;1F5 antigen;MEM43 antigen;Ly-6-like protein;T cell-activating protein;human leukocyte antigen MIC11;lymphocytic antigen CD59/MEM43;20 kDa homologous restriction factor;membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis;membrane attack complex inhibition factor;membrane attack complex (MAC) inhibition factor;surface anitgen recognized by monoclonal antibody 16.3A5;CD59 antigen p18-20 (antigen identified by monoclonal antibodies 16.3A5, EJ16, EJ30, EL32 and G344)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Pig
- Rabbit
- Rhesus macaque
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- T7
- S
- Non
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- rFc
Background
What is CD59 protein?
CD59 gene (CD59 molecule) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11p13. This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein that regulates complement-mediated cell lysis, and it is involved in lymphocyte signal transduction. This protein is a potent inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex, whereby it binds complement C8 and/or C9 during the assembly of this complex, thereby inhibiting the incorporation of multiple copies of C9 into the complex, which is necessary for osmolytic pore formation. This protein also plays a role in signal transduction pathways in the activation of T cells. The CD59 protein is consisted of 128 amino acids and CD59 molecular weight is approximately 14.2 kDa.
What is the function of CD59 protein?
As a membrane binding protein, CD59 prevents the insertion of the polymer of C9 by binding to C8 and/or C9 in the complement cascade, thereby inhibiting the formation of the complement membrane attack complex (MAC) and protecting cells from complement-mediated dissolution. CD59 plays a role in signal transduction activated by T cells, forming complexes with protein tyrosine kinases and participating in the signaling process. In the tumor immune microenvironment, the expression of CD59 may affect the function, invasion and phenotype of immune cells, and regulate the mechanism of tumor immune escape.
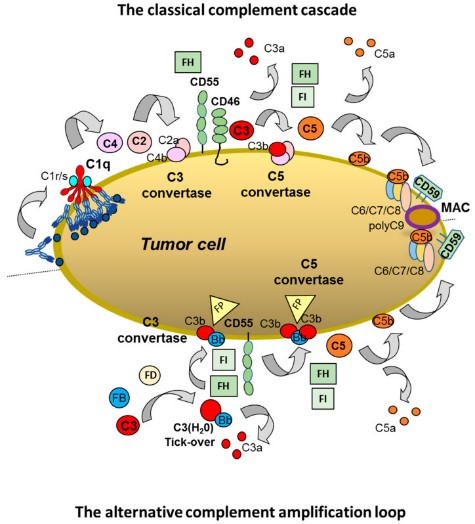
Fig1. The classical and alternative complement pathways. (Josée Golay, 2020)
CD59 Related Signaling Pathway
CD59 is involved in T cell signal transduction, forms complex with protein tyrosine kinase, and participates in T cell activation process. CD59 can directly or indirectly interact with a variety of viruses such as HIV-1, affecting the process of virus infection and replication. Studies have shown that CD59 promotes T cell proliferation through an LAT-mediated signal transduction pathway. CD59 acts as a major membrane attack complex (MAC) formation inhibitor, preventing MAC formation by binding to C8 and/or C9 in the complement cascade, protecting cells from complement-mediated dissolution.
CD59 Related Diseases
The CD59 protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, particularly those involving an imbalance in the complement system. Abnormal CD59 expression can cause a variety of autoimmune diseases, such as diabetes and multiple sclerosis. In diabetes, CD59 is glycosylated and inactivated at high blood sugar levels, resulting in an imbalance in the regulation of the complement system, and glycosylated CD59 is used as a marker for type 2 diabetes. In addition, the absence or abnormal function of CD59 is associated with paroxysmal sleep hemoglobinuria (PNH), a chronic acquired disorder characterized by intravascular hemolysis and hemoglobinuria, especially at night or in the early morning. In the tumor microenvironment, high expression of CD59 is associated with immune escape of tumor cells and may be associated with resistance to monoclonal antibody therapy.
Bioapplications of CD59
As a key regulator of the complement system, CD59 is of great value in the study of autoimmune diseases and complement-mediated pathological processes. In clinical diagnosis, the expression level of CD59 can be used as a biomarker for certain diseases, such as the diagnosis of paroxysmal sleep hemoglobinuria (PNH). In addition, the abnormal expression of CD59 is associated with the mechanism of tumor immune escape, making it a potential target for tumor immunotherapy. In drug development, inhibitors or activators of CD59 may help treat diseases involving an imbalance in the complement system.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ewelina Golec, 2022
Human pancreatic islets highly express CD59, which is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell-surface protein and is required for insulin secretion. How cell-surface CD59 could interact with intracellular exocytotic machinery has so far not been described. Researchers now demonstrate the existence of CD59 splice variants in human pancreatic islets, which have unique C-terminal domains replacing the GPI-anchoring signal sequence. These isoforms are found in the cytosol of β-cells, interact with SNARE proteins VAMP2 and SNAP25, colocalize with insulin granules, and rescue insulin secretion in CD59-knockout (KO) cells. Similar isoforms were also identified in the mouse CD59B gene, and targeted CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout showed that these intracellular isoforms, but not canonical CD59B, are involved in insulin secretion from mouse β-cells.
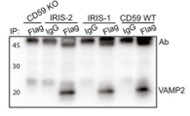
Fig1. Coimmunoprecipitation of IRIS-1, IRIS-2, and WT CD59 with VAMP2.
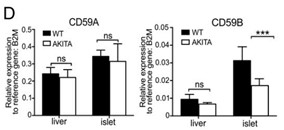
Fig2. qPCR of CD59A expression (Left) and CD59B expression (Right).
Case Study 2: Yuzhen Zhou, 2018
Radiation therapy is an important treatment modality for esophageal cancer. However, acquisition of radioresistance ultimately results in esophageal cancer relapse. CD59, a membrane-bound complement regulatory protein, can transduce signals via a Src kinase in the lipid raft, thus playing a complement-independent role. However, the effect of CD59 on the esophageal cancer response to ionizing radiation remains unclear. In this study, researchers found that the expression level of CD59 was positively correlated with the radioresistance of esophageal cancer cell lines and clinical specimens. High CD59 expression indicated poor overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients who received radiotherapy. Genetic alteration of CD59 expression modulated the radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells to ionizing radiation. CD59 deficiency exacerbated DNA damage, hindered cell proliferation, and induced G2/M cell cycle arrest and cellular senescence, leading to an impaired DNA damage repair ability. In addition, CD59 deficiency almost completely reduced the phosphorylation of Src at Y416 despite ionizing radiation.
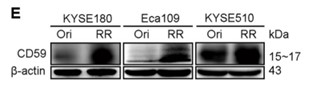
Fig3. CD59 was significantly upregulated in the three radioresistant cells.
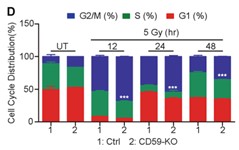
Fig4. CD59 deficiency exacerbated G2/M phase arrest compared with CD59 sufficiency.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD59-0836H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD59-151H)
Involved Pathway
CD59 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD59 participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades,Hematopoietic cell lineage, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD59 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | CD3G,CD1A,ITGA3,CSF3R,IL5,CD33,HLA-DRA,GM2002,CD19,Il6ra |
| Complement and coagulation cascades | C3AR1,CFI,CR1L,THBD,Hc,F3,C1R,SERPINA1E,F2R,SERPINA1D |
Protein Function
CD59 has several biochemical functions, for example, complement binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD59 itself. We selected most functions CD59 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD59. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| complement binding | CD46,C8G,C8A,CFB,CR2 |
| protein binding | UBTD1,SORT1,ARL16,LOC149950,MKNK1,C10orf46,FAM101A,SSX3,CD97,ZCCHC11 |
Interacting Protein
CD59 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD59 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD59.
TMED10;TMED2;C;EGFR;ganglioside_gm1;SMAD4;q7cgd4_yerpe;b3xyc5_sollc;ATP6AP2;CFTR
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Shi, H; Williams, J; et al. Exposure to the complement C5b-9 complex sensitizes 661W photoreceptor cells to both apoptosis and necroptosis. APOPTOSIS 20:433-443(2015).
- Ahmed, S; Kemp, MW; et al. Comparison of Complement Activity in Adult and Preterm Sheep Serum. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF REPRODUCTIVE IMMUNOLOGY 73:232-241(2015).




