GDF9
-
Official Full Name
growth differentiation factor 9 -
Overview
Growth factors synthesized by ovarian somatic cells directly affect oocyte growth and function. Growth differentiation factor-9 (GDF9) is expressed in oocytes and is thought to be required for ovarian folliculogenesis. GDF9 is a member of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. -
Synonyms
GDF9;growth differentiation factor 9;growth/differentiation factor 9;GDF-9
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Chicken
- Sheep
- CHO
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- His
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- Myc
Background
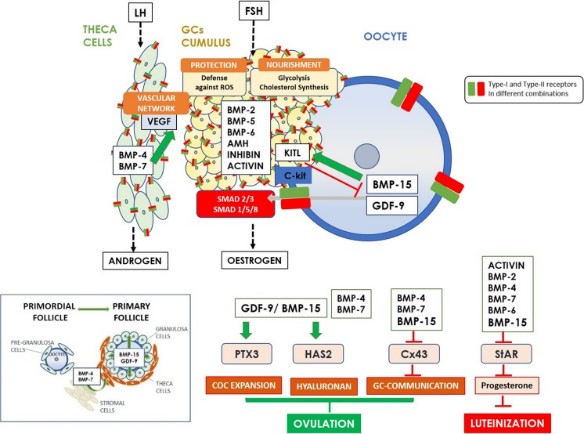
Fig1. Schematic diagram exhibiting the functional roles of the main TGF-β superfamily member proteins in regulating ovarian function. (Alexandra Sanfins, 2018)
What is GDF9 protein?
GDF9 (growth differentiation factor 9) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 5 at locus 5q31. This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Growth Differentiation Factor 9 (GDF9) is a protein that belongs to the Transforming Growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily. GDF9 plays a crucial role in the development and function of the reproductive system, particularly in regulating ovarian function and fertility. The GDF9 protein consists of a signal peptide, a mature protein region, and a possible glycosylation site. Its structural features include a typical TGF-β superfamily protein domain that is critical for its inhibitory activity. The GDF9 protein forms dimers through disulfide bonds, which are key to its biological activity. The GDF9 protein is consisted of 454 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 51.4 kDa.
What is the function of GDF9 protein?
GDF9 is mainly expressed in the oocytes of the ovaries and plays a role in the development and maturation of follicles. By binding to its receptor, it activates transcription factors of the Smad family, thereby regulating the expression of target genes. GDF9 is essential for promoting follicle growth, development, and survival, and it also affects steroid production in granulosa cells and is involved in regulating FSH receptor expression.
GDF9 Related Signaling Pathway
GDF9 activates phosphorylation of Smad2 by binding to its receptor, which in turn affects the expression of downstream genes. This is typical signaling for members of the TGF-beta superfamily. GDF9 may regulate the extracellular signaling kinase (ERK) pathway, c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, etc., which are part of the MAPK signaling pathway and participate in various biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. GDF9 may also affect the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which plays a central role in cell survival, metabolism, and growth.
GDF9 Related Diseases
Mutations or altered expression levels of the GDF9 gene have been associated with a variety of reproduction-related diseases. For example, reduced expression of GDF9 is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and mutations in certain GDF9 genes are more common in mothers of twins. In addition, GDF9 has been linked to early ovarian failure (POF), a condition that causes women to lose their fertility before the age of 40.
Bioapplications of GDF9
Because of its critical role in ovarian function and fertility, GDF9 has become an important target for reproductive medicine research. Research on GDF9 could help develop new treatments for improving female fertility, particularly in the field of assisted reproductive technology (ART). In addition, GDF9 is also used as a biomarker to assess ovarian reserve and embryo quality.
Case Study
Case Study 1: William A Stocker, 2020
Growth differentiation factor-9 (GDF9) and bone morphogenetic protein-15 (BMP15) are co-expressed exclusively in oocytes throughout most of folliculogenesis and play central roles in controlling ovarian physiology. Although both growth factors exist as homodimers, recent evidence indicates that GDF9 and BMP15 can also heterodimerize to form the potent growth factor cumulin. Within the cumulin complex, BMP15 "activates" latent GDF9, enabling potent signaling in granulosa cells via type I receptors (i.e. activin receptor-like kinase-4/5 (ALK4/5)) and SMAD2/3 transcription factors. In the cumulin heterodimer, two distinct type I receptor interfaces are formed compared with homodimeric GDF9 and BMP15. Previous studies have highlighted the potential of cumulin to improve treatment of female infertility, but, as a noncovalent heterodimer, cumulin is difficult to produce and purify without contaminating GDF9 and BMP15 homodimers. This study demonstrates that unique BMP15 finger residues at this site (Arg301, Gly304, His307, and Met369) enable potent activation of the SMAD2/3 pathway. Incorporating these BMP15 residues into latent GDF9 generated a highly potent growth factor, called hereafter Super-GDF9. Super-GDF9 was >1000-fold more potent than WT human GDF9 and 4-fold more potent than cumulin in SMAD2/3-responsive transcriptional assays in granulosa cells.
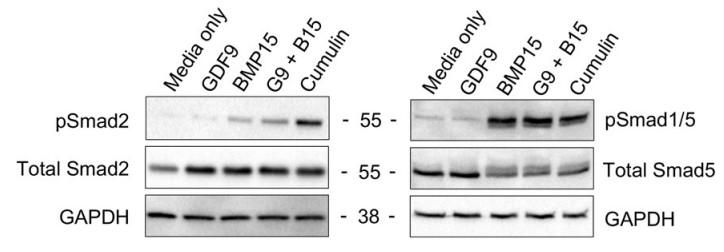
Fig1. Western blot analysis showing the protein expression. COV434 cells were treated for 1 h (50 ng/ml).
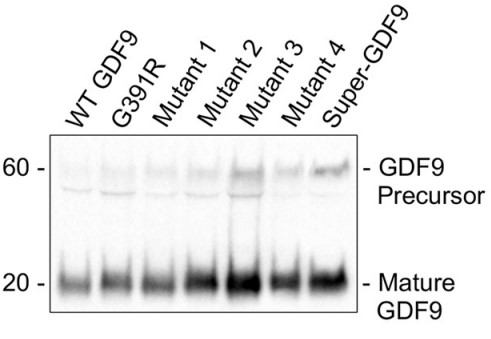
Fig2. BMP15 residues were substituted into GDF9 using in vitro site-directed mutagenesis.
Case Study 2: Sambit Roy, 2018
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) produced by ovarian granulosa cells (GCs) plays a crucial role in ovarian function. It is used as a diagnostic and/or prognostic marker of fertility as well as for pathophysiological conditions in women. This study investigated the underlying mechanism for regulation of AMH expression in GCs using primary mouse GCs and a human GC tumor-derived KGN cell line. The results showed that growth differentiation factor 9 (GDF9) and bone morphogenetic factor 15 (BMP15) together (GDF9 + BMP15), but not when tested separately, significantly induce AMH expression in vitro and in vivo (serum AMH). GDF9 + BMP15 through the PI3K/Akt and Smad2/3 pathways synergistically recruit the coactivator p300 on the AMH promoter region that promotes acetylation of histone 3 lysine 27 (H3K27ac), facilitating AMH/Amh expression. Intriguingly, the researchers also find that FSH inhibits GDF9 + BMP15-induced increase of AMH/Amh expression.
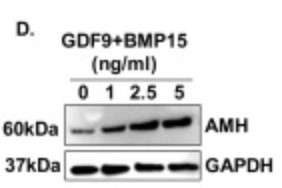
Fig3. Representative western blots with different concentrations of GDF9 and BMP15 treatment of 24 hours show increased AMH protein levels in KGN cells.
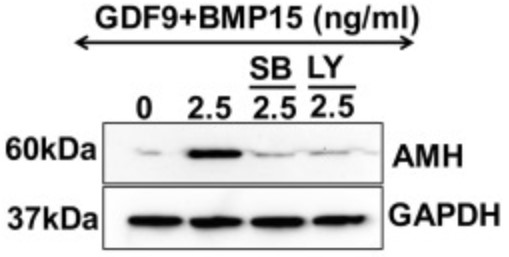
Fig4. Relative expression of AMH protein levels in GDF9 + BMP15 (2.5 ng/mL) stimulated mGCs.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GDF9-4830H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Gdf9-643M)
Involved Pathway
GDF9 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GDF9 participated on our site, such as Ovarian steroidogenesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GDF9 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Ovarian steroidogenesis | HSD3B1,LHB,CYP2J5,PTGS2,PLA2G4D,HSD17B7,HSD3B4,PRKACG,CYP2J6,FSHR |
Protein Function
GDF9 has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,growth factor activity,transforming growth factor beta receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GDF9 itself. We selected most functions GDF9 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GDF9. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transforming growth factor beta receptor binding | BMP15,BMP8B,LEFTY1,BMP2,MSTNA,MSTNB,FKBP1A,BMP7,BMP8A,NDR1 |
| cytokine activity | SCG2,SCGB3A1,SPAW,IFNB1,LIF,BMP8B,INHBE,TNF,NRG1,GM13287 |
| growth factor activity | FIGF,INHBE,NTF4,BTC,FGF20,IL3,FGF13A,DKK1,BMP3,THPO |
Interacting Protein
GDF9 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GDF9 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GDF9.
TK1;SMN1;PSMD11;DLEU1;KDM1A;PRKRA;GADD45G;S100A8;TDGF1;ANXA7;SAT1;CDKN1A;CDKN2C;SERPINB9;DNM2;RAB27A;FOXG1;SNRPG
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Pan, B; Toms, D; et al. MicroRNA-378 regulates oocyte maturation via the suppression of aromatase in porcine cumulus cells. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY-ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM 308:E525-E534(2015).
- Nakamura, T; Iwase, A; et al. CYP51A1 Induced by Growth Differentiation Factor 9 and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone in Granulosa Cells Is a Possible Predictor for Unfertilization. REPRODUCTIVE SCIENCES 22:377-384(2015).



