GPC5
-
Official Full Name
glypican 5 -
Overview
Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage.These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. -
Synonyms
GPC5;glypican 5;glypican-5;glypican proteoglycan 5;Glypican 5 precursor;GPC5_HUMAN;Secreted glypican-5;bA93M14.1;OTTHUMP00000018551
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- T7
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
Background
What is GPC5 protein?
GPC5 gene (glypican 5) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 13 at locus 13q31. Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. The GPC5 protein is consisted of 572 amino acids and GPC5 molecular weight is approximately 63.7 kDa.
What is the function of GPC5 protein?
GPC5 plays a role in a variety of biological processes, including cell signaling, cell proliferation, migration and differentiation. In lung cancer, GPC5 is generally considered a tumor suppressor. GPC5 can inhibit tumor growth by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which plays an important role in the occurrence and development of lung cancer. GPC5 is able to affect a variety of cell signaling pathways including Wnt, Hedgehog, and Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGF), which play key roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. GPC5 inhibits the progression and metastasis of lung cancer by regulating the intracellular CTDSP1/AhR/ARNT signaling axis and extracellular exosome secretion. GPC5 expression may be subject to epigenetic regulation, such as DNA methylation, which may play an important role in tumorigenesis.
Fig1. Schematic diagram shows molecular mechanisms of IR caused by palmitate exposure. (Yoshio Hirabayashi, 2022)
GPC5 related signaling pathway
GPC5 inhibits tumor growth by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which has received particular research attention in lung adenocarcinoma. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is a key cellular regulatory network involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumorigenesis. GPC5 exerts its tumor suppressor effect by inhibiting β-catenin activity in this pathway, reducing tumor cell proliferation and enhancing apoptosis. In addition to the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, GPC5 is involved in other signal transduction mechanisms. For example, it acts intracellular through the CTDSP1/AhR/ARNT signaling axis and influences the extracellular environment through exosome secretion, inhibiting the progression and metastasis of lung cancer.
GPC5 related diseases
GPC5 is a protein associated with a variety of diseases, including cancer, diabetes, obesity, and Alzheimer's disease. In the field of cancer, especially in the study of lung cancer, the role of GPC5 has received extensive attention. It is commonly expressed as a tumor suppressor gene in lung adenocarcinoma and is able to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In addition, GPC5 is involved in regulating the intracellular CTDSP1/AhR/ARNT signaling axis and influences tumor progression and metastasis through extracellular exosome secretion. In non-small cell lung cancer, the expression of GPC5 is reduced, while this phenomenon is not seen in other histological subtypes of lung cancer. The function of GPC5 may be subject to epigenetic regulation, such as DNA methylation, which may play an important role in tumorigenesis.
Bioapplications of GPC5
rhGPC5 protein has many potential applications in the biomedical field. It is mainly studied for use in cancer therapy, especially as a tumor suppressor in the treatment of lung cancer. rhGPC5 can inhibit the growth of tumor cells by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which is particularly important in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. In addition, rhGPC5 is involved in regulating the intracellular CTDSP1/AhR/ARNT signaling axis and influences tumor progression and metastasis through exosome secretion. These studies offer the possibility of developing new cancer treatment strategies, including using rhGPC5 as a drug target or in combination with other treatments to improve treatment effectiveness.
Case Study
Case Study 1: S Yuan, 2016
Glypican-5 (GPC5), a heparin sulfate proteoglycan, has inconsistently been linked to lung tumor development. This study confirmed lower GPC5 levels in lung adenocarcinoma versus normal lung tissue, with reduced expression correlating with worse patient outcomes. GPC5 downregulation was due to promoter hypermethylation in lung cancer tissues and cell lines, and demethylation could restore its expression. GPC5 overexpression hindered lung cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and slowed tumor growth in vivo, while GPC5 knockdown reversed these effects. GPC5 functions as a tumor suppressor by binding to Wnt3a and inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. These results position GPC5 as a new epigenetically regulated tumor suppressor in lung adenocarcinoma, controlling tumor growth through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
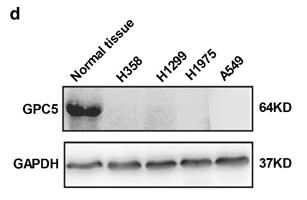
Fig1. WB analysis of GPC5 protein in lung cancer cell lines compared with that in normal lung tissue.
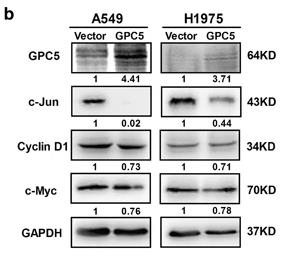
Fig2. Representative WB analysis of the typical Wnt signaling target proteins after transfection with control or GPC5 vector.
Case Study 2: Yu Sun, 2018
Glypican 5 (GPC5), a member of the heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG) family, was originally identified for its roles in modulating growth factors and morphogens. Its association with cancer development has been increasingly recognized, yet its function in prostate cancer (PCa) remains unclear. In this study, GPC5's expression and effects were investigated in PCa cells. GPC5 expression was low in PCa cell lines, and enhancing its expression significantly reduced cell proliferation and invasion in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Additionally, GPC5 overexpression suppressed the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which appeared to be regulated by Sp1.
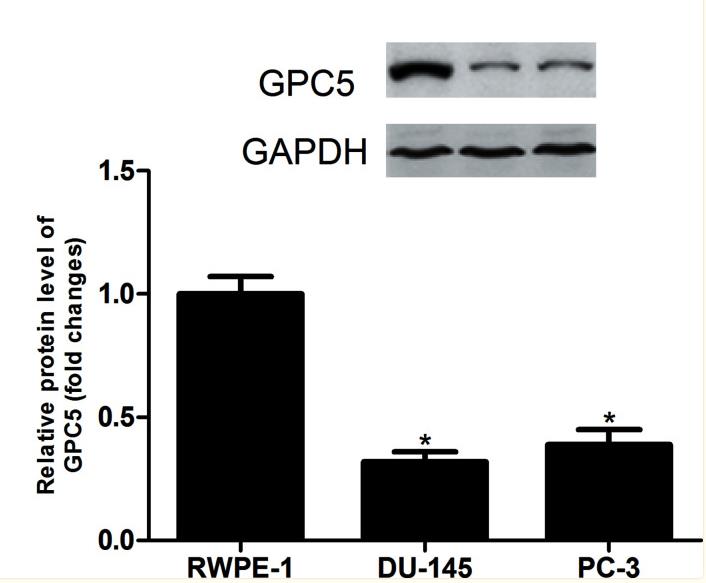
Fig3. The protein levels of GPC5 in PCa cell lines were determined.
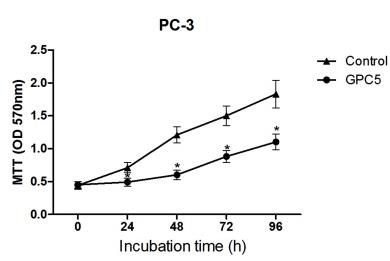
Fig4. The proliferative and invasive capabilities of PC-3 cells were greatly reduced by GPC5 overexpression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GPC5-5149H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GPC5-3285H)
Involved Pathway
GPC5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GPC5 participated on our site, such as A tetrasaccharide linker sequence is required for GAG synthesis,Chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate metabolism,Defective B3GALT6 causes EDSP2 and SEMDJL1, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GPC5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate metabolism | B4GALT7,NCAN,AGRN,CHST14,BGNB,VCAN,VCANB,GPC5A,CSPG4,CSPG5B |
| A tetrasaccharide linker sequence is required for GAG synthesis | GPC5A,VCANB,CSPG5,CSPG5B,GPC1A,VCAN,DCN,BCAN,Gpc2,CSPG4 |
| Defective EXT2 causes exostoses 2 | GPC6,AGRN |
| Defective B3GALT6 causes EDSP2 and SEMDJL1 | BGN,BCAN,AGRN,CSPG5,NCAN,VCAN,GPC6,CSPG4,DCN |
| Defective B4GALT7 causes EDS, progeroid type | VCAN,DCN,AGRN,BCAN,CSPG4,GPC6,CSPG5,NCAN,BGN |
| Defective EXT1 causes exostoses 1, TRPS2 and CHDS | AGRN,GPC6 |
| Disease | TCEB3,SYT2,AP2A2,PSIP1,APOBEC3G,FDX1,AP2B1,RBP1,gag,TIRAP |
| Defective B3GAT3 causes JDSSDHD | BGN,CSPG5,GPC6,BCAN,CSPG4,DCN,AGRN,VCAN,NCAN |
Protein Function
GPC5 has several biochemical functions, for example, heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GPC5 itself. We selected most functions GPC5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GPC5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding | GPC1B,GPC4,GPC1,UBE4A,GPC6,Gpc2,GPC1A,FST,CFH,HRG |
Interacting Protein
GPC5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GPC5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GPC5.
Shcbp1;DCPS
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Thway, K; Selfe, J; et al. Immunohistochemical Detection of Glypican-5 in Paraffin-embedded Material: An Optimized Method for a Novel Research Antibody. APPLIED IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR MORPHOLOGY 20:189-195(2012).
- Link, C; Hawlisch, H; et al. Selection of phage-displayed anti-guinea pig C5 or C5a antibodies and their application in xenotransplantation. MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY 36:1235-1247(1999).



