NEFL
-
Official Full Name
neurofilament, light polypeptide -
Overview
Neurofilaments are type IV intermediate filament heteropolymers composed of light, medium, and heavy chains.;Neurofilaments comprise the axoskeleton and they functionally maintain the neuronal caliber. They may also play a role;in intracellular transport to axons and dendrites. This gene encodes the light chain neurofilament protein. Mutations;in this gene cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease types 1F (CMT1F) and 2E (CMT2E), disorders of the peripheral nervous;system that are characterized by distinct neuropathies. A pseudogene has been identified on chromosome Y. -
Synonyms
NEFL;neurofilament, light polypeptide;neurofilament, light polypeptide 68kDa;neurofilament light polypeptide;CMT1F;CMT2E;NF68;NFL;neurofilament subunit NF-L;neurofilament triplet L protein;neurofilament protein, light chain;light molecular weig
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Bovine
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Pig
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- bovine Spinal Cord
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- MBP
- Avi
- Fc
Background
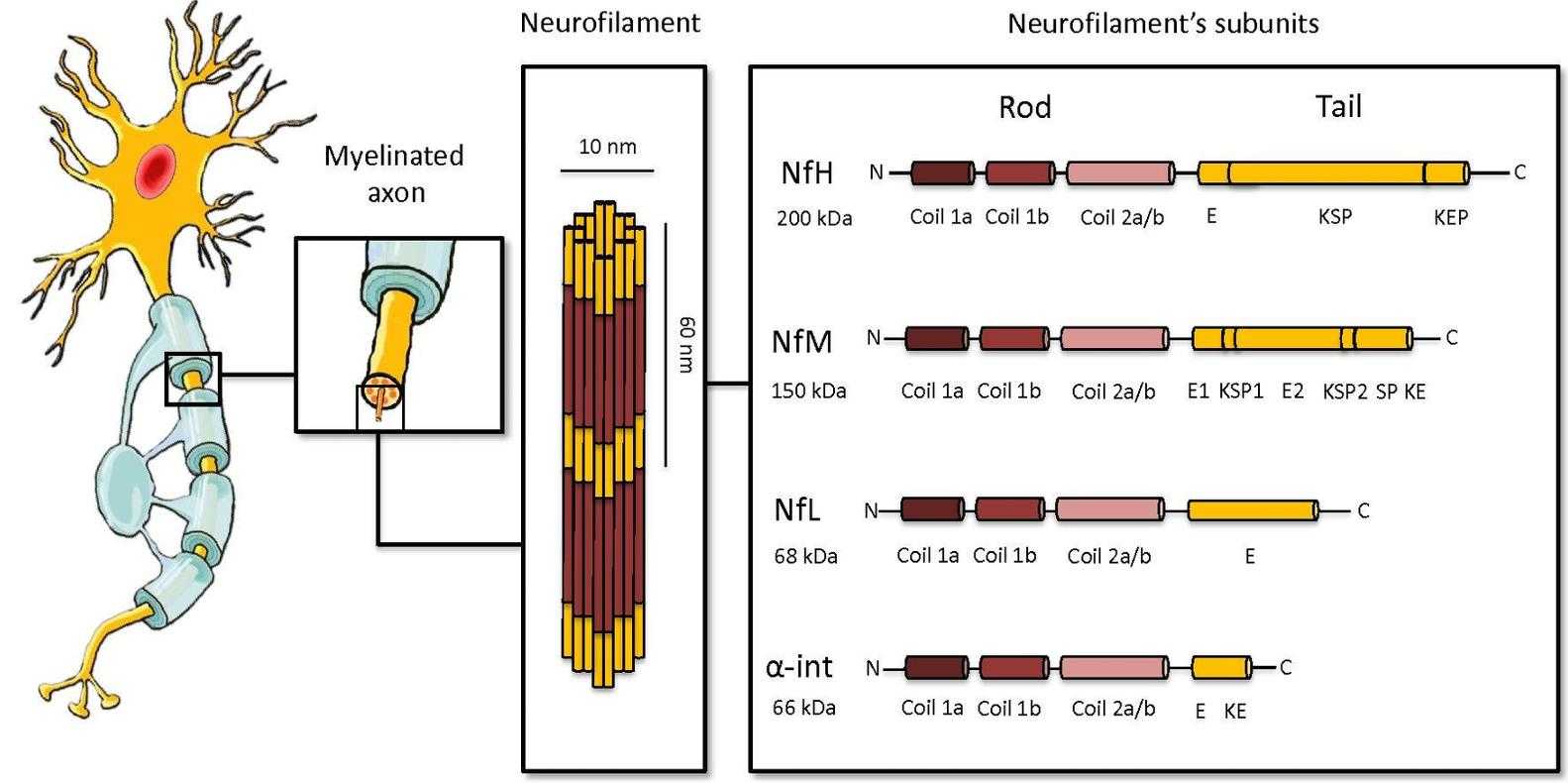
Fig1. Overview of the structure of neurofilaments and neurofilament light chain. (Lorenzo Gaetani, 2019)
What is NEFL Protein?
NEFL gene (neurofilament light chain) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8p21. Together with the medium chain (NF-M) and heavy chain (NF-H), NEFL forms heterogeneous polymers that are essential for maintaining the structural integrity of neurons, especially axons. The proteins encoded by the NEFL gene contain α-helically coiled rod-like domains, as well as amino-terminal head and carboxy-terminal tail domains, which vary widely in length. Abnormal aggregation of NEFL is a pathological feature of certain neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, etc. The NEFL protein is consisted of 543 amino acids and NEFL molecular weight is approximately 61.5 kDa.
What is the Function of NEFL Protein?
The NEFL protein, also known as the Neurofilament light chain (NF-L), is an important part of the intermediate filaments (IFs) that make up the cytoskeleton of neurons. Its functions are mainly involved in maintaining the morphological and mechanical stability of axons, regulating axon diameter and synaptic activity, and participating in the transport of organelles along axons. In addition, abnormal aggregation of NEFL has been associated with a variety of neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), giant axonal neuropathy (GAN), and spinal muscular atrophy. In these diseases, mutated or abnormal NEFL accumulation may lead to neurological dysfunction.
NEFL Related Signaling Pathway
The NEFL signaling pathway is involved in regulating the growth and development of neurons. NEFL is a neuronal intermediate filament protein that plays a critical role in maintaining the integrity of the neuronal cytoskeleton. When NEFL is expressed in the brain, it interacts with other proteins to form a complex that regulates the activity of various signaling pathways. This complex includes the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, and the Notch pathway. The MAPK pathway is involved in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is involved in regulating cell adhesion and polarity. The Notch pathway is involved in regulating cell fate decisions.
NEFL Related Diseases
NEFL proteins have been implicated in a variety of neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. As an indicator of disease activity in multiple sclerosis; As a biomarker of injury severity in HIV-associated nerve injury, brain injury and spinal cord injury; Affects the invasion and migration of tumor cells in certain types of cancer such as esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; It also plays a role in neurodevelopment, axon regeneration and hereditary anterior temporal degenerative diseases. Abnormal changes in NEFL levels can be used as biomarkers to diagnose and monitor these diseases.
Bioapplications of NEFL
NEFL-related applications are mainly related to the diagnosis and research of diseases in the field of neurology. As the main intermediate filament protein in neurons, the level change of NEFL can reflect the degree of damage of nerve tissue, therefore, by monitoring the level of NEFL, it can be used to assess the activity of a variety of acute and chronic neurological diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases, monitor treatment response, and serve as a biomarker to predict the prognosis of disease. In addition, antibodies against NEFL are widely used in various scientific studies, such as immunohistochemistry, ELISA, western blotting and other experimental techniques, to detect and locate the expression of NEFL in human and animal samples.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Stephan A Kaeser, 2021
Neurofilament light chain (NfL) has emerged as a promising blood biomarker for the progression of various neurological diseases. NfL is a structural protein of nerve cells, and elevated NfL levels in blood are thought to mirror damage to the nervous system. Researchers find that plasma NfL levels increase in humans with age (n = 122; 21-107 years of age) and correlate with changes in other plasma proteins linked to neural pathways. In centenarians (n = 135), plasma NfL levels are associated with mortality equally or better than previously described multi-item scales of cognitive or physical functioning, and this observation was replicated in an independent cohort of nonagenarians (n = 180). Plasma NfL levels also increase in aging mice (n = 114; 2-30 months of age), and dietary restriction, a paradigm that extends lifespan in mice, attenuates the age-related increase in plasma NfL levels.
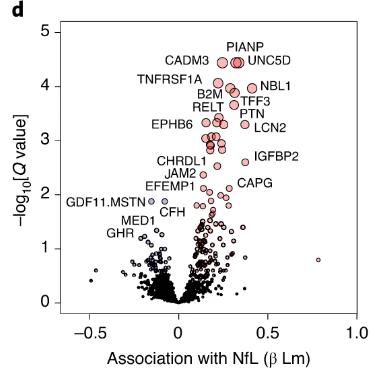
Fig1. Association between plasma NfL levels and levels of 1,305 plasma proteins.
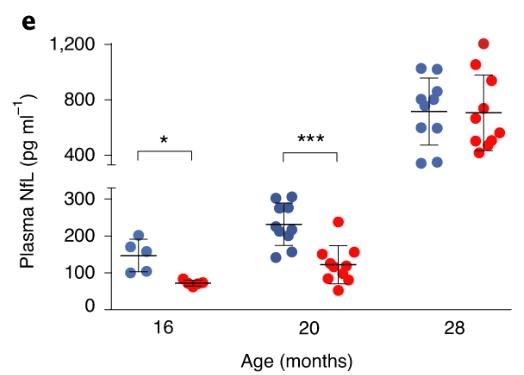
Fig2. Plasma NfL levels were significantly reduced in DR compared to AL mice at 16 months of age and 20 months of age but not in those at 28 months of age.
Case Study 2: Markus T Sainio, 2022
To understand the disease-causing mechanisms, researchers investigate here the functional effects of NFL loss in human motor neurons differentiated from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC). They used genome editing to generate NEFL knockouts and compared them to patient-specific nonsense mutants and isogenic controls. iPSC lacking NFL differentiated efficiently into motor neurons with normal axon growth and regrowth after mechanical axotomy and contained neurofilaments. Electrophysiological analysis revealed that motor neurons without NFL fired spontaneous and evoked action potentials with similar characteristics as controls. However, in the absence of NFL, human motor neurons 1) had reduced axonal caliber, 2) the amplitude of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSC) was decreased, 3) neurofilament heavy (NFH) levels were reduced and no compensatory increases in other filament subunits were observed, and 4) the movement of mitochondria and to a lesser extent lysosomes was increased.
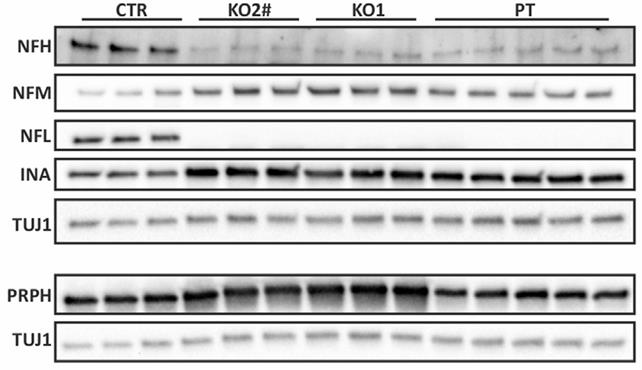
Fig3. NEFL KO motor neurons express other neurofilament proteins.
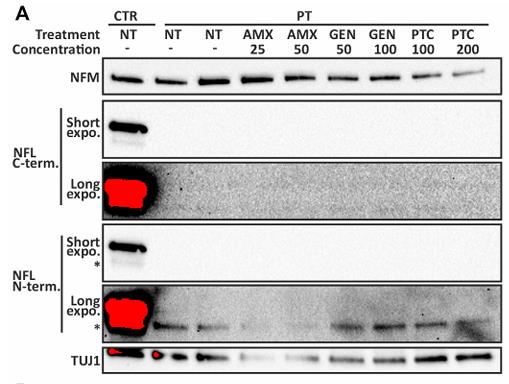
Fig4. Immunoblotting series shows no detectable full-length NFL in treated patient motor neurons.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (NEFL-13H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (NEFL-2484H)
Involved Pathway
NEFL involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways NEFL participated on our site, such as Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with NEFL were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | SLC1A2,GRIN2D,Casp3,PPP3R1,CASP9,GRIA2,RAC1,MAP2K3,TRP53,CASP1 |
Protein Function
NEFL has several biochemical functions, for example, identical protein binding,phospholipase binding,protein C-terminus binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by NEFL itself. We selected most functions NEFL had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with NEFL. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CD2AP,MED31,DSTN,Txn1,ZIC3,UBA1,PEX10,FAM124B,AKAP6,IFT43 |
| protein binding, bridging | FRMD4A,NEFH,TNNT2A,FSCN1A,VPS18,FKBP4,NCK1,MMS19,TRIM5,SPRR1B |
| protein C-terminus binding | PDZD3,HSPG2,IFT52,TJP2,CSK,ECM1,EFHC1,SCLT1,YWHAB,SDCBP |
| phospholipase binding | PARK2,PRKCZ,LMNB1,PTPN11,WAS,SERPINB1A,APOC2,Pla2r1,PDPK1,CALM3 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | HIST1H2AG,H2AFV,DDIT3,MCL1,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,TYR,PVRL1,CHRNB2,TCF4,TENM2 |
| identical protein binding | PSMA7,ERN1,MRI1,PLEKHH2,PPPDE2,TRP53,JMJD6,C1QL4,RBM10,BTK |
| structural constituent of cytoskeleton | MSN,TUBD1,KRT16,KRT2,TUBA2,ARPC4,DES,ADD3,ARPC2,TUBGCP3 |
| protein domain specific binding | DIXDC1,KCNN2,SNCA,HIST1H4L,MPP5,DVL2,ABCC2,PLAUR,SLC34A2,WNT3A |
Interacting Protein
NEFL has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with NEFL here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of NEFL.
APP;PPP1R18;TERF1;MTMR2;tax;TNF;YWHAG;SCHIP1;PHLPP1;VIM;RAN;CHD3
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


