CXC Chemokine Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CXC Chemokine Receptors Research
Creative BioMart is the leading destination for all of your research needs pertaining to CXC chemokine receptors. Our carefully selected range of products and personalized services are specifically designed to help you delve into the complex realm of CXC chemokine receptors and their crucial role in various physiological processes.
- Our product selection includes top-quality recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more, all meticulously tailored to meet your research requirements with unparalleled precision and expertise.
- Moreover, we offer a wealth of resources on CXC chemokine receptors, such as comprehensive insights on involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, relevant literature, and the latest research trends. You can rely on Creative BioMart to serve as your ultimate hub for all things related to CXC chemokine receptors.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CXCR3-261H | Recombinant Human CXCR3 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CXCR4-504H | Recombinant Human CXCR | Human | Wheat Germ | N/A |
About CXC Chemokine Receptors
CXC chemokine receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that specifically bind to and respond to chemokines with a CXC motif. CXC chemokine receptors are named after the presence of a conserved motif of two cysteine residues separated by a single amino acid (CXC) near the N-terminus of the chemokine ligands they bind. The family of CXC chemokines is diverse and includes both inflammatory and homeostatic chemokines that regulate immune cell functions and coordinate immune responses.
Several CXC chemokine receptors have been identified, including CXCR1, CXCR2, CXCR3, CXCR4, CXCR5, CXCR6, and CXCR7. Each receptor subtype has a specific ligand-binding profile and distinct signaling properties. These receptors are expressed on various immune cells, such as neutrophils, monocytes, T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
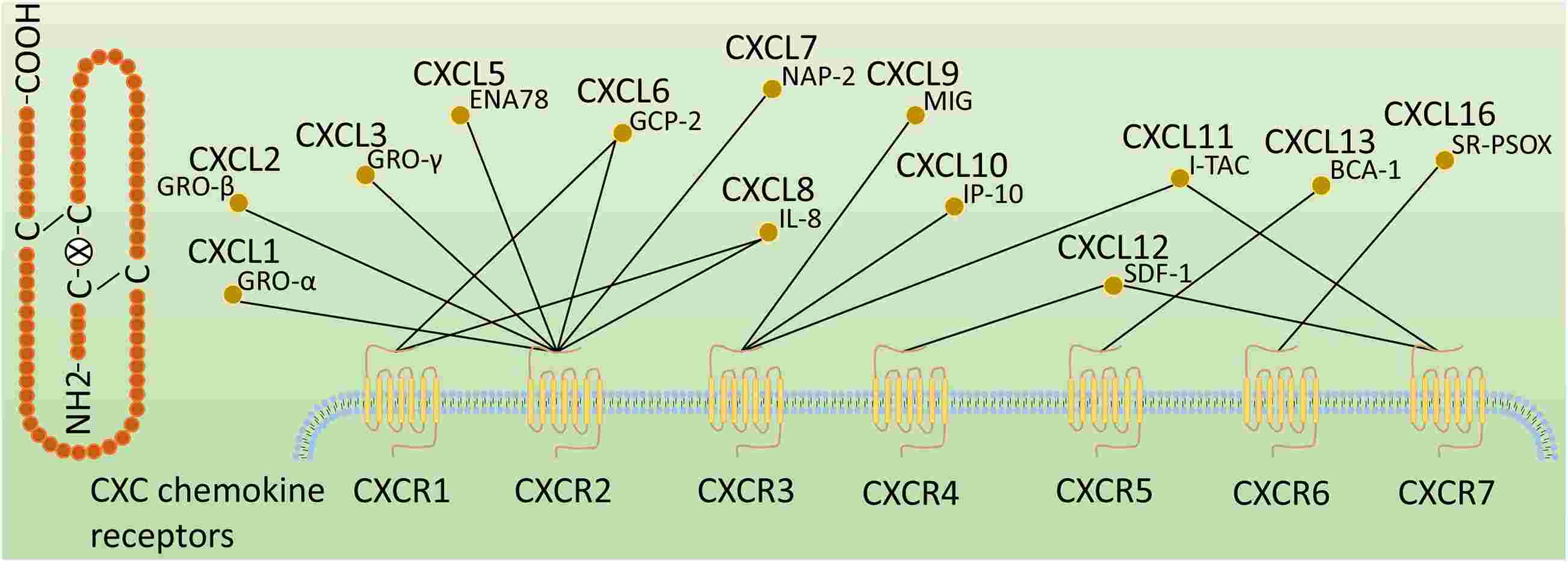 Fig.1 Classification of CXC chemokine receptors. (Wang S, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Classification of CXC chemokine receptors. (Wang S, et al., 2021)
CXC chemokine receptors are classified according to the ligands they bind, followed by an R (representing receptor) and a number corresponding to the order of discovery. These CXC chemokine ligands are also known as GRO-α (CXCL1), GRO-β (CXCL2), GRO-γ (CXCL3), ENA78 (CXCL5), GCP-2 (CXCL6), NAP-2 (CXCL7), IL-8 (CXCL8), MIG (CXCL9), IP-10 (CXCL10), I-TAC(CXCL11), SDF-1(CXCL12), BCA-1(CXCL13), and SR-PSOX(CXCL16).
CXC chemokine receptors bind to different CXC chemokines, which are produced in response to inflammatory stimuli or as part of immune surveillance. The ligand-receptor interactions regulate immune cell trafficking, directing immune cells to sites of inflammation or infection. CXC chemokines also play roles in angiogenesis, wound healing, and other physiological processes.
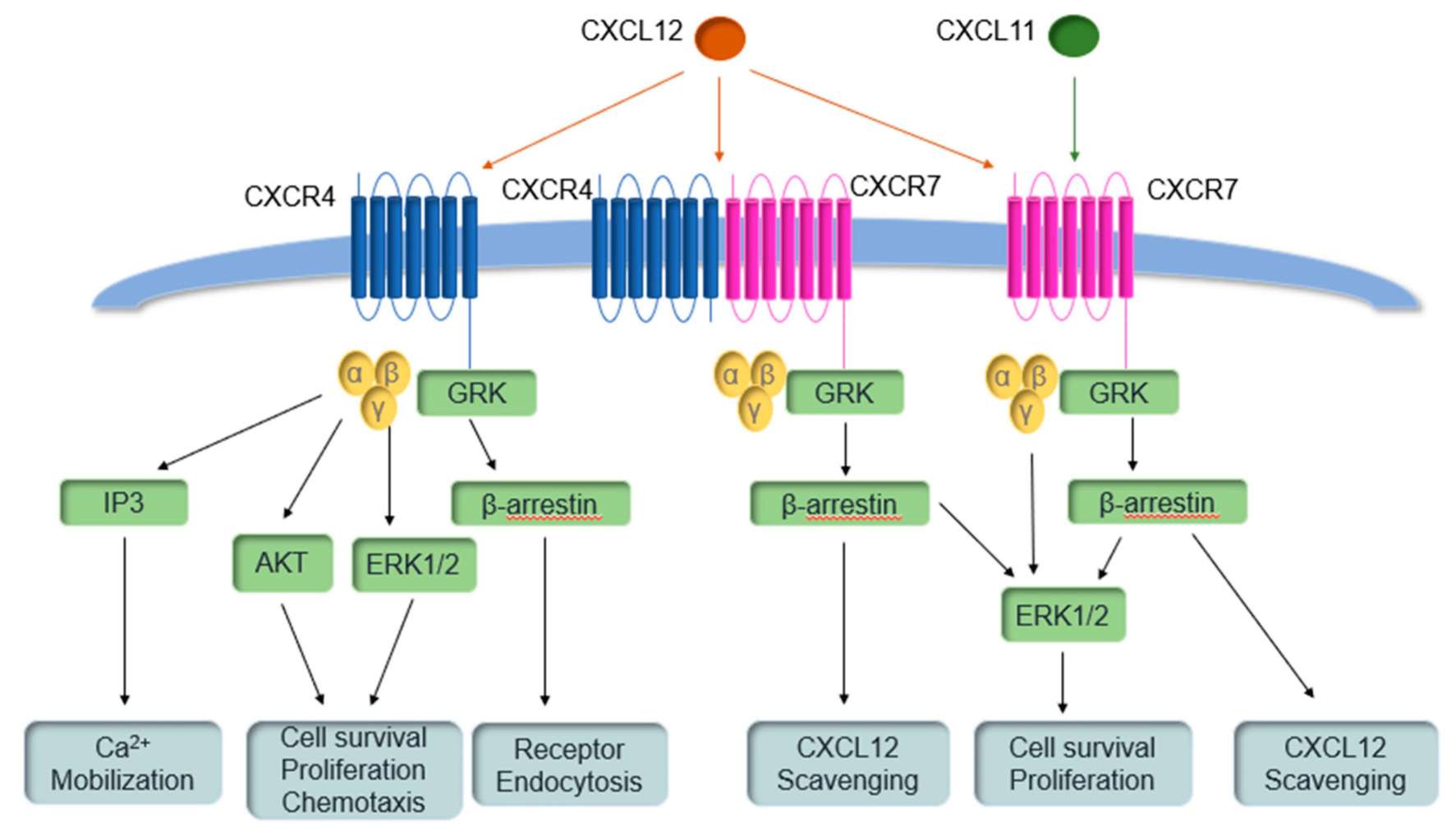 Fig.2 CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) and CXCR7 pathways. (Lounsbury N, 2020)
Fig.2 CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) and CXCR7 pathways. (Lounsbury N, 2020)
Role of CXC Chemokine Receptors in Immunomodulation and Cell Signaling
CXC chemokine receptors play crucial roles in immunomodulation and cell signaling within the immune system. They regulate the migration and activation of immune cells, including neutrophils, T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells, and contribute to the coordination of immune responses. Here are some key roles of CXC chemokine receptors in immunomodulation and cell signaling:
- Leukocyte Recruitment: CXC chemokine receptors are involved in the recruitment of leukocytes to sites of inflammation and infection. They mediate the chemotaxis of immune cells, particularly neutrophils, by promoting their migration toward the source of chemokine gradients. For example, CXCR1 and CXCR2 are critical for neutrophil recruitment to sites of bacterial infection and tissue damage.
- T Cell Migration and Activation: CXC chemokine receptors, such as CXCR3 and CXCR4, are expressed on T cells and regulate their migration and activation. CXCR3 directs the migration of T cells to sites of inflammation, where it is involved in the recruitment of effector T cells, particularly Th1 cells. CXCR4 is important for T cell development and homing to lymphoid organs.
- Neutrophil Activation: CXC chemokine receptors on neutrophils, such as CXCR1 and CXCR2, not only regulate their recruitment but also participate in their activation. Binding of CXC chemokines to these receptors triggers intracellular signaling pathways that promote neutrophil activation, including respiratory burst, degranulation, and phagocytosis.
- Dendritic Cell Migration and Antigen Presentation: CXC chemokine receptors are involved in the migration and positioning of dendritic cells (DCs), which are important antigen-presenting cells. CXCR4, for example, is critical for DC migration from peripheral tissues to lymphoid organs. The activation of CXC chemokine receptors on DCs also influences their maturation, antigen presentation, and immunomodulatory functions.
- Inflammatory Responses: CXC chemokine receptors play a significant role in regulating inflammatory responses. Upon activation, they enhance the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), by immune cells. This contributes to the amplification and regulation of inflammation.
- Cell Survival and Apoptosis: CXC chemokine receptors can impact cell survival and apoptosis. Activation of CXCR4, for instance, can promote cell survival and protect cells from apoptosis. The CXCR4 ligand, CXCL12 (also known as stromal cell-derived factor-1 or SDF-1), is involved in the survival and homing of various cell types, including immune cells and hematopoietic stem cells.
- Angiogenesis: CXC chemokine receptors participate in angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels. They regulate the migration and proliferation of endothelial cells, which are crucial for blood vessel formation. For instance, CXCR2 is involved in promoting angiogenesis by mediating the recruitment and activation of endothelial cells.
- Cell Signaling Crosstalk: CXC chemokine receptors can crosstalk and integrate with other signaling pathways, such as Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling and cytokine receptor signaling, to modulate immune cell responses. This crosstalk can enhance or dampen immune cell activation, cytokine production, and immune responses.
Understanding the functions of CXC chemokine receptors is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms underlying immune responses, inflammation, and various immune-related disorders.
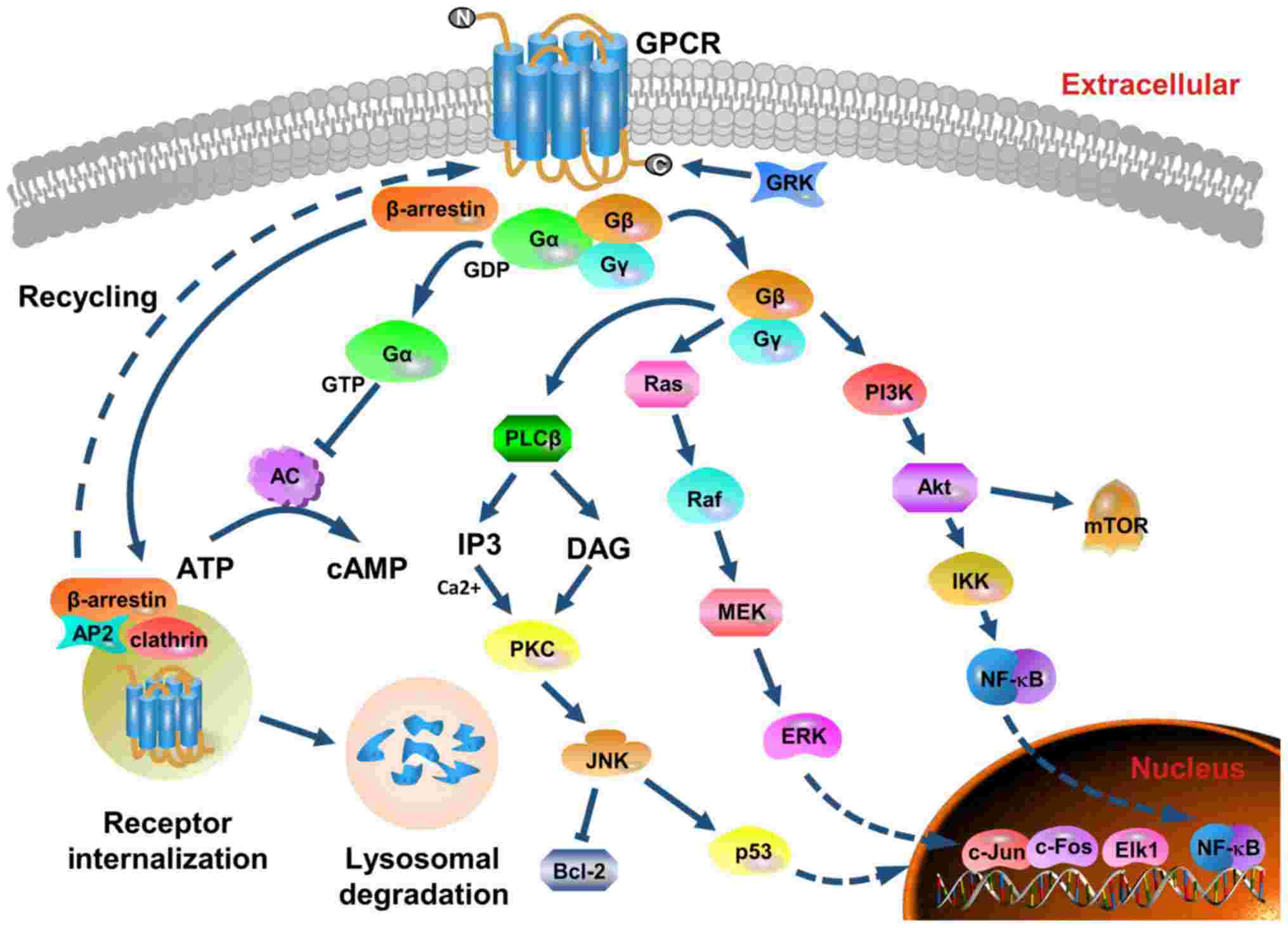 Fig.3 Structure, major signaling cascades and receptor recycling of CXCR2. (Guo F, et al., 2019)
Fig.3 Structure, major signaling cascades and receptor recycling of CXCR2. (Guo F, et al., 2019)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Lounsbury N. Advances in CXCR7 Modulators. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(2):33.
- Guo F, Long L, Wang J, et al. Insights on CXC chemokine receptor 2 in breast cancer: An emerging target for oncotherapy. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(6):5699-5708.
- Wang S, Gao S, Li Y, Qian X, Luan J, Lv X. Emerging Importance of Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 and Its Ligand in Liver Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:716842.

