What is CDC20 Protein?
The Cell Division Cycle 20 (CDC20) protein serves as a key regulator of cell division and has a critical role in the separation of sister chromatids and the formation of the mitotic spindle.
CDC20 Protein Discovery and Background
The discovery of CDC20 is rooted in the findings of genetic studies on Saccharomyces cerevisiae, where Hartwell (1971) identified an allele that disrupted the Cell Division Cycle. This gene named CDC20 was found to stall the cell cycle at metaphase. Cumulative research expanded its understanding in other eukaryotic organisms, encompassing humans to yeast, embodying conserved features in cell cycle regulation.
CDC20 gene locus and Protein Structure
The CDC20 gene is located on chromosome 1, precisely at 1p34.1. The CDC20 protein, encompassing 499 amino acids in humans, has a molecular weight of approximately 55 kDa. The protein architecture involves a WD-repeat domain that facilitates the assembly of multiprotein structures. It interacts with pertinent regulatory proteins for cell division, signifying its core role in the division process.
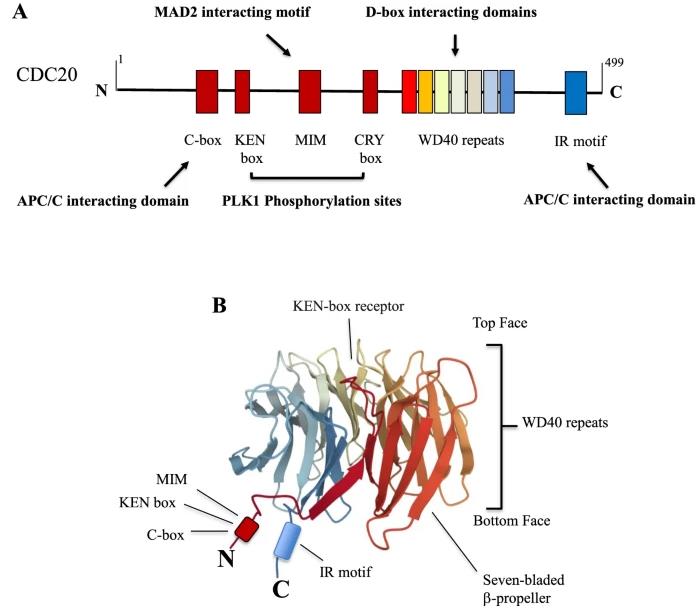
Fig1. CDC20 domains and motifs
Function of CDC20 Protein
A key function of CDC20 is regulating the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, which orchestrates crucial events in cell division. The APC/C, once activated by CDC20, catalyzes the ubiquitination of Securin, an inhibitory chaperone of Separase. The Separase is then activated, which dismantles the connection between sister chromatids, thereby enabling their separation. This critical role in the metaphase-anaphase transition underlines CDC20's part in chromosome segregation integrity, which is mandatory for cell division and cell cycle progression.
CDC20-Related Signal Pathway
One significant signaling pathway involving CDC20 is the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). The SAC is a surveillance mechanism that ensures proper chromosome segregation during cell division; it inhibits CDC20 from activating the APC/C until all chromosomes are adequately attached to the spindle. On recognition of this completion, SAC inhibition is lifted, allowing CDC20 to catalyze the APC/C, thus propelling the cell into the anaphase.
CDC20-Related Diseases
Given its vital role in cell division, it comes as no surprise that dysregulation of CDC20 protein can lead to various diseases, primarily cancer. Abnormal CDC20 expression has been associated with tumorigenesis, disease progression, and poor survival rates in many types of cancer, including breast cancer, colon cancer, glioblastoma, and gastric cancer. Several studies suggest CDC20 as a promising biomarker for cancer prognosis. Furthermore, CDC20 abnormalities are also linked to non-cancer diseases like Alzheimer's, which implicates CDC20 in neuronal death regulation.
Biomedical Applications of CDC20 Protein
The recognized involvement of CDC20 in disease progression has opened avenues for its exploitation in medicine. As a diagnostic biomarker, CDC20 protein could be exploited for early detection and disease monitoring. Furthermore, therapeutic aspects are promising as CDC20 could be a target for drug development. Specifically, in oncology, the identification of small molecule inhibitors to disrupt the CDC20-APC/C interaction holds promise for antitumor treatment. Several preclinical studies have shown that pharmaceutical inhibition of CDC20 exhibits effective anticancer activity.
As research delves deeper into the molecular interactions and regulatory mechanisms involving CDC20, new horizons may open in understanding and treating diseases even better. Importantly, the biomedical applications serve as a testament to the critical role of fundamental molecular research, bearing practical implications for humanity's health and wellbeing.
CDC20 has emerged as a crucial player in maintaining the integrity of cell division, thereby influencing organismal life cycles. Though primarily seen as a villain in diseases, understanding its specific roles provides immense potential to harness this villain as a hero in diagnostics and therapeutics. As we unearth more significant insights into the molecular world of CDC20, the door to innovative biomedical applications continues to widen.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDC20-0910H | Recombinant Human CDC20 Protein, GST-Tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| CDC20-27897TH | Recombinant Human CDC20 | Human | Wheat Germ | N/A |
| CDC20-001H | Recombinant Human CDC20 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| CDC20-553H | Recombinant Human CDC20 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CDC20-5841H | Recombinant Human CDC20 protein, His&Myc-tagged | Human | E.coli | His&Myc |
| CDC20-715H | Recombinant Human CDC20 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
Reference
- Bruno, S., Ghelli Luserna di Rorà, A., Napolitano, R. et al. CDC20 in and out of mitosis: a prognostic factor and therapeutic target in hematological malignancies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 41, 159 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-022-02363-9

