What is CXCL13 Protein
The CXCL13 protein, a member of the CXC chemokine family, has emerged as a pivotal regulator in immune responses, orchestrating the migration and positioning of B cells within the body.
What is CXCL13 Protein?
CXCL13, or C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 13, is a small signaling protein integral to immune system function. As a chemokine, CXCL13 plays a crucial role in guiding immune cells, particularly B cells, to specific anatomical locations. This protein is prominently expressed in follicular dendritic cells and stromal cells within lymphoid tissues, contributing to the organization of immune responses.
The Function of CXCL13 Protein
The primary function of CXCL13 revolves around its ability to attract and guide B cells to lymphoid tissues and follicles. Through its interaction with the CXCR5 receptor on B cells, CXCL13 initiates a cascade of events leading to chemotaxis, cell adhesion, and activation. This orchestrated process is essential for the formation and maintenance of lymphoid follicles, facilitating effective immune responses.
CXCL13-Related Diseases
- Autoimmune Diseases
Elevated levels of CXCL13 have been implicated in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and Sjögren's syndrome. The dysregulation of CXCL13 may contribute to the formation of ectopic lymphoid structures, perpetuating chronic inflammation in these conditions.
- Cancer
The involvement of CXCL13 in cancer is multifaceted. Studies indicate its role in the formation of tertiary lymphoid structures within tumors and its association with B cell recruitment in certain malignancies. CXCL13's influence on the tumor microenvironment suggests its potential as a target for cancer therapeutics.
- Infectious Diseases
CXCL13 is a key player in the immune response against infections. Increased expression of CXCL13 is observed in certain viral infections, highlighting its role in orchestrating antiviral immune responses. Understanding its involvement in infectious diseases could pave the way for targeted interventions.
CXCL13 Related Signaling Pathways
- Chemotaxis
The CXCL13/CXCR5 pathway initiates chemotaxis, guiding B cells along concentration gradients to lymphoid follicles. This directed movement is essential for the proper functioning of immune responses, ensuring B cells reach specific anatomical sites for optimal interactions.
- Cell Adhesion
CXCL13 promotes the adhesion of B cells to endothelial cells, facilitating their extravasation from blood vessels into lymphoid tissues. This step is critical for B cells to reach the sites where immune responses are orchestrated, reinforcing the importance of CXCL13 in immune system regulation.
- Cell Activation
The CXCL13/CXCR5 interaction triggers intracellular signaling events leading to the activation of B cells. This activation is a prerequisite for B cells to participate in immune responses, including the production of antibodies and the coordination of effective defense mechanisms.
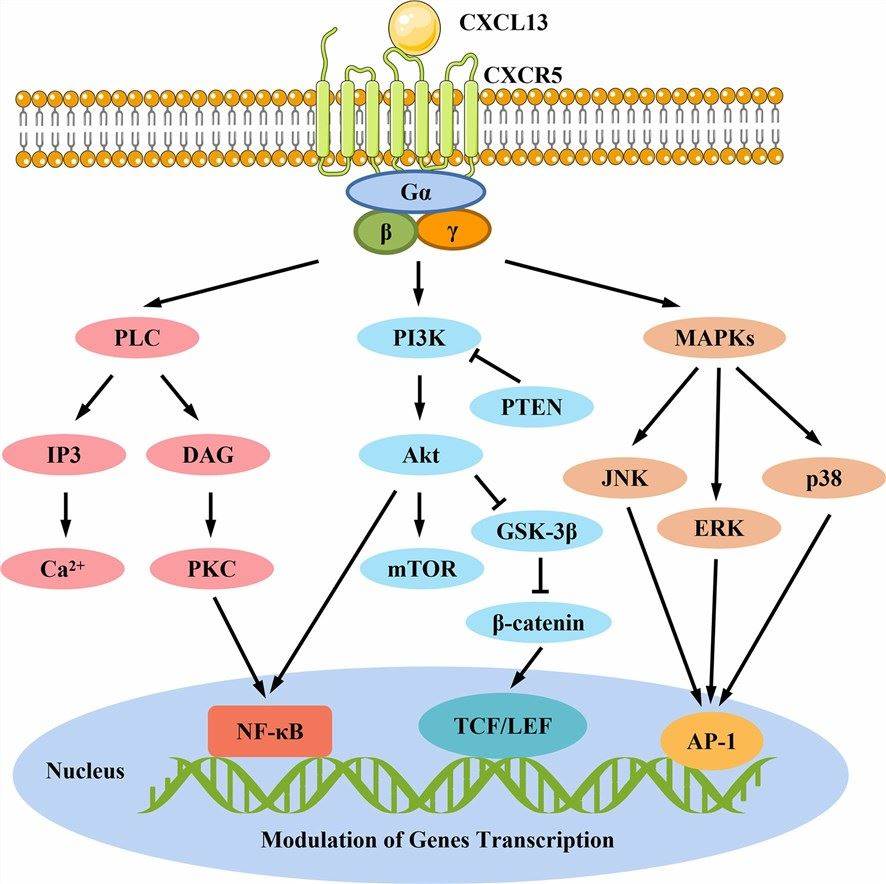
Figure 1. CXCL13/CXCR5-mediated signaling pathways. (Pan, Z., et al. 2022)
Applications of CXCL13 in Biomedical Research
- Diagnostic Marker
Elevated CXCL13 levels serve as potential diagnostic markers in various diseases. Measuring CXCL13 levels in biological samples could aid in the early detection and monitoring of autoimmune diseases and certain infections, providing clinicians with valuable insights.
- Therapeutic Target
Given its association with autoimmune diseases and cancer, CXCL13 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target. Inhibiting the CXCL13/CXCR5 interaction holds potential for modulating immune responses, offering new avenues for the development of targeted therapies in diverse pathological conditions.
- Vaccine Adjuvant
The role of CXCL13 in organizing immune responses suggests its potential as a vaccine adjuvant. Incorporating CXCL13 or its mimetics into vaccine formulations could enhance the generation of protective immune responses, particularly in the context of infectious diseases and cancer immunotherapy.
- Inflammatory Disease Research
Studying CXCL13 provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying inflammatory diseases. Targeting CXCL13 may offer therapeutic avenues for managing chronic inflammation associated with autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, paving the way for innovative treatment strategies.
The CXCL13 protein stands as a pivotal player in immune regulation, disease pathogenesis, and biomedical applications. As research continues to reveal the complexity of CXCL13, its potential for diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccine development will continue to advance our understanding of immunology.
Recommended Products for CXCL13 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CXCL13-123H | Human | Active Recombinant Human Chemokine (C-X-C motif) Ligand 13, HIgG1 Fc-tagged | CHO | |
| CXCL13-024H | Human | Active Recombinant Human CXCL13 Protein | E.coli | |
| CXCL13-2161H | Human | Recombinant Human CXCL13 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | |
| CXCL13-2437H | Human | Recombinant human CXCL13, His-tagged | E.coli | |
| CXCL13-4101M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse CXCL13 Protein | Mammalian Cell | |
| Cxcl13-7160M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Cxcl13 protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | |
| CXCL13-5240R | Rat | Recombinant Rat CXCL13 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | |
| CXCL13-299C | Canine | Recombinant Canine CXCL13, His tagged | E.coli | |
| CXCL13-432C | Cynomolgus Monkey | Recombinant Cynomolgus CXCL13 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cell | |
| CXCL13-1108R | Rhesus Macaque | Recombinant Rhesus monkey CXCL13 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cell |
Reference
- Pan, Z., et al. Role of the CXCL13/CXCR5 Axis in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2022, 13: 850998.

