CXCL13
-
Official Full Name
chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 -
Overview
C-X-C motif chemokine 13 (CXCL13), also known as B lymphocyte chemoattractant (BLC) and B cell-attracting chemokine 1 (BCA-1), is a 109 amino acid secreted protein that belongs to the intercrine alpha (chemokine CxC) family. It functions as a chemotactic for B-lymphocytes but not for T-lymphocytes, monocytes and neutrophils. CXCL13 does not induce calcium release in B-lymphocytes. It binds to BLR1/CXCR5. The highest level of CXCL13 is found in the liver, followed by spleen, lymph node, appendix and stomach. Low level of CXC13 is found in salivary gland, mammary gland, and fetal spleen. -
Synonyms
ANGIE;ANGIE2;BCA-1;BCA1;BLC;BLR1L;SCYB13;B-cell chemoattractant;B-cell-attracting chemokine 1;B-cell-homing chemokine (ligand for Burkitts lymphoma receptor-1);B-lymphocyte chemoattractant;C-X-C motif chemokine 13;CXC chemokine BLC;b cell-attracting chemokine 1;b lymphocyte chemoattractant;chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 (B-cell chemoattractant);small inducible cytokine B subfamily (Cys-X-Cys motif), member 13 (B-cell chemoattractant);small-inducible cytokine B13
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Canine
- Mouse
- Porcine
- Pig
- Hamster
- E.coli
- CHO
- N-His-Sumo
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- Fc
- SUMO
- Avi
- Myc
Background
What is CXCL13 protein?
CXCL13 gene (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 13) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4q21. B lymphocyte chemoattractant, independently cloned and named Angie, is an antimicrobial peptide and CXC chemokine strongly expressed in the follicles of the spleen, lymph nodes, and Peyer's patches. It preferentially promotes the migration of B lymphocytes (compared to T cells and macrophages), apparently by stimulating calcium influx into, and chemotaxis of, cells expressing Burkitt's lymphoma receptor 1 (BLR-1). It may therefore function in the homing of B lymphocytes to follicles. The CXCL13 protein is consisted of 109 amino acids and CXCL13 molecular weight is approximately 12.7 kDa.
What is the function of CXCL13 protein?
As a member of the cytokine family, CXCL13 plays a role in recruiting immune cells, activating lymphocytes and activating inflammatory responses through interaction with its receptors. CXCL13 was originally identified in stromal cells of B-cell follicles, which regulate the homing of B cells and certain T cell subpopulations. CXCL13 plays a key role in coordinating cell migration within different regions of the secondary lymphoid organ space, strongly attracting B lymphocytes while promoting the migration of small numbers of T cells and macrophages. CXCL13 and its receptor CXCR5 play an important role in inflammation, infection, cancer, and immune response. CXCL13: The CXCR5 axis coordinates cell-cell interactions and regulates lymphocyte infiltration in the tumor microenvironment.
CXCL13 Related Signaling Pathway
It is particularly influential in the development and maintenance of lymphoid follicles by attracting B cells through its receptor CXCR5. Additionally, CXCL13 is implicated in angiogenesis, promoting the formation of new blood vessels necessary for tumor growth and metastasis through pathways like PI3K/AKT and MAPK. It also plays a role in inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, where it's involved in chronic inflammation and the formation of ectopic lymphoid structures. Furthermore, CXCL13 activates intracellular signaling cascades upon binding to CXCR5, including the PLC pathway, which is critical for immune cell migration and positioning.
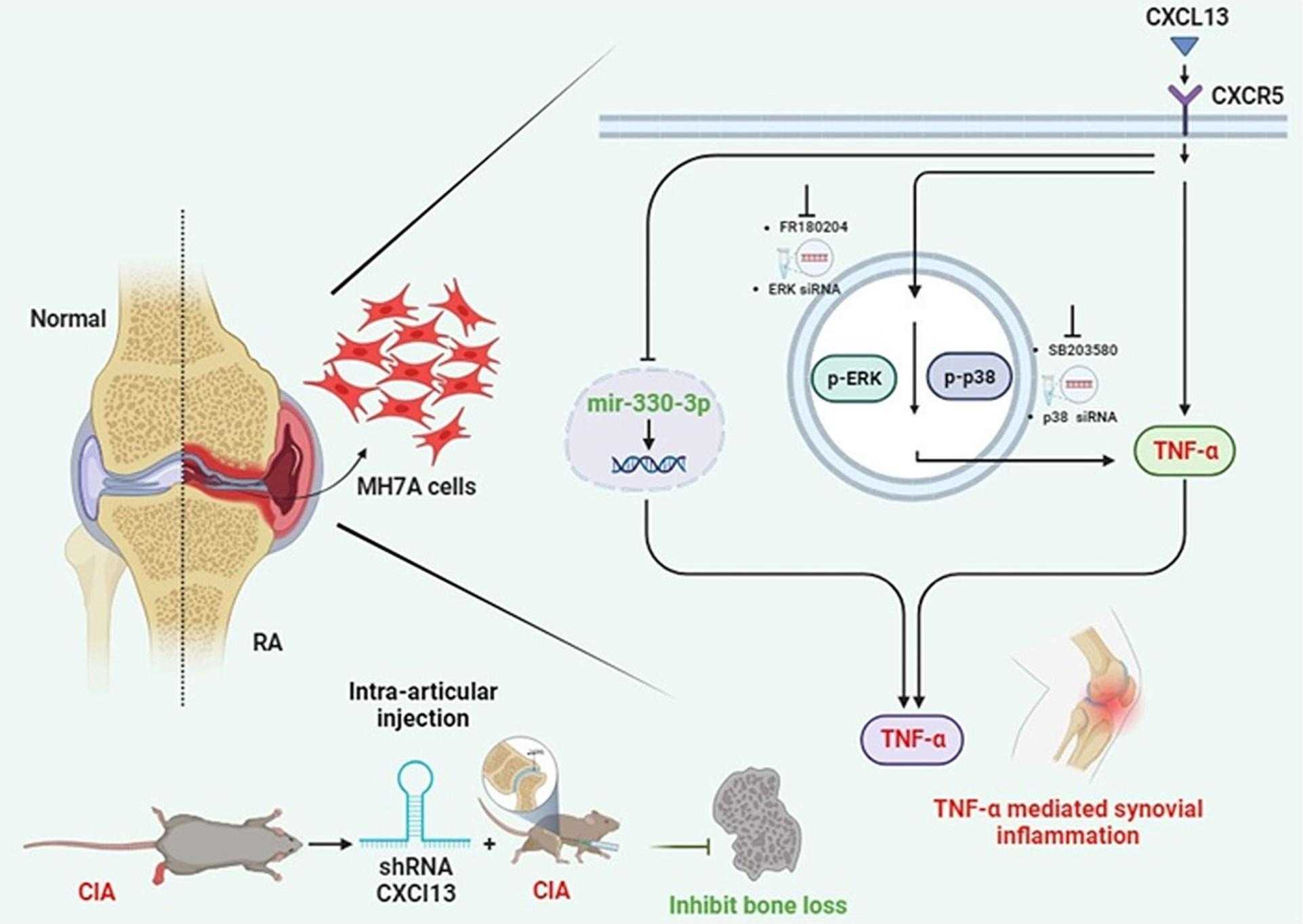
Fig1. Schematic diagram summarizes the mechanisms in the CXCL13/CXCR5 axis that endorse TNF-α expression in RA. (David Achudhan, 2024)
CXCL13 Related Diseases
It plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and Sjogren's syndrome, where it contributes to the formation of ectopic lymphoid structures and the recruitment of autoreactive B and T cells. In the context of cancer, CXCL13 is implicated in the development and progression of several types of malignancies, including non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. It can both promote tumor growth by attracting immune cells that support the tumor microenvironment and potentially inhibit tumor growth by facilitating the recruitment of immune cells that mount an anti-tumor response. Furthermore, CXCL13 is involved in inflammatory conditions like inflammatory bowel disease and is being studied for its potential role in infectious diseases such as HIV.
Bioapplications of CXCL13
As a diagnostic marker, CXCL13 aids in the identification and monitoring of various diseases, particularly autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, as well as different types of cancer. In therapeutics, CXCL13's role in immune cell trafficking and angiogenesis makes it a potential target for drug development. Furthermore, CXCL13 is utilized in research for understanding the complex interactions within the immune system, including B cell migration and lymphoid organogenesis. In the realm of regenerative medicine, CXCL13's influence on angiogenesis and cell migration suggests its potential use in tissue repair and wound healing strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: David Achudhan, 2024
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a well-known autoimmune disorder associated with joint pain, joint swelling, cartilage and bone degradation as well as deformity. CXCL13 plays a crucial role in multiple cellular pathogenesis processes, including RA. TNF-α is a vital proinflammatory factor in the progression of RA. However, the role of CXCL13 in TNF-α production in RA has not been fully explored. The analysis of both database and clinical samples revealed higher levels of CXCL13 and TNF-α in RA samples compared to healthy controls. CXCL13 concentration-dependently induces TNF-α synthesis in RA synovial fibroblasts. CXCL13 enhances TNF-α expression by interacting with the CXCR5 receptor, activating the ERK/p38 pathways, and inhibiting miR-330-3p generation. Importantly, treatment with CXCL13 shRNA counteracted the upregulation of TNF-α production induced by collagen-induced arthritis.
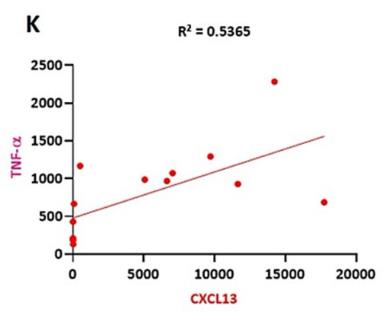
Fig1. The correlation between CXCL13 and TNF-α.
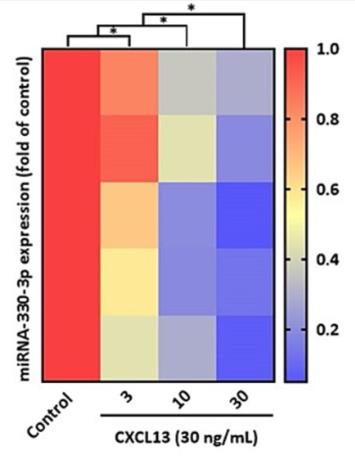
Fig2. RASFs were treated with different concentrations of CXCL13 and miRNA-330-3p expression levels were examined by RT-qPCR.
Case Study 2: Jin Meng, 2022
The molecular mechanism underlying hyperuricemia-induced lipid metabolism disorders is not clear. The purpose of the current study was to investigate the mechanism of lipid disturbances in a hyperuricemia mice model. RNA-Seq showed that differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the fatty acid synthesis signaling pathway were mainly enriched and CXCL-13 was significantly enriched in protein-protein interaction networks. Western blotting, Q-PCR, and immunofluorescence results further showed that hyperuricemia upregulated CXCL-13 and disturbed lipid metabolism in vivo and in vitro. Furthermore, CXCL-13 alone also promoted the accumulation of lipid droplets and upregulated the expression of FAS and SREBP1, blocking AMPK signaling and activating the PKC and P38 signaling pathways.
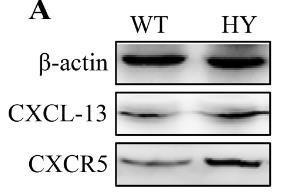
Fig3. Protein density of CXCL-13.
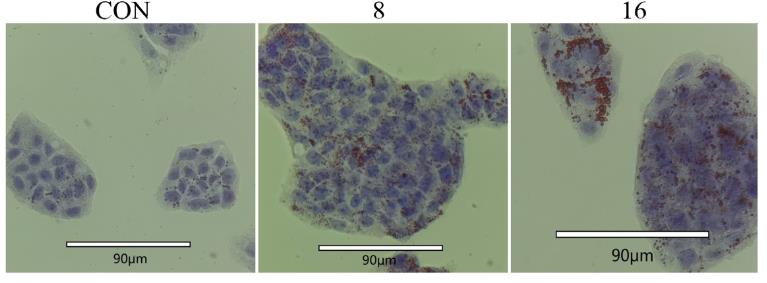
Fig4. HepG2 treated by CXCL-13 stained using Oil Red O staining.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CXCL13-2161H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CXCL13-1695H)
Involved Pathway
CXCL13 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CXCL13 participated on our site, such as CXCR3-mediated signaling events,Chemokine receptors bind chemokines,Chemokine signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CXCL13 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| CXCR3-mediated signaling events | MAPKAP1,DNM1 |
| GPCR downstream signaling | EDN3,ECT2,TAAR1,TRIO,ITSN1,CHRM1,RGS7,GPR18,CCR9,GAL |
| G alpha (i) signalling events | RGS11,NMU,RGS12,PENK,RGS1,TAS2R16,RGS6,RGS21,CCR3,OXER1 |
| Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) | ADRA2A,GPR120,EDNRAB,NMUR1,CXCR6,ADRB1,SST1.1,MLN,DRD3,RXFP2 |
| Chemokine receptors bind chemokines | CCR3,CXCL11.8,CCR9,CCBP2,CCL27,CXCR6,CCR6,CCL35.1,CXCR7B,ACKR4 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | CXCL12,INHBA,KITA,CCR8,HGF,IL6,IL15RA,TNFSF4,CCL25B,NGFRB |
| GPCR ligand binding | OPN1MW,ADM2A,RLN3,PROK2,CX3CR1,TAS2R3,TAS2R16,ADCYAP1R1,TAC2,PPY |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | PIK3CA,PRKCB,CCL1,Ccl21c,CCR3,ADRBK1,SHC3,FOXO3,PRKCD,Ccl27a |
Protein Function
CXCL13 has several biochemical functions, for example, CCR10 chemokine receptor binding,CXCR3 chemokine receptor binding,CXCR5 chemokine receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CXCL13 itself. We selected most functions CXCL13 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CXCL13. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| receptor agonist activity | WNT1,WNT5A,VEGFA,WNT2,NODAL,GAS6,GREM1,WNT7A,WNT8A,WNT3A |
| chemokine activity | CCL3,PF4V1,CXCL11,CCL33.2,XCL1,CCL28,IL-8,CXCL2,CCL11,CCL34A.3 |
| heparin binding | WISP3,APP,FGFBP3,CTGFA,HSD17B12,APLP1,LXN,ZNF207,SERPIND1,ABI3BP |
| fibroblast growth factor binding | FGFR4,FGFR2,FGFBP1,GPC1,FGFR1A,FIBPB,FIBP,KLB,GLG1B,Api5 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | TENM2,CABYR,PDSS2,TWIST1,ABTB2,CAV2,HEXB,RAF1,GABRR1,H2AFY2 |
| CXCR3 chemokine receptor binding | CXCL11.8,PF4,CXCL10,CXCL9,CXCL11 |
| CCR10 chemokine receptor binding | CCL19,CCL25 |
Interacting Protein
CXCL13 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CXCL13 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CXCL13.
EEF1G;ftsK
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Asquith, DL; Bryce, SA; et al. Targeting cell migration in rheumatoid arthritis. CURRENT OPINION IN RHEUMATOLOGY 27:204-211(2015).
- Klimatcheva, E; Pandina, T; et al. CXCL13 antibody for the treatment of autoimmune disorders. BMC IMMUNOLOGY 16:-(2015).




